What if your next cardiac MRI report arrives before you finish your coffee?
Fully automatic deep-learning segmentation combines a CNN-powered ROI detector, U-Net–based backbone, and deformable-model refinement to deliver pixel-perfect chamber masks in seconds. The result is clinician-grade contours, Dice scores above 0.90, and reproducible ejection-fraction measurements.
Discover the architecture, training recipes, benchmark results, and real-world applications that make rapid, reliable cardiac MRI segmentation a reality.

Why Deep Learning Is Revolutionizing Cardiac MRI?
Cardiac MRI traditionally requires experts to manually trace chamber borders, a slow process that can take 15–30 minutes per scan and varies between readers. These inconsistencies can significantly impact key metrics, such as ejection fraction and stroke volume, which are crucial for informed treatment decisions.
Deep learning MRI segmentation flips this workflow on its head.
Convolutional networks learn to identify heart structures directly from image data. Once trained, they produce pixel-perfect contours in seconds. This speed unlocks same-day reports, freeing specialists to focus on complex cases rather than routine outlining.
Beyond speed, automated segmentation slashes inter-observer variability. Studies show that deep-learning models achieve Dice scores above 0.90 for both the left and right ventricles—on par with, and often exceeding, those of human experts. Consistent measurements build clinician trust and support reliable monitoring of disease progression.
Finally, modern networks adapt to diverse imaging protocols. Through data augmentation and robust training on multi-vendor datasets, they tolerate differences in scanner make, field strength, and acquisition parameters. This generalizability means the same model can serve hospitals worldwide without painstaking re-tuning.

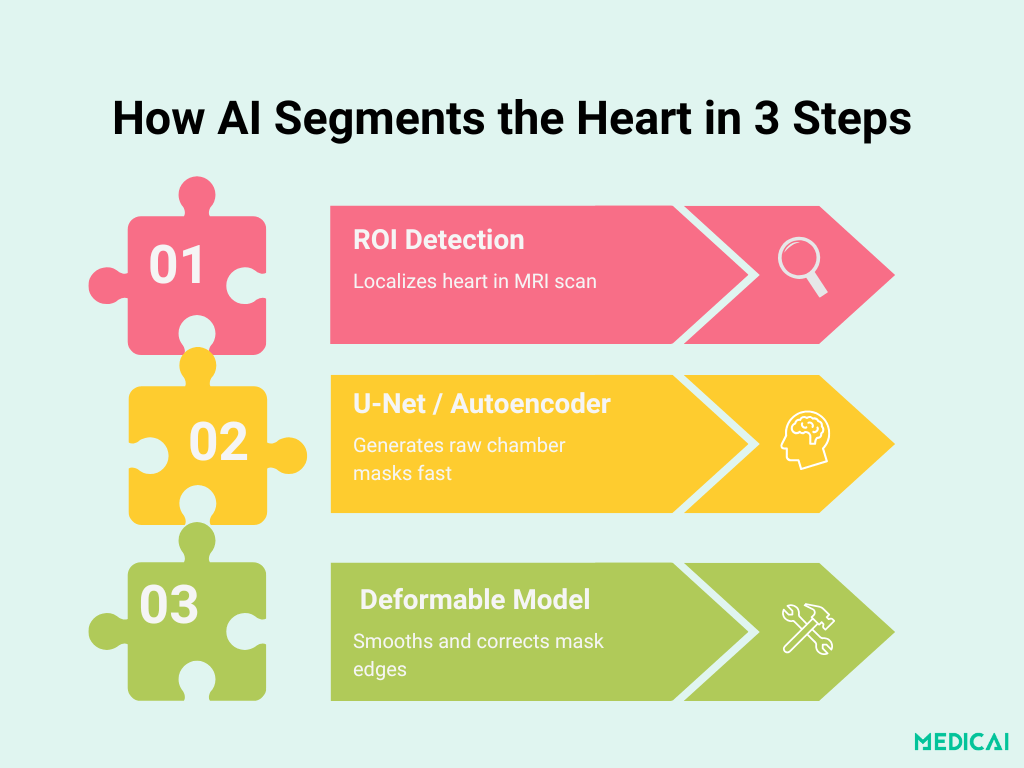
Anatomy of the Pipeline: From ROI to Final Contour
Deep learning–based chamber segmentation unfolds in three clear stages. Each step builds on the previous one to deliver fast, accurate, and anatomically consistent masks.
