The digital wheel is magically changing healthcare, and telehealth and telemedicine are two significant magical creations of this revolution.
These two streams make healthcare services more accessible, efficient, and patient-centered.
However, what are the differences between telehealth and telemedicine?
Telehealth is a broad term covering all remote healthcare services, including education and administration, while telemedicine focuses on clinical care, such as diagnosis and treatment. Together, they transform the delivery and access to healthcare.
Let me guide you more about telehealth vs telemedicine and how they change the healthcare ecosystem.
Telehealth vs Telemedicine: The Key Differences
Technology has changed the game in healthcare services. And two significant inventions making waves in this transformation are telehealth and telemedicine.
While they may sound the same, their scope and applications differ significantly.
Telehealth and Telemedicine: What Are They?
What Is Telehealth?
Telehealth is a way to provide healthcare services remotely using digital tools. It includes both medical and non-medical services. Telehealth helps make healthcare easier to access, more efficient, and focused on patients’ needs.
For example, platforms like Medicai provide seamless remote patient monitoring by integrating wearable devices with cloud-based systems. It enhanced timely interventions and care coordination.
What is Telemedicine?
Telemedicine is a part of telehealth that provides clinical care to patients from a distance. Its main goal is to diagnose, treat, and manage health conditions using communication technology. It connects patients with healthcare providers, allowing them to meet virtually instead of in person.
For example, a patient with flu symptoms can consult their doctor via video call, get a diagnosis, and receive a prescription through telemedicine. Isn’t it great?
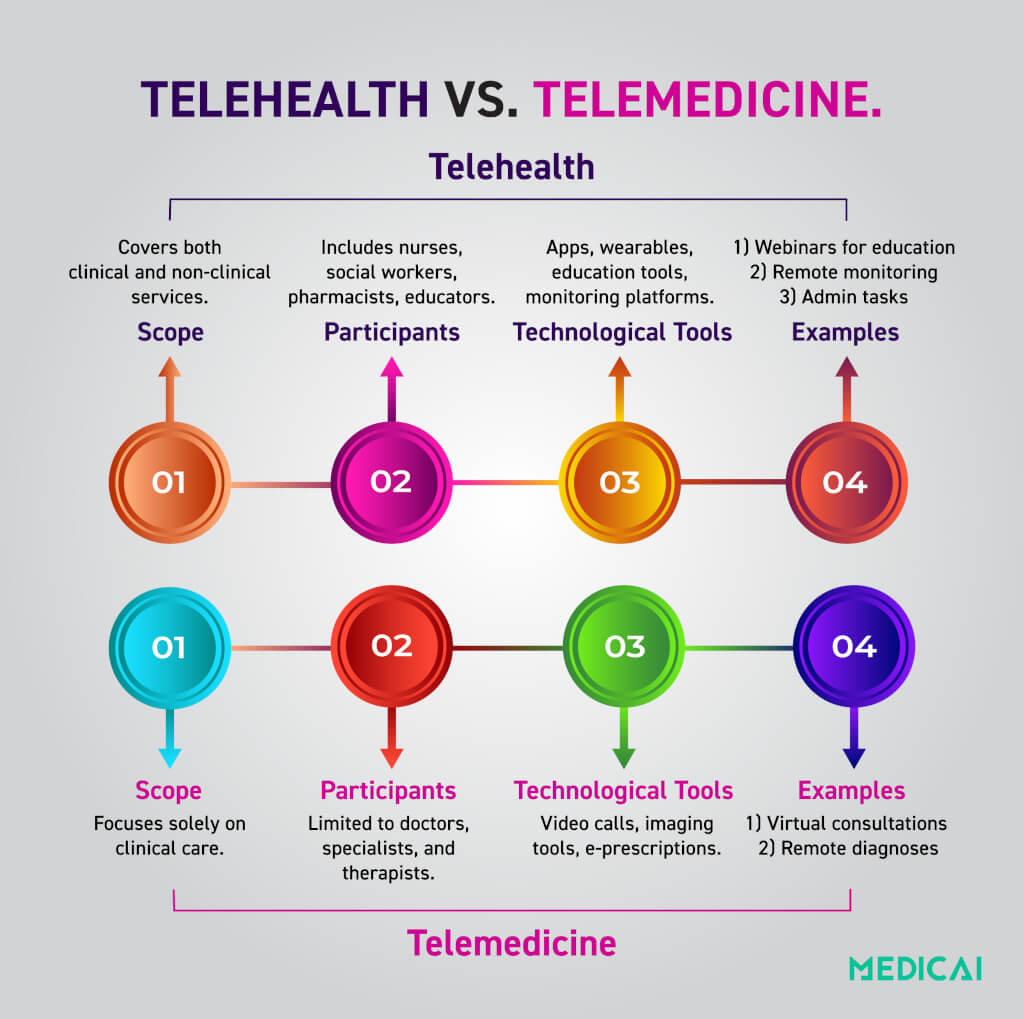
Scope of Services
While telehealth addresses the entire healthcare ecosystem, including education and administration, telemedicine focuses exclusively on clinical interaction between patients and doctors.
