Release of Information (ROI) in healthcare is the workflow for disclosing protected health information (PHI) to a specific person or organization under a defined legal basis, with documented permissions and safeguards.
In this context, ROI means Release of Information, not return on investment. A clean ROI workflow makes the “who, what, why, and how” of each disclosure easy to verify, audit, and complete without leaking extra data.
Use ROI when a patient wants records, when a third party needs records, or when a covered entity must share records under an allowed use or disclosure. The operational goal remains the same: disclose the minimum necessary information to the appropriate recipient within the required timeframe, with proof that the disclosure was permitted.
Release of Information balances the need for accessible health data with protecting patient privacy. It also ensures that your sensitive medical information is shared appropriately, securely, and in compliance with legal standards.
Innovations from platforms like Medicai are developing how medical imaging information is exchanged, enhancing collaboration among healthcare professionals and improving patient outcomes.
Whether it’s for continuing care, billing, legal reasons, or transitioning between providers, understanding ROI empowers you to take control of your health information.

What is the Release of Information?
Release of Information (ROI) is the process a healthcare organization uses to receive a request, validate permission, retrieve the right data, and disclose it to an authorized recipient while preserving privacy and compliance.
ROI typically includes three moving parts:
- The request: who is asking, what they want, and where it should be delivered.
- The permission basis: a HIPAA right of access request, a HIPAA authorization, or another permitted/required disclosure category.
- The disclosure controls: identity verification, scope control (only the requested records), secure delivery, and documentation.
A practical way to explain ROI to non-legal readers: ROI is the operational bridge between “someone asked for records” and “records were disclosed safely, lawfully, and traceably.”
A release of information formauthorizes healthcare providers to disclose a patient’s health information to specified parties. This form is a critical tool in the release of information process, as it ensures that the patient consents to the release of their information.
The form outlines the details of the disclosure, including what information will be shared, with whom, and for what purpose. A copy of the completed form should also be kept on file for documentation and reference purposes.
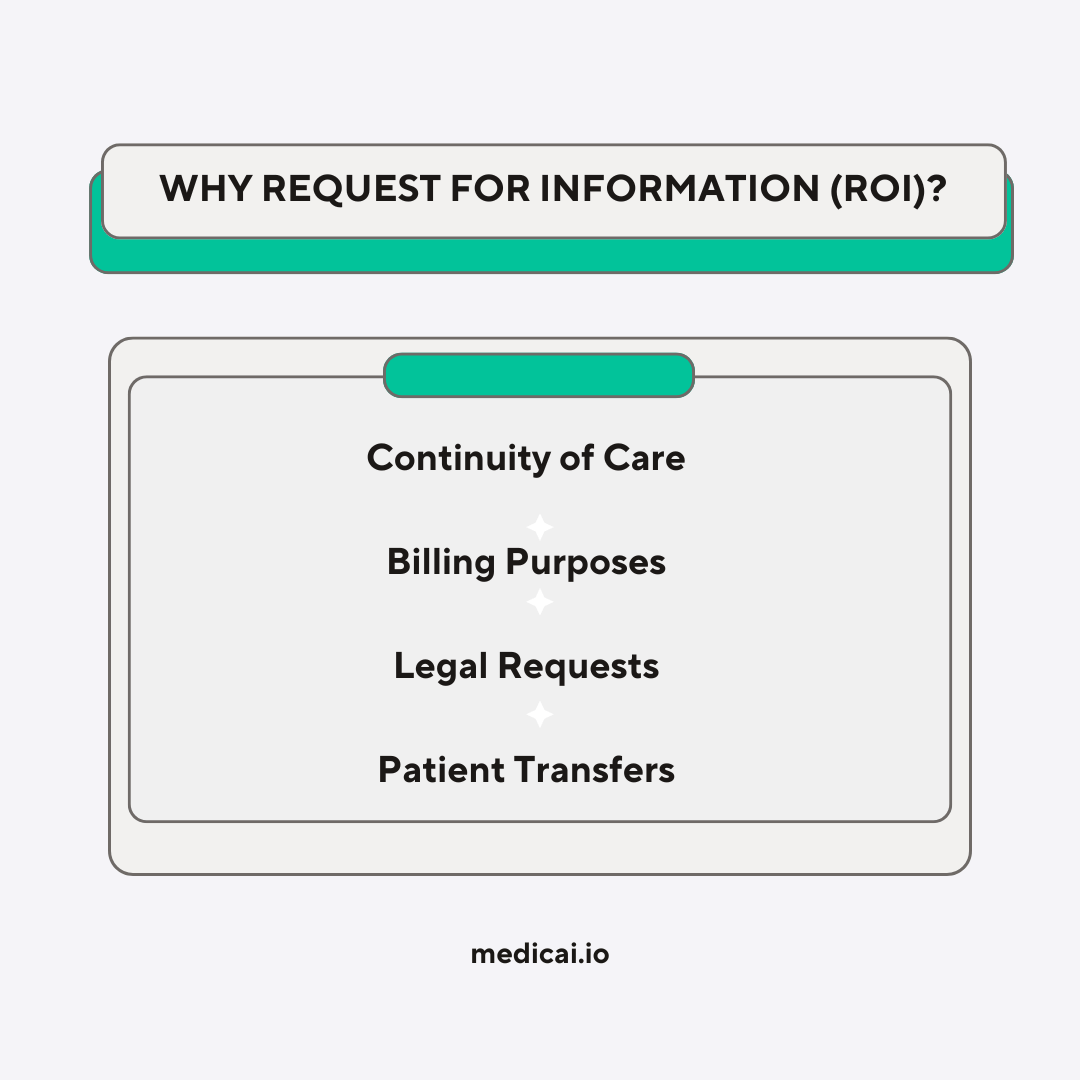
Why Do People Ask For the Release of Information?
