Healthcare has always been a data-rich industry — but much of that data still lives in silos, trapped in faxes, scanned PDFs, and unstructured reports.
Every day, hospitals and clinics juggle thousands of forms: patient consents, referrals, imaging requests, insurance claims, and release-of-information (ROI) documents.
For CIOs and healthcare leaders, this manual document handling is not just an operational headache — it’s a massive drag on efficiency, compliance, and patient experience.
The good news? Artificial Intelligence (AI) is changing that.
AI document processing is quietly becoming the backbone of digital healthcare administration, bridging the gap between people, paperwork, and technology.
What Is AI Document Processing in Healthcare?
AI document processing in healthcare refers to the use of machine learning (ML), optical character recognition (OCR), and natural language processing (NLP) to digitize, extract, and analyze information from medical documents — automatically and at scale.
It goes beyond simple data entry automation.
Modern systems understand the context and content of medical forms, reading and interpreting data much like a human administrator would. For example, they can:
- Extract patient identifiers from scanned referral letters.
- Match imaging requests with modality types.
- Verify consent forms for ROI requests.
- Classify and tag documents for EHR integration.
A recent study published in IJSRA indicates that AI-powered document processing systems can reduce administrative workloads by up to 45% while improving data accuracy by over 30%.
This represents a shift from document storage to document intelligence — where every piece of paper or file becomes structured, searchable, and actionable.
The Hidden Cost of Manual Paperwork in Hospitals
Administrative inefficiency is one of the healthcare sector’s most persistent and expensive problems. According to the National Library of Medicine, up to 25% of total healthcare spending in the United States goes to administrative functions — much of it related to manual paperwork and redundant data entry.
In a typical hospital, staff spend hours daily processing:
- Referral letters from physicians.
- Insurance forms and prior authorizations.
- Patient intake forms and consent documents.
- Imaging reports and ROI authorizations.
These workflows are prone to human error, delayed turnaround times, and compliance risks. Misfiled ROI forms or missing referral data can cause care delays, insurance denials, or even HIPAA violations.
The World Economic Forum’s “Future of AI-Enabled Health” report emphasizes that administrative automation is now as critical as clinical AI adoption. Reducing paperwork bottlenecks directly improves access to care, speeds diagnosis, and enhances collaboration between departments — from radiology to billing.
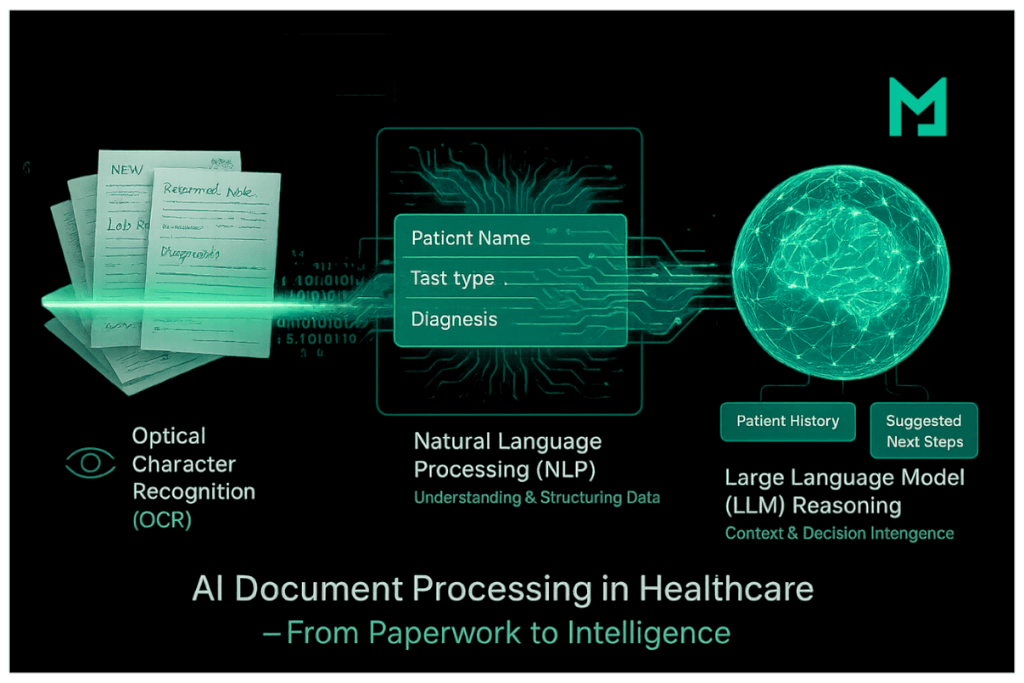
How AI Document Processing Works (OCR + NLP + LLM Reasoning)
At its core, AI document processing combines three layers of intelligence:
Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
OCR converts images or scanned documents into machine-readable text. In healthcare, this means digitizing handwritten referral notes, printed lab results, or faxed ROI forms.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP algorithms understand and extract structured data from unstructured text — such as patient names, test types, or diagnostic impressions.
Large Language Model (LLM) Reasoning
This is where the next generation of AI systems excels. By integrating LLMs — models trained on vast amounts of clinical and administrative language — the system can reason about document context.
For example, an LLM-enhanced workflow can:
- Detect if a referral form is missing mandatory information.
- Identify discrepancies between imaging orders and patient demographics.
- Suggest the correct imaging modality (CT vs MRI) based on clinical notes.
We have found a recent research in IEEE Xplore that demonstrates how combining OCR and LLM reasoning can reduce processing time per document from minutes to seconds, while achieving 97% classification accuracy.
This fusion of OCR, NLP, and LLMs marks the transition from rule-based automation to cognitive healthcare systems capable of understanding and improving workflows autonomously.