Telehealth
Telehealth includes both clinical and non-clinical services.
- Provider Training: Telehealth platforms often educate healthcare providers via virtual training sessions on new medical technologies, implementing updated treatment protocols, or addressing public health crises like pandemics.
- Administrative Meetings: Hospitals and clinics use telehealth for staff meetings and administrative coordination. Remote collaboration reduces in-person gatherings, saving time and resources.
- Health Education: Patients benefit from webinars and online courses on managing chronic illnesses, maintaining healthy lifestyles, and understanding preventive care.
Telemedicine
- Virtual Doctor Consultation: Patients can talk to doctors by phone or video to get diagnoses and prescriptions without going to a clinic. It’s great for those with mobility issues or who live far away.
- Remote Diagnosis: Telemedicine helps healthcare providers to evaluate medical conditions remotely. Medicai provides an advanced imaging infrastructure that helps doctors to access, review, and share diagnostic images instantly.
- Treatment and Follow-Up: After diagnosing a condition, providers can offer a treatment plan, prescribe medications, and recommend lifestyle changes. It also makes follow-up visits seamless, ensuring continuity of care.
- Specialized Care: Specialists such as cardiologists, oncologists, etc., can evaluate patients remotely, often using imaging or real-time video feeds.
Technological Tools
Telehealth employs various technologies to support healthcare delivery at all levels, while telemedicine focuses on tools that help in direct clinical interaction.
Telehealth
Technologies in telehealth include-
- Mobile Health Apps: Patients can track their fitness, manage medications, or monitor chronic conditions. Providers can also communicate with patients, send reminders, and collect data.
- Remote Monitoring Devices: Wearable devices like smartwatches, glucose monitors, blood pressure cuffs, etc., collect health data and transmit it to providers in real-time.
- Educational Platform: Telehealth platforms often feature digital libraries, video tutorials, and live webinars to educate patients and providers.
Telemedicine
Telemedicine uses technologies that help in direct doctor-patient interaction. These include-
- Telecommunication Devices: Video conferencing, secure messaging systems, and telephonic consultations are key components of telemedicine’s telecommunication technology.
- Digital Imaging Tools: Telemedicine platforms help providers view and analyze high-resolution images remotely in specialties like radiology or dermatology.
- Electronic Presentation Systems: Providers can prescribe medications digitally, sending prescriptions directly to a pharmacy for patient pickup.
Medicai’s cloud platform offers several telehealth services, from health education to help with admin tasks. It also has telemedicine tools that let you share images and consult in real-time, making connecting clinical and non-clinical needs easier.
Participants
Telehealth involves various professionals, supporting roles beyond direct patient care, while telemedicine focuses on the clinical relationship between doctors and their patients.
Telehealth
Telehealth engages a broad spectrum of healthcare workers.
- Nurses: involved in remote monitoring, patient education, and follow-up care.
- Pharmacists: involve patients in counseling on medication usage or monitoring.
- Social Workers: Telehealth often connects social workers with patients to address broader determinants of health, such as housing, employment, or access to resources.
Telemedicine
Telemedicine is more specific in its focus. The participants include-
- Physician: Doctors use telemedicine to diagnose illnesses, recommend treatments, and provide follow-up care.
- Specialists: Cardiologists, oncologists, psychiatrists, and other specialists deliver targeted care through virtual telemedicine consultations.
- Therapists and psychiatrists: Mental health providers use telemedicine to offer therapy sessions and manage medications.
Check what is waiting for the future of teleradiology.
Applications
Telehealth and telemedicine serve distinct yet complementary soles in healthcare. Telehealth supports the broader ecosystem, while telemedicine focuses on delivering clinical care directly.
Telehealth Application
- Chronic Disease Management: Continuous monitoring of conditions like diabetes or heart disease.
- Preventive Care: Programs promoting vaccination awareness, lifestyle changes, and regular check-ups.
- Workforce Training: facilitating ongoing education and coordination among healthcare staff.
- Public Health Monitoring: During pandemics, telehealth helps by tracking outbreaks and disseminating vital information.
- Case Discussion: Multidisciplinary teams collaboration.
Telemedicine Application
- Urgent Care: Consulting doctors virtually for immediate care with acute illness or injuries
- Specialist Referrals: Primary care providers can refer to specialists remotely, reducing wait time.
- Post-Surgical Follow-Up: Surgeons can monitor recovery progress without traveling to the clinic.
- Telepsychiatry: Telemedicine benefits mental health services greatly by providing individual therapy, group therapy, counseling, psychiatric evaluation, and medication.
Benefits of Telehealth and Telemedicine for Patients And Providers
Let’s see how telehealth and telemedicine have changed medical services for patients and providers.

Benefits for Patients
The benefits of telemedicine and telehealth are immense in the case of patient care.