People request the Release of Information (ROI) for various reasons, such as accessing, sharing, or managing their health information. Here are some common reasons why individuals might request the release of their medical information:
- Continuity of Care: When switching to a new healthcare provider or seeking a specialist’s opinion, patients request their medical records to ensure the new provider completely understands their health history. This helps in providing effective and personalized care.
- Personal Access: Patients have the right to access their medical records. They may request this information to stay informed about their health, manage chronic conditions, or keep personal copies of their health history.
- Second Opinions: Patients who want to confirm a diagnosis or explore alternative treatment options might request their records to consult another healthcare professional.
- Legal Reasons: Medical records may be needed for legal proceedings, such as personal injury cases, medical malpractice claims, or disability applications. Attorneys often require detailed medical information to support their client’s case.
- Insurance Claims and Billing: To process insurance claims or resolve billing disputes, patients or insurance companies may need access to specific medical records that verify treatments and services provided.
- Transferring Care: When moving to a new city or country, patients may request their medical information to provide to new healthcare providers, ensuring seamless continuation of care.
- Employment Requirements: Certain jobs require proof of medical fitness or immunization records. Employees might need to provide health information for pre-employment screenings or ongoing health assessments.
- Educational Purposes: Students entering programs in healthcare fields may need to provide medical records to meet immunization requirements or demonstrate fitness for clinical placements.
- Research Participation: Individuals participating in medical research studies may authorize the release of their health information to researchers who contribute to scientific advancements.
- Personal Record-Keeping: Some people prefer to maintain their comprehensive health records for personal organization, especially if they manage multiple health conditions.
- Family Medical History: Accessing personal medical records can help individuals understand genetic conditions or health risks that may affect family members.
- Immigration or Travel: Visa applications or international travel may require proof of vaccinations or overall health status, necessitating access to medical records.
- Social Security or Disability Benefits: Applications for government benefits often require detailed medical documentation to prove eligibility.