Key Benefits: Speed, Accuracy, Compliance, Integration
AI document processing offers clear and measurable benefits across healthcare operations:
Speed
Automation eliminates manual data entry and form sorting. AI systems can process thousands of documents in minutes, accelerating workflows like patient registration or ROI handling.
Accuracy
AI reduces typographical errors, mismatched IDs, and misfiled records. When integrated with existing PACS or EHR systems, it ensures consistent metadata mapping between imaging studies and patient profiles.
Compliance
HIPAA, GDPR, and HITECH compliance are built into AI document processing platforms. Audit trails, data encryption, and access logs safeguard sensitive health information throughout its lifecycle.
Integration
Modern solutions integrate directly with cloud PACS, EHRs, and document management systems. This interoperability ensures that structured data from forms flows seamlessly into patient records — no duplicate entry required.
A detailed analysis from Caria AI highlights how automated processing improves data traceability while supporting healthcare organizations in achieving ISO 27001 and GDPR compliance benchmarks.
Medicai’s Role: Extending AI From Imaging to Documents
Medicai’s mission has always been to simplify medical imaging workflows — securely connecting patients, physicians, and radiologists through its cloud PACS infrastructure.
But imaging is only part of the clinical data story. The other half lies in the documents that guide, authorize, and complement those images.
By extending its capabilities into AI document processing, Medicai now connects imaging data with every supporting document — referrals, ROI forms, and clinical reports — in one intelligent, unified ecosystem.
Here’s how Medicai bridges the gap:
- Automated document ingestion: Scanned or uploaded documents are instantly classified (referral, consent, or report).
- AI data extraction: Key fields such as patient name, modality, or referring physician are identified automatically.
- Smart linkage: The system links documents with corresponding imaging studies inside Medicai’s viewer.
- Secure sharing: Users can send structured data to third parties (e.g., specialists, lawyers, or insurers) without violating HIPAA.
Healthcare organizations that adopt document automation frameworks see significant gains in workflow speed, interoperability, and administrative ROI. Medicai’s cloud-native platform is extending those same benefits to imaging operations.
Use Cases
Prior Reports & Medical Documents for Imaging
Before interpreting an imaging study, a radiologist needs full context: previous imaging reports, lab results, patient history, and other documents that allow comparative measurements and continuity of care.
With Medicai, all such documents — whether DICOM, PDF, or scanned referral packets — are processed using AI document workflows and automatically added to the patient’s case.
For example, solutions like Tennr streamline intake and document classification so that each document is correctly tagged and routed, reducing front-office delays. Meanwhile, Reducto’s ingestion API shows how unstructured documents can be parsed and transformed into structured data for downstream workflows, which is exactly what enables radiologists to seamlessly link prior reports to new imaging.
Patient Intake / Referral for Highly Specialized Medical Practices
In specialty practices — oncology, cardiology, orthopedics — patients often arrive via email, fax, or printed packets containing referrals and medical documents.
These documents must be added to the patient record, validated, and correlated with imaging and treatment viability. Medicai’s platform automates the intake: the documents are ingested, classified, and linked with imaging and treatment-planning workflows.
The front-office burden is drastically reduced. Tennr’s model for converting fax-based referrals into structured data and routing them automatically illustrates how this process can go from weeks to hours.
Multi-Disciplinary Tumor Boards (Oncology, Radiotherapy)
Tumor boards require assembling documents from multiple sources: imaging, pathology reports, diagnostic results, treatment plans, and evolution of disease.
Medicai processes and organizes these automatically: AI extracts diagnostic information, staging (stadialization), treatments, follow-up events, and timelines. Then it presents these within a unified case view alongside imaging.
Reducto highlights how modern document-processing systems can extract complex clinical fields and deliver them in structured form, ready for analytics and decision-making.
All of the above use-cases derive strong value from automated data extraction: building patient timelines (diagnostic → intervention → treatment follow-up), consolidating interventions, and creating data flows across systems (EHR, advanced dictation, patient portals).
Medicai’s architecture supports these integrations—linking document intake with imaging workflows, linking into EHRs and PACS, and generating a modern, data-driven pathway rather than manual siloed processes.
A recent study on PubMed Central confirms that automating data extraction and EHR synchronization leads to measurable improvements in care coordination, particularly in radiology and oncology departments.
Future: Agentic AI Systems for Healthcare Workflows
The next frontier in automation isn’t just smarter models — it’s autonomous AI agents that can collaborate, reason, and make workflow decisions.
Agentic AI systems—go beyond simple extraction. They act like intelligent assistants that can:
- Understand document relationships (e.g., link a referral with an ROI).
- Ask clarifying questions when data is missing.
- Trigger downstream actions (e.g., notifying radiologists or updating patient portals).
These multi-agent frameworks will redefine how healthcare systems operate, moving from reactive data entry to proactive coordination. This agentic evolution will transform back-office processes into intelligent, self-optimizing ecosystems.
Medicai is actively exploring Agentic Document Processing capabilities — embedding AI “co-workers” into its cloud PACS ecosystem to handle repetitive documentation, flag inconsistencies, and enhance communication between systems and staff.
Conclusion: The Path to a Paperless, Intelligent Healthcare Ecosystem
The transition to AI-driven document processing isn’t just a matter of efficiency — it’s a fundamental shift toward data interoperability and digital maturity in healthcare.
By transforming static paperwork into actionable intelligence, AI allows hospitals and clinics to achieve:
- Faster decision-making
- Fewer administrative delays
- Better compliance and data security
- Stronger connections between imaging, documentation, and patient care
As healthcare systems move toward value-based models, AI document processing will be the connective tissue linking clinical intelligence with administrative excellence.
Medicai’s expansion into document automation ensures it remains at the forefront of this transformation — helping healthcare organizations build a truly paperless, intelligent, and patient-centered ecosystem.



