The days of ambiguous reports are gone—Structured Radiology Reporting (SRR) in radiology guarantees every detail is clear, concise, and actionable.
Now, imagine pairing SRR with the power of cutting-edge AI. Enter the large language models (LLMs) application, the transformative technology changing the game.
These AI marvels don’t just simplify workflows; they supercharge report structure, optimize processes, and bridge the gap between complex medical jargon and patient understanding. They promise a future where speed and accuracy meet seamlessly.
Let me explain how LLMs are driving the future of SRR, solving challenges, and shaping a smarter, more connected radiology world.

What Are Large Language Models (LLMs)?
Large Language Models (LLMs) are advanced AI systems that understand and generate human-like text. These models are trained on vast amounts of data and can perform various language-related tasks, such as answering questions, summarizing information, and creating content.
LLMs are built on a type of neural network architecture called transformers. Introduced in 2017, transformers revolutionized AI by making models faster, more efficient, and capable of understanding long and complex texts.
The key component of transformers is the attention mechanism, which allows the model to focus on the most relevant parts of the input text. Then transformers break down text into smaller units, called tokens, which are processed mathematically to find patterns and relationships between words.
LLMs have come a long way since their early beginnings. Early language models, like ELIZA (1960s), were rule-based, following predefined patterns. Modern LLMs, however, rely on deep learning and massive datasets, making them far more intelligent and versatile.
Today, models like GPT-4 and ChatGPT have billions of parameters (the building blocks of AI models), enabling them to perform complex tasks like summarizing radiology reports, translating medical terms, and answering patient queries.
LLMs Relevance to Healthcare and Radiology
In healthcare, especially radiology, LLMs are proving to be game-changers. Radiology relies heavily on textual data, such as reports and diagnostic interpretations. LLMs excel at processing and generating human-like text, making them ideal for:
- Report Structuring
- Summarization and Translation
- Triage and Workflow Optimization
- Diagnosis Support
Some notable LLMs include:
- GPT-4: used in radiology for report generation, question answering, and educational purposes.
- BioBERT: A model fine-tuned for biomedical text, making it suitable for analyzing medical literature and assisting in clinical decision-making.
- ClinicalBERT: Designed to interpret clinical notes, this model supports tasks like identifying patient conditions and predicting outcomes.

Structured Radiology Reporting – Large Language Models application
Structured Radiology Reporting (SRR) ensures that radiology reports are standardized, consistent, and actionable for clinical decision-making. LLMs can improve SRR by simplifying the report generation process, optimizing workflows, and enhancing communication.
Discover how LLMs are reshaping SRR:
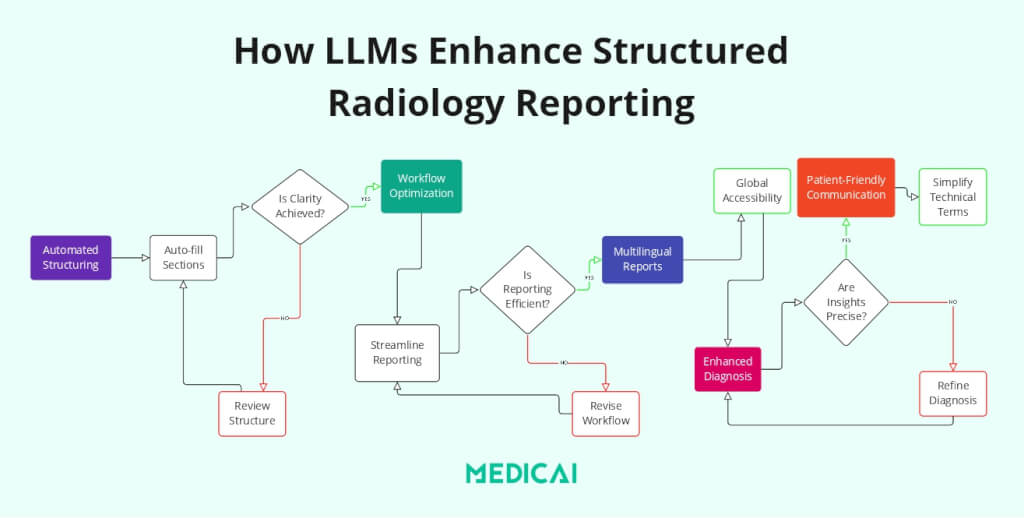
Automating Report Structuring and Summarization
LLMs excel at converting unstructured or semi-structured text into standardized formats, which is at the heart of SRR.
- Consistency and Clarity: Using advanced natural language processing (NLP) techniques, LLMs can structure free-text radiology reports into predefined templates, ensuring clarity and uniformity in content.
- Efficiency in Report Creation: LLMs like GPT-4 can segment reports into specific sections (e.g., findings, impressions, recommendations) without omitting critical details. For example, an unstructured report detailing multiple findings can be automatically categorized into distinct organ systems, improving readability.
- Multilingual Support: Structured radiology reports can be translated into different languages, maintaining format and meaning while enhancing accessibility for non-English-speaking patients and practitioners.