- Military Service: Veterans or active military personnel might request medical records for benefits, reassignment, or retirement purposes.
- Legal Compliance: In some cases, individuals may be legally required to provide medical information, such as complying with court orders or government regulations.
What are the steps in the Release of Information process?
The release of information (ROI) process involves several key steps to ensure the proper handling and disclosure of a patient’s electronic health information. These steps are crucial for maintaining compliance with privacy regulations and protecting patient confidentiality.
Here is an overview of the typical steps involved in the ROI process:
- Request for Access: The process begins when a patient or an authorized party submits a request for access to their health information. This request can be made for various reasons, including medical billing, continuity of care, or legal proceedings.
- Verification of Identity: The healthcare provider verifies the identity of the individual making the request. This step ensures the information is released only to authorized persons.
- Authorization Review: The healthcare provider reviews the authorization form to ensure it is completed and signed. The form must include specific details, such as the type of information to be disclosed, the purpose of the disclosure, and the identity of the recipient.
- Data Retrieval: Once the authorization is validated, the healthcare provider retrieves the requested electronic health information from their records. This may involve accessing electronic health records (EHR) systems or other data repositories.
- Information Review: Before releasing the information, it is reviewed to ensure that only the authorized data is disclosed. Any sensitive information that is not covered by the authorization is excluded.
- Accounting of Disclosures: The healthcare provider maintains an accounting of disclosures, documenting when and to whom the information was released. Privacy regulations require this record-keeping to help track the flow of information.
- Release and Transmission: The authorized health information is securely transmitted to the requesting party. Depending on the nature of the request and the preferences of the involved parties, this can be done through various means, including secure email, electronic health information exchanges, or physical copies.
- Notification: The patient is notified that their request has been processed and their health information has been released. This step ensures transparency and keeps the patient informed about their data handling.
What information must be on a HIPAA authorization for ROI?
A HIPAA authorization for ROI must contain core elements and required statements; missing any of them can make the authorization invalid.
Core elements (what the authorization must specify)
- Description of the PHI to be used/disclosed, specific and meaningful
- Who is allowed to disclose the PHI (person(s) or class of persons)
- Who may receive the PHI (person(s) or class of persons)
- Purpose of the disclosure (or “at the request of the individual”)
- Expiration date or expiration event
- Signature and date
If a personal representative signs, include a description of their authority
Required statements (what the authorization must warn the person about)
- Right to revoke the authorization in writing, with instructions or a reference to the Notice of Privacy Practices
- Conditioning statement: whether treatment/payment/enrollment/benefits can or cannot be conditioned on signing
- Redisclosure risk: once disclosed, the recipient may redisclose, and the PHI may no longer be protected by HIPAA
Two operational requirements that teams forget
- Copy to the individual: provide a copy of the signed authorization.
- Plain language: write it so a patient can understand it.
ROI request vs HIPAA authorization: when you need which
| Scenario (common ask) | What it is (permission basis) | What you collect (minimum intake) | What you must do next (operational steps) |
|---|
| A patient wants a copy of their own records | HIPAA Right of Access (individual request for their PHI) | Identity verification + the scope (which records, format, delivery method) | Provide access within the required timeframe; charge only permitted, cost-based fees; document fulfillment |
| A patient wants you to send records to another person/entity | HIPAA Right of Access — third-party direction | Written, signed request that clearly identifies the recipient and where to send the PHI + identity verification | Transmit the copy as directed (to the designated recipient/destination); document the disclosure and method of delivery |
| A third party requests records for its own purpose (law firm, insurer not in your payment workflow, employer, etc.) | HIPAA Authorization (or another explicit legal basis) | A valid HIPAA authorization (elements + required statements), signed and in scope; if signed by a representative, proof of authority | Validate authorization completeness and scope; disclose only what the authorization permits; log the disclosure |
| A provider requests records for care coordination, or a payer requests for payment | Permitted disclosure for Treatment/Payment/Health Care Operations (TPO) (authorization not required) | Verification of requester role/relationship + purpose + minimum necessary controls (per policy) | Disclose under TPO policy with appropriate safeguards; document disclosure per your compliance process |
HIPAA right of access: timelines and fee limits ROI teams must follow
A HIPAA right of access request must be acted on within 30 calendar days, with only one allowable extension of up to 30 more days when necessary and documented in writing.
