For many, the thought of an X-ray or MRI conjures images of specialized machines in quiet hospital rooms. Yet behind these scans lies a rapidly changing field where technology and connectivity are bridging gaps once thought insurmountable.
Remote radiology services take these images beyond the walls of any single facility, allowing experts to review and interpret patient scans from anywhere in the world. It means faster diagnoses, broader access for underserved communities, and solutions for overburdened providers who face high patient volumes.
The road to successful remote imaging isn’t always straightforward: legal, technical, and data security challenges can hamper its rollout.
In this blog I’ll explore the benefits of this transformative approach, weigh the practical obstacles, and show how a well-planned strategy can unlock remarkable advantages for patient care.

Understanding the Core Concepts
It helps to clarify how these services function before discussing teleradiology benefits and the pros and cons of radiologist roles in remote setups.
At its core, remote radiology relies on digital transmission protocols to send images from imaging centers to radiologists who may be located in a completely different region—or even in another country.
Remote imaging encompasses Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS), secure cloud-based platforms, and advanced compression technologies to ensure data integrity and quick transfer speeds.
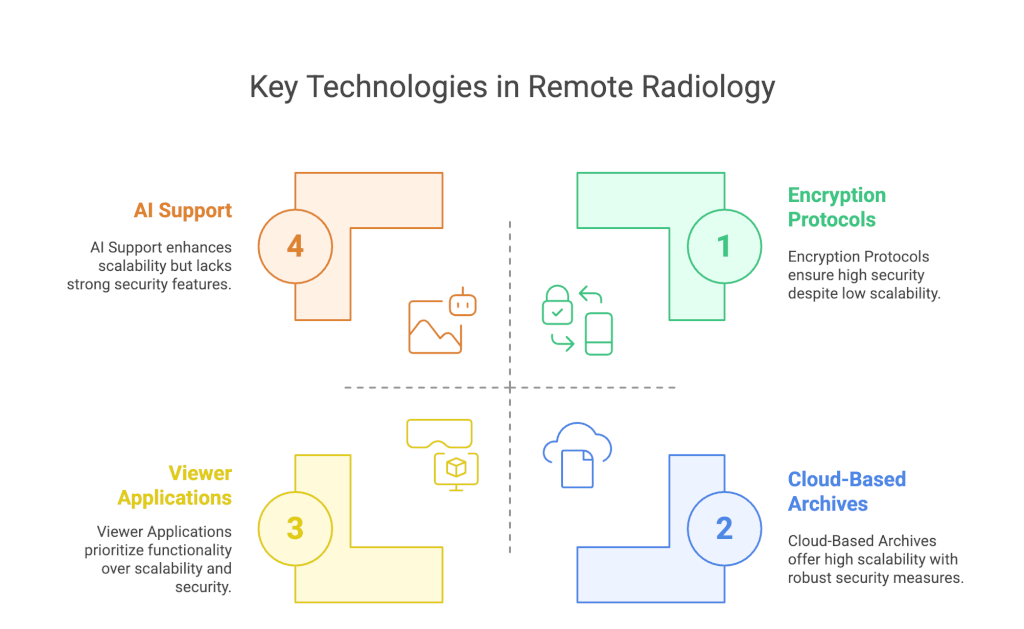
Key technologies include
- Cloud-Based Archives: Storing large volumes of digital images in a cloud environment improves scalability.
- Encryption Protocols: Secure data transmission protects patient privacy, demanding sophisticated encryption mechanisms.
- Viewer Applications: Radiologists require specialized software to handle modalities ranging from standard X-rays to remote MRI scanning.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Support: Increasingly, AI aids in triaging and identifying abnormalities, expediting the interpretation of remote MRI scans, CT scans, or ultrasound images.
Why it matters
These platforms enable healthcare facilities to handle large patient volumes more effectively, provide specialized knowledge for complex cases, and potentially cut down on costs. Nevertheless, the interplay among compliance, bandwidth, and user training can pose persistent obstacles, highlighting the cons of radiology in an unprepared environment.