Heart ROI Localization with CNNs
The first stage uses a lightweight convolutional neural network to pinpoint the heart region in each MRI slice. By training on raw images with manually annotated bounding boxes, the network learns to crop out irrelevant anatomy (such as the lungs and chest wall) and focus solely on the cardiac chambers.
This targeted “Region of Interest” (ROI) crop reduces downstream complexity and boosts both speed and accuracy.
Segmentation Backbone: U-Net & Stacked Auto-Encoders
Once the ROI is extracted, a segmentation network delineates chamber boundaries:
- U-Net Variants: Many top-ranked studies employ a 2D U-Net architecture, characterized by an encoder–decoder path that uses 3×3 convolutions, batch normalization, ReLU activations, and skip connections to preserve spatial context. Filter depths typically progress from 32 to 64 to 128 to 256, balancing detail capture against computational cost.
- Stacked Auto-Encoder (Poster Method): The poster’s pipeline instead uses a stacked auto-encoder trained to reproduce the ROI input, implicitly learning chamber shape priors. Its bottleneck forces the network to distill essential cardiac features, producing an initial pixel-wise mask that feeds into the refinement stage.
Deformable-Model Fusion for Flawless Boundaries
Raw deep-learning masks can be slightly jagged or misaligned at complex borders. To enforce anatomical plausibility, the initial contour integrates into a classic deformable (active contour) model:
- Initialization: The auto-encoder or U-Net output provides the starting curve.
- Energy Minimization: Shape and intensity terms guide the contour to follow the real chamber edges closely.
- Output Smoothing: The final mask is both smooth and adherent to accurate anatomy, correcting minor deep-learning artifacts without manual intervention
This three-stage design combines the speed and learning power of CNNs with the geometric rigor of deformable models.

Training the Network: Recipes for Strong Segmentation
Building a model that generalizes across patients and scanners hinges on carefully chosen loss functions, smart augmentation, and rigorous validation protocols.
Smart Losses: Dice Meets Cross-Entropy
Pure cross-entropy optimizes pixel-wise accuracy but can struggle with class imbalance when chambers occupy only a fraction of the image. Dice loss maximizes overlap but can be unstable early in training. Combining them produces the best of both worlds:
- Weighted Cross-Entropy: penalizes misclassified pixels, keeping the network grounded in per-voxel correctness.
- Dice Loss: directly maximizes the overlap between the prediction and the ground truth, thereby improving boundary delineation.
- L2 Regularization: Tames overly large weights to achieve smoother convergence.
Studies report that this hybrid loss outperforms either component alone—boosting mean Dice scores on held-out MRI datasets by 2–3 percentage points.
Data Augmentation to Beat Scanner Variability
Cardiac MRI protocols vary wildly—field strengths, slice thicknesses, imaging planes—so augmentations simulate this diversity.
- Geometric Transforms: rotations (e.g., multiples of 60°), scaling, translations, flips
- Elastic Deformations: random smooth warps mimic anatomical variability and respiratory motion.
- Intensity Shifts: contrast and brightness jitter account for differences in scanner calibration.
Augmenting on-the-fly ensures the model sees a near-infinite variety of examples, dramatically reducing overfitting and improving cross-vendor performance.
Optimization & Validation Strategy
An intense training regimen ensures you’re really learning heart anatomy, not dataset quirks.
- Optimizers: Adam or SGD with an initial learning rate ~1×10⁻⁴, halved every 10–20 epochs to refine weights.