Timing rules (write these as “outer limits,” not targets)
- 30 days to act on the request
- One extension of up to 30 additional days
- Extension requires written notice within the initial 30 days, stating the reason and the expected completion date
Fee rules (what you can charge, and what you cannot)
The Privacy Rule permits only a reasonable, cost-based fee for copies, limited to:
- Labor for copying (creating and delivering the copy)
- Supplies for paper copies or requested portable media (CD/USB)
- Postage (if mailed)
- Preparing a summary/explanation, only if the individual agrees
The fee may not include searching/retrieving records, verification/documentation overhead, system maintenance, infrastructure, or “data access” platform costs.
When access can be denied or limited in ROI
Denials exist, but the allowable reasons are narrow; vague discomfort with the requester is not a compliant denial rationale.
Common denial/limitation grounds called out in access guidance include:
- Psychotherapy notes (excluded from the access right)
- A professional judgment that access is reasonably likely to endanger life or physical safety
- Access is reasonably likely to cause substantial harm to a person referenced in the PHI
- In limited cases, disclosure to a personal representative may be restricted if it is likely to cause substantial harm
One clean writer rule: name the denial category explicitly (“psychotherapy notes” or “life/physical safety risk”) so Google does not have to fan out to validate what you meant.
What is the Primary Purpose of a Release of Information Form for the Patient?
The primary purpose of a release of information form is to protect the patient’s privacy and ensure that their medical information is only shared with their consent. It empowers patients to control who has access to their personal health data and under what circumstances.
Sometimes, patients need some encouragement to share health data from healthcare professionals.

This is vital for maintaining trust between patients and healthcare providers and complying with privacy laws such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
The HIPAA Privacy Rule governs the handling of personal health information, including the release of information services. It ensures that personal health information is handled and disclosed appropriately during the release of information process.
This regulation helps healthcare providers safeguard sensitive medical records and protect patient data integrity throughout the information ROI processing, maintaining trust within the patient-provider relationship.
How Long is a Release of Information Good For?
The duration of a release of information authorization can vary. Typically, the form will specify an expiration date or event.
For instance, it may be valid for a specific period (e.g., six months or one year) or until a particular event occurs (e.g., the conclusion of a treatment episode).
Patients and providers must be aware of these timeframes to ensure the authorization remains valid and compliant with legal standards. Additionally, keeping a copy of the authorization form on file is crucial for documentation and reference purposes.
Personal representatives and minors: who can sign and what proof is required
A personal representative is generally someone with authority under state law to make healthcare decisions for the individual, and that representative can exercise the individual’s access rights within the scope of that authority.
Use this checklist in ROI intake:
- Identify whether the requester is the individual or a personal representative
- Verify identity using reasonable steps that do not create barriers
- If a representative signs a HIPAA authorization, record the representative’s authority to act (do not treat it as optional)
For minors, the controlling question is not “is this a parent,” but “does this person have authority under applicable law for this type of decision and record category.” Keep the page at the workflow level unless you plan a dedicated state-law section.