Key Benefits of Radiology in a Remote Context
The benefits of radiology in a remote setup often revolve around efficiency, specialized expertise, and broader patient access. Below are some of the primary teleradiology benefits that will ensure why it’s the future of imaging:
- Extended Availability of Specialists
Remote radiology services facilitate access to niche expertise, whether that is a subspecialist in neuroimaging or a pediatric radiologist focused on congenital conditions. Smaller clinics or rural hospitals can effectively “import” expertise that would otherwise be unreachable. - Faster Turnaround for Urgent Cases
Telemedicine radiology allows images to be transmitted to on-call radiologists in real time. This improves response times for critical cases like trauma or stroke, where every minute is crucial. By employing remote radiology, healthcare professionals can drastically reduce wait times for interpretation. - Cost-Effective Operations
In some scenarios, remote imaging models can be less expensive than maintaining a full in-house team of radiology specialists around the clock. Outsourcing interpretations, particularly during night shifts or weekends, can offer economic advantages without sacrificing quality. - Expansion of Care to Underserved Areas
Rural and low-resource settings benefit from immediate access to specialists through remote MRI scanning and X-ray interpretations. This improved accessibility aligns with global health initiatives that aim to reduce disparities in care. - Optimized Workflows
Digital integration allows automated workflows to consolidate patient data, imaging, and preliminary AI findings, streamlining collaboration among healthcare teams.
Each of these elements underlines the radiologist pros and cons in remote settings, although most are distinctly positive when adequately managed. A robust technical infrastructure further cements these advantages, but a lack of preparation can open the door to the potential cons of radiology in a virtual environment.

The Pros and Cons of Radiology in a Remote Framework
Providing remote radiology services brings a unique blend of benefits and drawbacks. Below is a concise look at radiology pros and cons in remote contexts, exploring how they can manifest in operational reality:
Pros of Remote Radiology
- Scalability: As imaging volumes grow, remote platforms can be scaled or outsourced without needing permanent on-site expansions.
- Specialized Expertise on Demand: Healthcare facilities can consult experts across various subfields, offering patients top-tier diagnostic opinions.
- Faster Interpretations in Emergencies: Turnaround times can drop significantly when digital pipelines and telemedicine radiology tools are established.
- Potential for Cost Savings: Reduced overhead may be possible if fewer on-site specialists are required around the clock.
Cons of Radiology in Remote Contexts
- Quality Assurance Gaps: Variability in image quality or resolution can hamper diagnostic accuracy if data compression is too aggressive or bandwidth is insufficient.
- Technical Hurdles: Limited or unstable internet connections, software incompatibilities, and data security concerns can disrupt services.
- Regulatory Complexities: Licensing requirements and cross-border regulations can complicate the delivery of remote imaging for different regions.
- Lack of Face-to-Face Interaction: Some clinical scenarios benefit from direct collaboration among radiologists, technologists, and patients, which may be limited in remote setups.
Like many technological developments, the pros and cons of radiologist roles in remote practice reflect the interplay between innovation, regulatory frameworks, and end-user readiness. Organizations adopting remote radiology must balance these dimensions to remain compliant, efficient, and patient-focused.
Addressing the Challenges of Remote Imaging
Although the benefits of remote radiology are significant, there are distinct hurdles to consider. Often, these arise from technological limitations, data security requirements, and professional oversight.
- Connectivity and Infrastructure
High-resolution images—especially those derived from remote MRI scans—can be massive files. Reliable, high-speed internet connections and servers equipped to process large volumes of data are prerequisites. Institutions lacking this infrastructure may experience delayed transmission or suboptimal image clarity. - Regulatory Compliance
International borders can complicate licensure and legal obligations for professionals providing remote radiology services. Different states or countries maintain unique regulations on patient data privacy, encryption standards, and liability. A thorough understanding of these frameworks is critical to avoid legal pitfalls. - Data Security and Patient Privacy
Healthcare data remains a prime target for cyber threats. Ensuring HIPAA or GDPR compliance often demands advanced encryption, two-factor authentication, and regular penetration testing. Even minor security lapses can undermine trust and open the door to liabilities. - Integration with Existing Systems
Smooth interoperability between hospital information systems and telemedicine radiology platforms is vital. Legacy systems with outdated protocols may require substantial updates or specialized middleware, adding to cost and complexity. - Radiologist Training and Adoption
Changes in workflow necessitate training, especially if the transition from in-house to remote radiology is sudden. If staff members are unfamiliar with new software tools, interpretation lag times can arise, eroding some teleradiology benefits.
