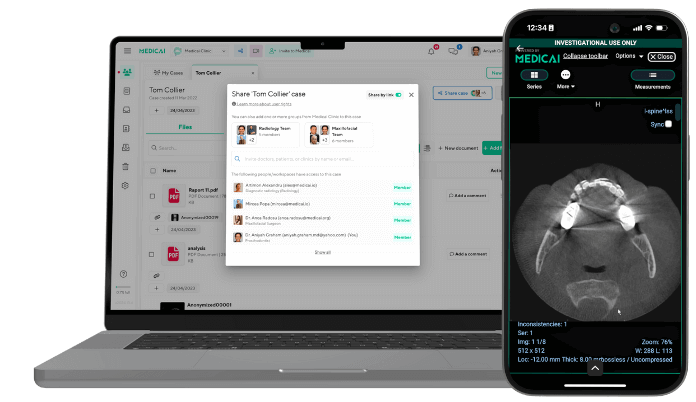
Challenges of interoperability in healthcare
The capacity of various systems, devices, and applications to efficiently share and use data is referred to as interoperability in the healthcare industry. Interoperability is a critical component of the healthcare sector, yet several obstacles still prevent its mainstream adoption and implementation. This essay will highlight some of the significant challenges to healthcare interoperability.
1. Technical Incompatibility
Technical incompatibility is one of the biggest obstacles to interoperability in the healthcare industry. Different healthcare organizations use a variety of electronic health record (EHR) systems, medical devices, and other technologies that may not be compatible with one another. This lack of compatibility makes it difficult for healthcare providers to share patient data, leading to a fragmented healthcare system that can negatively impact patient care.
2. Data standardization
Another challenge to interoperability in the healthcare sector is data standardization. To store and exchange patient data, healthcare institutions employ different terminologies, codes, and formats. This lack of standardization makes it difficult for systems and devices to exchange data effectively, leading to errors and inconsistencies in patient records.
3. Data Security and Privacy
In the healthcare sector, data security and privacy are major concerns. Interoperability in healthcare requires the exchange of sensitive patient data, and the risk of data breaches and privacy violations increases as more systems and devices are connected. Healthcare organizations must ensure that the data exchanged between systems and devices is secure and protected from unauthorized access.
4. Legacy Systems
Many healthcare organizations still rely on legacy systems that were not designed with interoperability in mind. These systems may not have the capabilities or functionality to exchange data with other systems and devices, making it difficult to achieve interoperability. Upgrading legacy systems to more modern technologies can be a time-consuming and expensive process that requires significant resources.
5. Cost
Implementing interoperability in healthcare can be a costly endeavor. Healthcare organizations must invest in new technologies, infrastructure, and personnel to achieve interoperability.
In order to sustain interoperability, systems and devices must be maintained and updated on a continuing basis.
6. Resistance to Change
Healthcare providers and organizations may resist the implementation of interoperability due to concerns about the cost and disruption to their existing processes and systems. Some providers may also be skeptical about the benefits of interoperability and may not see the value in investing in new technologies and systems.
7. Regulatory Issues
Regulatory issues also pose a challenge to interoperability in healthcare. Different countries and regions have different laws and regulations regarding the exchange and use of patient data, and healthcare organizations must ensure that they comply with these regulations. This can be a difficult process that takes a long time and a lot of money.
In conclusion, while interoperability in healthcare presents numerous challenges, it is a crucial aspect of the healthcare industry that must be addressed. By overcoming these challenges, healthcare providers can create a more seamless and integrated system that provides better care to patients. Healthcare organizations must invest in new technologies, standards, and processes to achieve interoperability, and work together to address the technical, regulatory, and cultural barriers that stand in the way.
Related Articles
 Cloud PACS Data Security and Interoperability DICOM Viewer
DICOM Modality Worklist (MWL): How It Works, Why It Fails, and What Happens When It Does DICOM Modality Worklist is a DICOM service that allows an imaging device — a CT scanner, MRI machine, X-ray unit, or any DICOM-compliant modality — to query a server (typically the RIS) for the list of scheduled examinations it is...
Cloud PACS Data Security and Interoperability DICOM Viewer
DICOM Modality Worklist (MWL): How It Works, Why It Fails, and What Happens When It Does DICOM Modality Worklist is a DICOM service that allows an imaging device — a CT scanner, MRI machine, X-ray unit, or any DICOM-compliant modality — to query a server (typically the RIS) for the list of scheduled examinations it is...
 Healthcare Trends and Innovations Cloud PACS Data Security and Interoperability Patient Empowerment and Data Security
Radiology Information System (RIS): Modules, Chain Position, KPIs, and How It Connects HIS and PACS RIS is the administrative and operational nervous system of a radiology department. It manages every event in the patient’s radiology journey, excluding the image itself — the referral, scheduling, patient check-in, exam tracking, report distribution, billing, and department statistics. While...
Healthcare Trends and Innovations Cloud PACS Data Security and Interoperability Patient Empowerment and Data Security
Radiology Information System (RIS): Modules, Chain Position, KPIs, and How It Connects HIS and PACS RIS is the administrative and operational nervous system of a radiology department. It manages every event in the patient’s radiology journey, excluding the image itself — the referral, scheduling, patient check-in, exam tracking, report distribution, billing, and department statistics. While...
 Medical Imaging Technology Cloud PACS Data Security and Interoperability
Hospital Information System (HIS): Why It Is the Centre of Every PACS Workflow Every radiology order that reaches your PACS starts in your Hospital Information System. Every patient identity mismatch that breaks your PACS workflow traces back to a data problem in your HIS. Understanding HIS is not optional knowledge for imaging informatics...
Medical Imaging Technology Cloud PACS Data Security and Interoperability
Hospital Information System (HIS): Why It Is the Centre of Every PACS Workflow Every radiology order that reaches your PACS starts in your Hospital Information System. Every patient identity mismatch that breaks your PACS workflow traces back to a data problem in your HIS. Understanding HIS is not optional knowledge for imaging informatics...
Lets get in touch!
Learn more about how Medicai can help you strengthen your practice and improve your patients’ experience. Ready to start your Journey?
Book A Free Demo