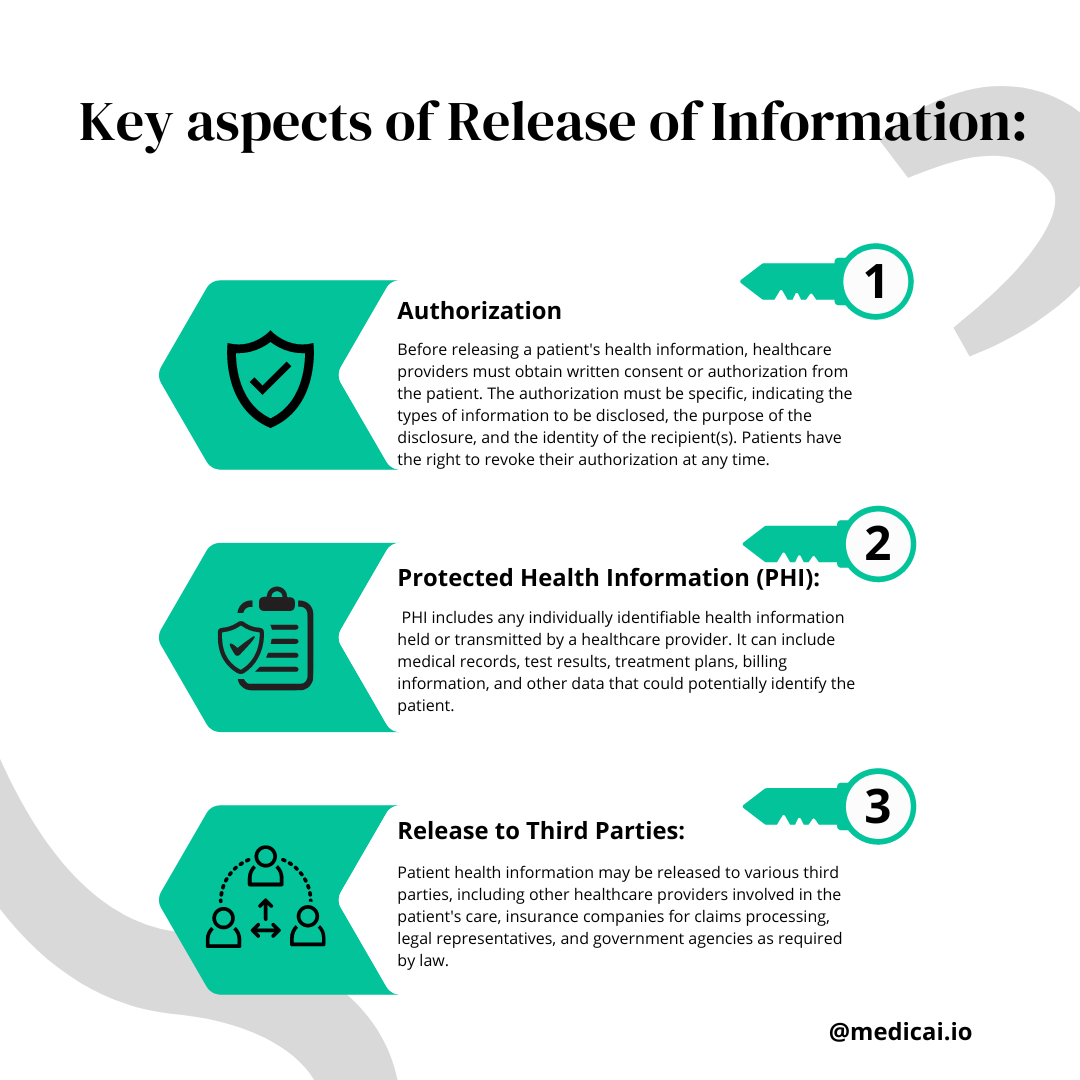
What Must Be Collected Before Release of Protected Health Information?
Before releasing protected health information (PHI), healthcare providers must obtain a properly completed and signed health information form from the patient or their authorized representative.
Additionally, providers must verify the identity of the person requesting access to the information and ensure that the request complies with applicable laws and regulations.
This may include reviewing the patient’s consent, checking the validity of the authorization, and confirming that the information requested is necessary and appropriate for the intended purpose.
A copy of the completed health information form is often kept on file to document compliance with these requirements.