By proactively confronting these challenges, healthcare providers can create a sustainable model that captures the best aspects of remote imaging while minimizing potential drawbacks.
Teleradiology Benefits in Emergency Situations
The speed and efficiency of remote imaging can become literal life-savers in emergency or acute scenarios. Instances such as severe trauma, stroke, or internal bleeding demand immediate interpretation to guide surgical or medicinal interventions.
- Rapid Access to Specialists: Trauma centers that partner with remote radiology services can ensure immediate access to specialists who might otherwise be unavailable locally.
- Improved Collaboration: Advanced platforms can facilitate real-time consultations between multiple specialists, leading to more robust decision-making.
- Efficient Transfer of Patient Data: Rather than moving critically ill patients to off-site imaging centers, scanning can be done locally, with images sent instantly for expert review.
These scenarios underscore why remote imaging is integral to modern healthcare systems, which aim to reduce morbidity and mortality linked to delayed diagnoses.
Emerging Trends: AI and Advanced Analytics
Artificial intelligence is reshaping the practice of radiology, influencing both onsite and remote workflows. Automated triage solutions can analyze incoming images—particularly from remote MRI or CT scans—and highlight potential abnormalities. Such pre-reading can accelerate critical findings prioritization, effectively harnessing human expertise and machine learning.
- Workflow Automation: Integrating AI into remote radiology services can route images to the most appropriate specialist based on detected anomalies (e.g., suspected neurological, orthopedic, or oncological issues).
- Consistency and Accuracy: Machine learning algorithms excel at detecting subtle patterns, potentially flagging issues a human might miss.
- Reducing Burnout: AI tools can help radiologists focus on complex images by filtering routine cases and highlighting urgent ones, easing their work burdens.
Despite these advantages, AI integration presents its own learning curve and requires thorough validation. Questions about algorithmic bias, data integrity, and accountability must be resolved to ensure safety and reliability.
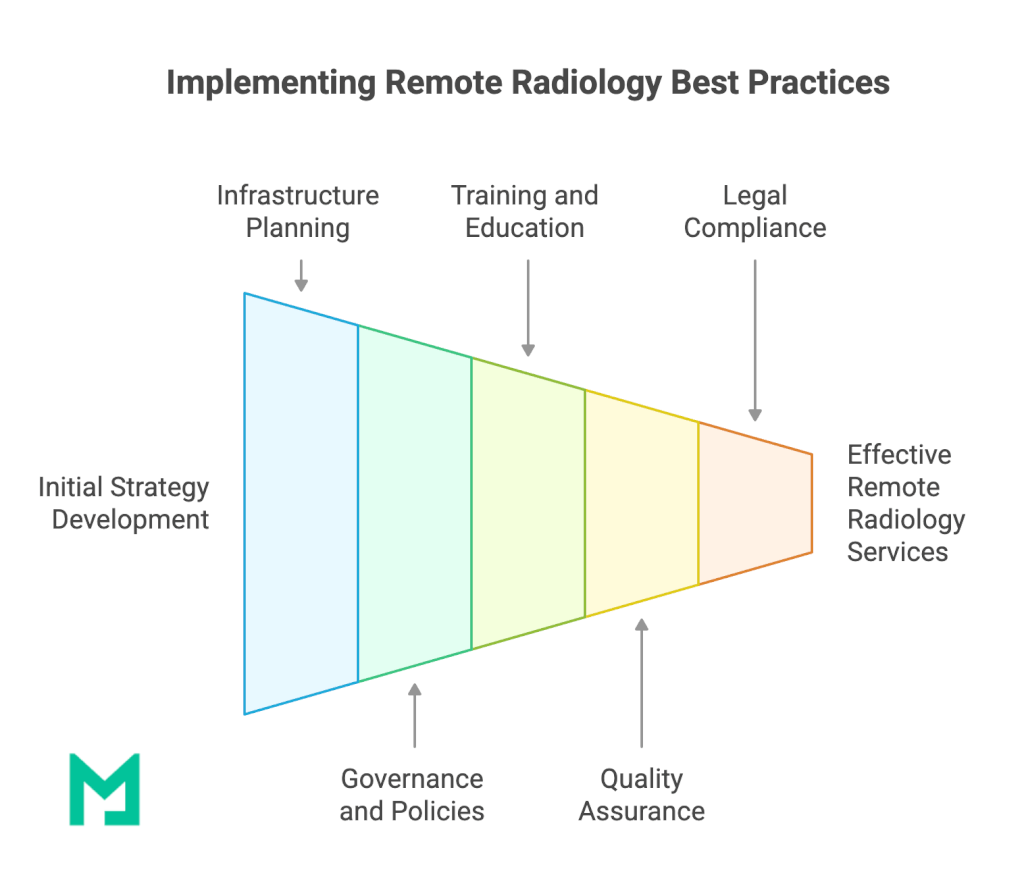
Best Practices for Implementation
Establishing a successful remote radiology program involves more than simply procuring technology. Below are some best practices gleaned from institutions that have effectively navigated teleradiology benefits and the pros and cons of radiology in virtual settings:
- Robust Infrastructure Planning
Conduct an internal audit of bandwidth capabilities, server capacity, and data security protocols. Prepare a detailed plan for scaling as image volume grows. - Clear Governance and Policies