Workflow Optimization for SRR
Efficient workflows are crucial for implementing SRR in high-volume radiology departments, and LLMs play a key role in streamlining these processes.
- Radiology Request Interpretation: LLMs analyze imaging orders and clinical histories to suggest appropriate imaging protocols. This ensures the procedure matches the diagnostic need, reduces variability, and aligns results with SRR standards.
- Integration with PACS and RIS: By integrating with Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) and Radiology Information Systems (RIS), LLMs allow radiologists to retrieve, structure, and populate reports quickly. For instance, they can respond to queries like, “Retrieve all abnormal MRI reports from the past week,” streamlining structured data retrieval.
- Triage and Prioritization: LLMs can prioritize imaging studies based on urgency and integrate findings into structured reports, ensuring prompt attention to critical cases.
Supporting Accurate Image Interpretation and Diagnosis
While SRR focuses on report structuring, accurate and contextual interpretation of imaging findings is integral to meaningful reporting.
- Differential Diagnosis Generation: LLMs analyze imaging patterns and clinical data to suggest differential diagnoses. It enhances the diagnostic depth of structured reports, ensuring completeness and reliability.
- Knowledge Integration: By cross-referencing current medical literature and prior imaging cases, LLMs enrich structured reports with evidence-based recommendations and clinical correlations.
Enhancing Communication through SRR
Clear communication is a key goal of SRR, not only among healthcare providers but also with patients.
- Simplifying Technical Language: LLMs can simplify complex medical jargon into patient-friendly language while maintaining the integrity of structured reports. For example, findings like “hypodense lesions in the liver” can be rephrased as “areas in the liver that need further testing” to improve patient understanding.
- Patient Query Handling: LLMs can generate simplified explanations of structured radiology reports, answer common patient questions, and ensure transparency.
Innovations Driving LLMs Integration in Structured Radiology Reporting
Cutting-edge innovations in natural language processing (NLP), multimodal capabilities, and privacy-preserving AI have catalyzed the integration of large language models (LLMs) into structured radiology reporting (SRR).
Advanced NLP Techniques
LLMs like GPT-4 are built on transformer-based architectures, which are instrumental in powering SRR. These advanced NLP techniques allow LLMs to handle vast, complex radiology-related datasets with remarkable efficiency and accuracy.
- Zero-Shot Learning: LLMs can generate structured reports without explicit training on specific radiology datasets. For instance, they can format or translate reports into structured templates based on general medical knowledge.
- Few-Shot Learning: LLMs adapt to radiology-specific tasks, such as organ segmentation or specialized imaging protocols, with minimal examples. This is invaluable for creating tailored SRR workflows in unique clinical settings.
- Prompt Engineering for Radiology-Specific Tasks: Prompt engineering allows users to guide LLM outputs for SRR. Prompts can include radiology-specific terminology to ensure accurate and relevant content generation.
LLMs can automate the structuring and standardization of radiology reports by leveraging advanced NLP techniques.
Multimodal LLMs
Multimodal LLMs analyze radiological images alongside textual patient data to provide comprehensive diagnostic insights. These models can correlate imaging findings with clinical notes, generating structured reports enriched with clinical context.
LLMs can incorporate findings from multiple modalities (e.g., MRI, CT, and X-rays) into a single structured report, ensuring holistic patient assessments. By integrating visual data, LLMs provide radiologists with detailed summaries and evidence-based recommendations within SRR formats.
Privacy-Preserving AI
Data privacy and security are paramount in radiology, where sensitive patient information is routinely handled. LLMs must comply with healthcare regulations while delivering SRR benefits.
LLMs can process de-identified radiology data, removing personally identifiable information (PII) while retaining clinical utility. Also, algorithms within privacy-preserving frameworks ensure that structured reports generated by LLMs comply with HIPAA and GDPR regulations.
Privacy-preserving AI models can be deployed on secure hospital servers, keeping patient data within the organization. Open-weight LLMs benefit from this, as they can be customized and implemented locally in radiology departments for safe, compliant SRR workflows.
Advanced security features like encryption and role-based access control are integrated into LLM systems. These features ensure that only authorized personnel can access structured reports and related data.
Challenges and Limitations in Structured Radiology Reporting Using LLMs
While Large Language Models (LLMs) offer significant potential for enhancing Structured Radiology Reporting (SRR), their implementation comes with specific challenges and limitations.
Data Privacy and Security
LLMs process large datasets, increasing the risk of exposing sensitive information.
Also, when data is sent to external servers for processing, it becomes susceptible to unauthorized access.
Besides, radiology reports often contain personally identifiable information (PII), and any data breaches could have severe legal and ethical implications.
End-to-end encryption can protect sensitive information during storage and transfer, ensuring data integrity. Also ensures all patient data is anonymized before being processed by LLMs, removing PII while maintaining the clinical value of the report.
Medicai offers privacy-preserving AI models that can be deployed on secure, internal hospital servers. This ensures data never leaves the organization’s infrastructure, adhering to regulations like HIPAA and GDPR.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
Using LLMs in radiology raises ethical questions and requires compliance with stringent regulations.
LLMs are trained on vast datasets, which may include biases related to gender, age, ethnicity, or geography. These biases could lead to inaccuracies in structured reports, particularly for underrepresented populations.
The absence of universally accepted standards for LLM deployment in radiology creates uncertainty, especially regarding accountability and liability in clinical settingsDIR-30-80.
Medicai provides radiologists with interpretability tools, enabling them to understand how LLMs generate structured reports and ensuring accountability.
Accuracy and Reliability
LLMs are powerful but not infallible.
One significant challenge is their tendency to generate “hallucinations”—fabricated information that appears plausible but is factually incorrect. Without rigorous validation, these errors could compromise patient safety and trust in AI-driven systems .
.
Medicai integrates LLM outputs into workflows where radiologists have the final authority, ensuring no automated report is used without human oversight. Our systems also learn from errors through continuous feedback loops, improving reliability and minimizing the likelihood of hallucinations over time.
Conclusion
Large Language Models are transforming Radiology Reporting for better accuracy and efficiency. LLMs enhance healthcare by automating report structuring and improving patient communication. Advancements in privacy-preserving AI and NLP techniques promise streamlined, patient-centric care.
As a leader in innovation, Medicai empowers radiology professionals to harness LLMs confidently, delivering better outcomes and transforming modern medical practice.