When is the Release of Information Not Required?
HIPAA permits certain disclosures without individual authorization for treatment, payment, and healthcare operations, and it permits disclosures required by law, while still requiring safeguards and minimum necessary where applicable.
- For treatment purposes: Sharing information between healthcare providers involved in a patient’s care.
- For payment purposes: Disclosing information to insurance companies for billing and payment processing.
- For healthcare operations: Quality assessment, training, and administrative functions.
- Legal requirements: Situations where disclosure is mandated by law, such as reporting certain infectious diseases to public health authorities or complying with a court order.
In these cases, the information can be shared without the patient’s explicit authorization, but it must still be handled in accordance with privacy laws and regulations.
ROI in Medical Billing: Ensuring Accuracy, Compliance, and Faster Reimbursements
While Release of Information (ROI) is often discussed in the context of patient access and continuity of care, it also plays a critical role in medical billing. The ROI process ensures that healthcare organizations share medical information securely, accurately, and in compliance with HIPAA when handling insurance claims, audits, or payment disputes.
A properly managed ROI workflow helps billing departments verify claims, provide supporting documentation, and respond to payer requests efficiently — all while protecting patient privacy.
Why ROI Matters in Medical Billing
The billing process relies heavily on accurate health information exchange. Every claim submitted to an insurer must include the correct documentation — treatment details, imaging results, physician notes, and consent forms.
The Release of Information process ensures:
- HIPAA-Compliant Data Sharing – Only authorized personnel can access patient data for billing purposes.
- Accurate Claim Validation – ROI ensures billing teams receive complete and verified records before claims are sent to payers.
- Faster Reimbursements – Timely release of records prevents claim denials due to missing or delayed information.
- Audit Readiness – Proper documentation of disclosures makes it easier to respond to payer or regulatory audits.
In short, an efficient ROI process protects patient data and strengthens the billing pipeline.
How the Release of Information Process Supports Billing Workflows
- Verification of disclosure basis (payment vs authorization)
Before sharing records for billing or insurance claims, healthcare providers must confirm that the patient’s authorization allows such use. This step ensures that data released to payers is both compliant and specific to the claim’s purpose. - Data Retrieval and Accuracy Check
The ROI team retrieves the required medical records — imaging results, lab reports, or visit notes — from EHR or PACS systems. Data is reviewed to ensure it matches the billing codes and treatment details on the claim. - Secure Transmission to Billing Departments or Payers
Once verified, the records are transmitted securely through encrypted digital channels to billing teams or insurance companies. This prevents delays caused by faxing or manual data transfer. - Documentation of Disclosure
Each release is logged for compliance tracking. If questions arise from insurers or auditors, healthcare organizations can easily verify when and why data was shared.
The Benefits of Digital ROI in Billing
Digital Release of Information platforms — like Medicai’s cloud-based solution — simplify and secure how medical data is exchanged for billing purposes.
- Automation: Reduces manual document handling and eliminates paperwork delays.
- Interoperability: Integrates directly with EHRs, HIS, and PACS for seamless data retrieval.
- Security: Ensures all billing-related disclosures are encrypted and HIPAA-compliant.
- Traceability: Tracks every document shared, providing an audit trail for compliance.
- Efficiency: Cuts down on claim denials caused by missing or incomplete documentation.
By digitalizing ROI, healthcare organizations can streamline their billing processes while maintaining patient trust and regulatory compliance.
How Medicai Enhances ROI in Medical Billing
Medicai’s platform facilitates the secure release and exchange of medical imaging and health data — directly supporting billing workflows.
- Cloud Accessibility: Billing teams can access authorized imaging files and medical records anytime, from any facility.
- Integrated Data Exchange: Connects imaging data to billing systems, reducing administrative friction.
- Faster Claim Processing: Enables billing teams to quickly gather the right documents for payer review.