Institute formal policies for data handling, role-based access, and incident response. Written guidelines help maintain consistent standards, especially when multiple stakeholders and external partners are involved. - Training and Continuous Education
Provide regular workshops and refresher courses on new software, AI tools, and best practices for remote imaging. Ongoing education helps staff adapt to evolving technologies. - Quality Assurance Measures
Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) such as turnaround times, accuracy rates, and user satisfaction scores. Continuous monitoring allows for timely course corrections. - Legal and Ethical Compliance
Consult legal experts versed in international healthcare law to navigate cross-border licensing and privacy regulations. Understanding your obligations upfront can prevent legal complications down the line.
Implementing these recommendations helps mitigate the cons of radiology when performed remotely, positioning an organization for sustained success.
Conclusion
Remote radiology has become a cornerstone of efficient, patient-centric healthcare worldwide. By embracing digital transmission systems, facilities can access specialized expertise, expedite critical case evaluations, and widen the reach of radiological services to remote or underserved areas. When examined holistically, it’s clear that the teleradiology benefits far outweigh potential drawbacks—yet comprehensive planning and a deep commitment to data security and quality assurance remain essential.
The radiologist pros and cons in remote frameworks ultimately hinge on a facility’s ability to address connectivity, compliance, and training challenges. With strategic infrastructure and robust policies, the pros and cons of radiologist roles in remote environments can lean sharply toward a net gain: improved patient outcomes, reduced operational burdens, and scalable, cost-effective service delivery.
As technological advancements continue—particularly in AI-driven diagnostics—remote MRI scanning and other high-resolution modalities will likely become even more precise and accessible. The future of remote radiology services will revolve around seamless interoperability, real-time collaboration, and enriched data analytics. Those who adopt these innovations can offer an elevated standard of care and remain competitive in a rapidly evolving healthcare landscape.
Ultimately, the pros and cons of radiology are shaped by how well the industry harnesses technology without losing sight of rigorous clinical standards and patient well-being. For institutions seeking to modernize, this represents a pivotal moment: striking the right balance can lead to cost savings and efficiency and a profound, positive shift in how diagnostic imaging is delivered and experienced by all.