- Early Stopping: monitor validation Dice; stop when improvement stalls for 10 consecutive epochs.
- Cross-Validation: 5-fold splits on benchmark sets (ACDC, MICCAI RV/LV) to assess stability and avoid lucky splits.
Together, these choices strike a balance between convergence speed and generalization, delivering clinician-grade contours under real-world conditions.
Proving Performance: Metrics That Matter
Assessing MRI segmentation quality relies on three core metrics. Each captures a distinct aspect of how closely the automatic mask matches expert delineations.
Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC)
The DSC measures volumetric overlap between predicted and ground-truth masks. Values range from 0 (no overlap) to 1 (perfect overlap). State-of-the-art models routinely achieve DSC > 0.90 for both left and right ventricles, placing their accuracy on par with that of expert readers.
Hausdorff Distance (HD)
HD quantifies the worst-case boundary error in millimeters, defined as the greatest distance from any point on one contour to the nearest point on the other. A low HD (< 10 mm) indicates that the mask accurately follows fine anatomical edges.
Reporting both mean and standard deviation of HD helps reveal consistency across patient scans.
Volume Correlation (R)
Correlation coefficients are used to compare automatic and manual measurements of end-diastolic volume (EDV), end-systolic volume (ESV), and ejection fraction (EF). High R values (≥ 0.99) signal that the model produces clinically equivalent quantitative metrics, ensuring trust in downstream functional indices.
Clinical Impact: Faster, Consistent, Scalable
Deep learning–powered chamber segmentation transforms clinical workflows in three key ways.
Automated Ejection-Fraction Reporting
By delivering accurate ventricular volumes within seconds, AI-driven segmentation enables the same-day calculation of end-diastolic volume (EDV), end-systolic volume (ESV), and ejection fraction (EF). This rapid turnaround accelerates diagnosis and supports timely treatment adjustments without manual tracing delays.
Minimized Inter-Observer Variability
Traditional manual delineation suffers from reader-to-reader differences—small contour shifts can translate into significant EF discrepancies.
Deep-learning models achieve Dice scores of ≥ 0.90 and volume correlations of ≥ 0.99, ensuring consistent measurements and boosting clinician confidence in patient monitoring.
Seamless PACS/RIS Integration
Once trained, the pipeline can be directly embedded into Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) provided by platforms like Medicai or Radiology Information Systems (RIS).
Fully automatic processing requires no user interaction, routing finalized contours and quantitative reports into the electronic medical record. They streamline radiology workloads.
Overcoming Obstacles: Limitations & Solutions
Despite their promise, AI in MRI segmentation pipelines must address three persistent challenges to achieve widespread clinical adoption.
Scanner Variability
Differences in field strength, vendor-specific sequences, and slice thickness can degrade model performance.
Solutions include extensive data augmentation during training (rotations, intensity jitter, elastic deformations) and fine-tuning on small batches of new-site scans to adapt to local protocols.
Rare Pathologies (e.g., Hypertrophy)
Uncommon conditions such as asymmetric septal hypertrophy or congenital malformations may not appear in standard training sets. It can lead to under-segmentation or shape distortions.
Mitigation strategies include targeted case collections, synthetic augmentation for extreme anatomies, and using uncertainty estimation to flag low-confidence outputs for review.
Data Annotation Bottlenecks
High-quality manual contours are labor-intensive and costly, limiting the size of training corpora.
Methods such as semi-supervised learning, federated learning, and active learning can reduce the need for labeled data by utilizing unmarked scans, sharing updates without transferring data, and focusing on key cases.
Conclusion
Automated deep learning enables fast and accurate segmentation of heart chambers in cardiac MRI, providing precise outlines in seconds. It combines CNN for localization, U-Net for processing, and deformable models for refinement to provide clinicians with reliable results.
With Medicai’s turnkey PACS integration, federated model updates, and explainable dashboards, you can deploy this cutting-edge pipeline instantly. With us, you can deliver faster, smarter cardiac care to every patient.