- Compliant and Transparent: All releases are logged automatically to meet HIPAA and GDPR requirements.
With Medicai, healthcare organizations can achieve both operational efficiency and compliance confidence when managing patient information for billing and reimbursement.
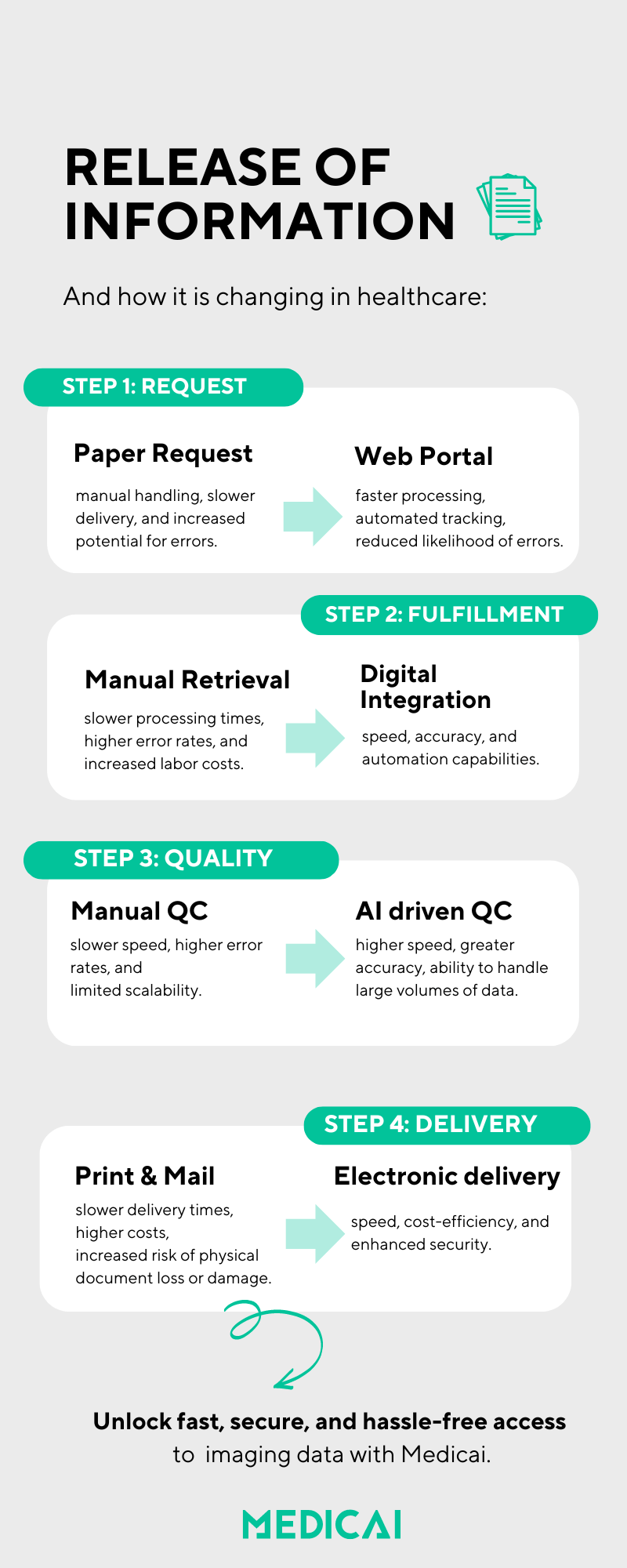
What is the Digital Release of Information?
Digital Release of Information is an ROI executed through electronic workflows that make the permission check, record retrieval, delivery, and disclosure logging faster and easier to audit.
A digital ROI workflow is defensible when it enforces these controls:
- Status transparency so the requester can track progress without calling staff repeatedly
- Identity verification tied to the request channel (portal, email, in-person)
- Permission capture that matches the use case (access request vs authorization)
- Scope restriction so only the requested/authorized records leave the system
- Secure transmission appropriate for the destination and risk level
- Disclosure logging that proves who accessed what, when, and why

How does digital ROI affect the patient experience?