Increased Access to Healthcare Services
It’s not always possible to access healthcare services in rural places. However, telehealth and telemedicine have bridged the gap and brought healthcare to patients’ doorsteps. The beneficiaries include-
- Geographic accessibility, no need to travel long distance
- Mobility issues like disabilities or chronic conditions
- Specialist availability, such as cardiology or oncology consultation
Convenience
Virtual healthcare indeed saves time and money by optimizing travel. They help with-
- Time-saving – no travel, no sitting in the waiting room, no taking time off work
- Cost-effective – no spending money on fuel, public transport, or lodging for long-distance care
- Comfort as you can be at your home while getting the consultation from the specialists
Enhanced Engagement
A more active role in managing your health as a patient – once it was a dream. However, it is the actual scenario thanks to telehealth with its tools and resources. Platforms like Medicai empower patients by giving them access to their imaging and health records.
Telehealth and telemedicine help with the following:
- Continuous monitoring with wearable devices and mobile apps that track vital signals, activity levels, medication adherence, etc.
- Health education – webinars, tutorials, and interactive tools.
- Better communication with secure messaging
Benefits for Providers
For healthcare professionals, telehealth and telemedicine are the answer to efficiency, growth, and reach. Let’s see how.
Improved Efficiency
Telehealth and telemedicine streamline workflow and reduce administrative burdens. Medicai integrates smoothly with the existing system to enrich both services with automating processes like image retrieval and sharing.
Thus, providers can focus mainly on patient care rather than administrative tasks. Telehealth and telemedicine help with:
- Faster consultation – address minor concerns, review test results, follow-up treatments, etc.
- Streamlined workflows – automate appointment scheduling, billing, record-keeping, etc.
- Reduced No-Shows as patients are less likely to miss virtual appointments.
Broader Patient Reach
With telehealth and telemedicine, the providers can reach diverse patient groups, including-
- Underserved or rural areas.
- Out-of-state patients where regulations allow.
- Patients with mobility issues, transportation challenges, etc.
Increased Professional Development Opportunity:
Telehealth provides tools and resources that help professionals to develop their skills. These resources may involve:
- Webinars and online training – virtual conferences, workshops, certification programs, etc.
- Peer collaboration.
- Access to cutting-edge tools such as AI-driven diagnostic tools or advanced remote monitoring.
Challenges And Consideration With Telehealth And Telemedicine
Telehealth and telemedicine have magically transformed medical services but also come with challenges.
Regulatory and Licensing Issues Across Different States
In the U.S., healthcare providers must hold licenses in their patient’s state. Also, state policies on telehealth reimbursement, service delivery, and the patient-provider relationship are all over the place, making things complicated for patients and providers.
Efforts like the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact (IMLC) aim to streamline licensing to help physicians practice across multiple states.
Ensuring Data Security And Patient Privacy
Data security and patient privacy are challenging in telehealth and telemedicine, which depend primarily on digital platforms. To safeguard information, providers need to invest in strong cybersecurity measures.
Besides, providers must ensure that all platforms comply with HIPAA to protect sensitive data.
Medicai’s platform always prioritizes regulatory compliance. Its HIPAA-compliant infrastructure guarantees secure storage and transmission of patient data.
Addressing Technological Barriers
Adoption and accessibility to technologies are other challenges in telehealth and telemedicine. Not all patients have smartphones, tablets, or computers for virtual consultations.
Besides, senior citizens or rural patients may struggle with using telehealth platforms or devices. Some places may need more reliable high-speed internet, which is crucial for telemedicine sessions.
Telehealth, Telemedicine, and Telecare: What are the Difference?
Although telehealth, telemedicine, and telecare may sound interchangeable, they differ in focus, scope, and application.
| Aspect | Telehealth | Telemedicine | Telecare |
| Definition | Remote healthcare, including clinical and non-clinical services. | Clinical care focuses on diagnosis and treatment. | Remote support for daily living and safety. |
| Scope | Monitoring, education, training, and admin tasks. | Direct patient-provider clinical interactions. | Non-clinical safety and support. |
| Examples | Monitoring devices, health webinars, and admin meetings. | Virtual consultations, remote diagnosis, therapy. | Fall-alert wearables, home monitoring. |
| Participants | Patients, providers, educators, administrators. | Patients and medical professionals. | Patients, caregivers, and support teams. |
| Technology Used | Apps, wearables, video calls, education tools. | Video calls, secure messaging, imaging tools. | Home sensors, safety devices, and care apps. |
| Primary Goal | Enhance healthcare access, education, and management. | Deliver remote clinical care. | Support safety and independence. |
Conclusion
Telehealth and telemedicine are transforming healthcare, making it more accessible and patient-focused. While telehealth covers a wide range of remote services, telemedicine focuses on clinical care.
Platforms like Medicai enhance these innovations by offering secure, efficient tools for seamless collaboration, better outcomes, and a connected healthcare future.