Digital Release of Information ROI significantly enhances the patient experience by making sharing health information more efficient and accessible.
Patients can request and receive their information more quickly, often through secure online portals. This reduces wait times and improves the overall coordination of care. Additionally, digital systems provide greater transparency, allowing patients to track the status of their requests and see how their information is being used.
Such increased accessibility and transparency can lead to higher patient satisfaction and engagement and better health outcomes.
Strategies for Adopting a ‘No Barriers’ Approach to Digital Release of Information

How an imaging platform supports ROI for medical images
Imaging ROI often adds a practical constraint: the disclosure may include large studies and image viewers, not just documents, so delivery, access control, and auditability matter more. Medicai is one example of a cloud platform used to retrieve, share, and store medical imaging data in ROI workflows.
Instead of listing features, anchor the platform to workflow controls:
- A centralized store can reduce “where is the exam?” delays when records must be compiled across sites.
- A request workflow can limit access to the specific imaging studies covered by the request or authorization.
- A controlled sharing method can support clinician collaboration while keeping an audit trail of access.

What is HIPAA authorization for the Release of Information?
A HIPAA consent for the release of information is a document that authorizes a healthcare provider to disclose a patient’s health records to a specified party. This consent form ensures that the sharing of medical information complies with the HIPAA Privacy Rule, designed to protect patient privacy and secure their health information.
When a patient signs a HIPAA consent for the release of information, they are granting access to their health records to a third party, such as another healthcare provider, a health plan, or an individual. This is often necessary for coordinating care, processing insurance claims, or handling legal matters.
A HIPAA compliant online form must comply with release of information guidelines, including specific details such as the type of information to be shared, the identity of the receiving party, and the purpose of the disclosure.This process can often be managed through an online patient portal, where patients can conveniently complete a medical release form electronically.
Overall, HIPAA consent for the release of information ensures that any transfer of health records is conducted by HIPAA privacy standards, safeguarding the patient’s sensitive information throughout the process.
What is the HIPAA privacy rule?
The HIPAA Privacy Rule is a set of standards established to protect patients’ medical records and other personal health information held by healthcare providers and other covered entities.
It ensures that patients have control over their health information while balancing the need for healthcare providers to access and share this information for treatment, payment, and healthcare operations.
Key aspects of the HIPAA Privacy Rule include:
- Access: Patients can access and obtain a copy of their health records. This ensures they can review their medical history and make informed decisions about their care.
- Use and Disclosure: The rule outlines when and how healthcare providers can access, use, and disclose personal health information. It mandates that disclosures be limited to the minimum necessary information to achieve the intended purpose.
- Types of Healthcare Audits: The HIPAA Privacy Rule requires healthcare entities to undergo various healthcare audits to ensure compliance. These audits can include internal audits, external reviews by third parties, and government inspections to verify that health information is being handled properly and securely.
- Patient Rights: The HIPAA Privacy Rule grants patients several rights, including the right to request corrections to their health information, the right to an accounting of disclosures, and the right to request restrictions on specific uses and disclosures.
- Safeguards: Healthcare providers must implement appropriate administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to protect the privacy of health information. This includes measures to secure electronic health records, maintain a copy of authorization forms and related documentation, and train staff on privacy practices.
Conclusion
Releasing information in healthcare is critical to patient data management and privacy. With the advent of digital Release of Information systems, the process has become more efficient, secure, and patient-friendly.
Understanding the importance and mechanics of ROI is essential for anyone involved in the healthcare sector. It ensures that patient information is handled responsibly and in compliance with legal standards.
As technology continues to evolve, the methods and practices surrounding the Release of Information ROI will undoubtedly continue to improve, further enhancing the protection and accessibility of health information.





