AI is transforming neuroimaging by enhancing MRI, CT, PET, and EEG analysis with unmatched speed and accuracy. It detects tumors, strokes, and neurodegenerative changes early, assists radiologists in diagnostics, and personalizes treatment through predictive analytics, improving precision, efficiency, and patient outcomes.
Are you interested in how AI revolutionizes neurology imaging, diagnosis, and treatment? Read on to explore the breakthroughs, challenges, and future of AI in neurology imaging.

The Role Of AI in Neurology Imaging
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing neurology imaging, making diagnoses faster, more precise, and more efficient. Traditional methods, such as MRI, CT, PET, and EEG, rely on time-consuming manual interpretation, often leaving subtle abnormalities undetected.
AI is changing this by analyzing large datasets in seconds, identifying patterns invisible to the human eye, and providing real-time diagnostic insights.
AI-powered imaging also enhances image quality by
- reducing noise
- sharpening diagnostic features
- improving contrast.
It is crucial for low-resolution scans. By reconstructing and refining imaging data using deep learning algorithms, AI allows radiologists to visualize brain structures more clearly without additional radiation exposure or extended scan times.
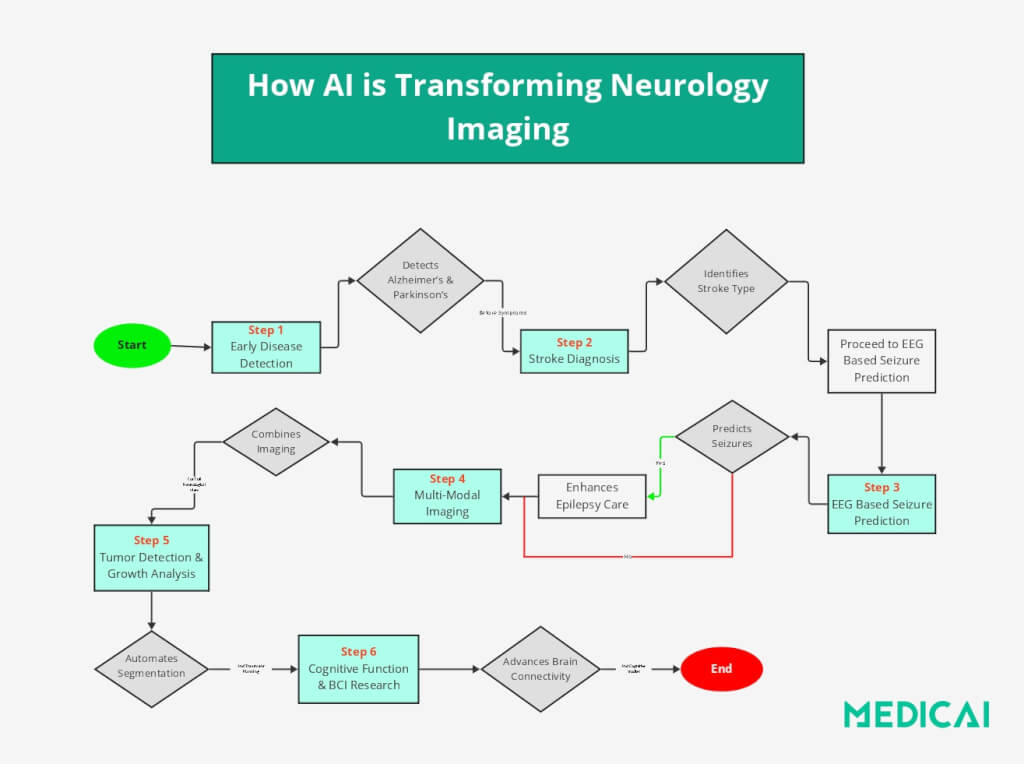
Beyond static imaging, AI is advancing functional imaging techniques like fMRI, Diffusion Tensor Imaging (Dti), and Neuroelectrophysiology (EEG and MEG). These innovations enhance brain connectivity and activity insights, enabling more accurate assessments of cognitive and neurological function.
- In fMRI, AI analyzes brain activity in real time, aiding research on interactions between brain regions and how disorders like depression, schizophrenia, and PTSD affect brain function. AI models explore consciousness, cognitive function, and brain-computer interfaces (BCIs).
- DTI is an MRI technique that maps white matter tracts in the brain. AI-enhanced DTI detects subtle disruptions in neural pathways and helps doctors understand cognitive decline and motor impairments. It is valuable for stroke recovery, multiple sclerosis, and traumatic brain injury.
- In EEG and neuroelectrophysiology, AI automates the detection of abnormal brainwave patterns, aiding in diagnosing and monitoring epilepsy, sleep disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases. Machine learning models analyze real-time EEG signals to identify seizure patterns and predict episodes, enabling proactive management.
Medicai’s AI-powered imaging solutions integrate seamlessly with existing neurology workflows, enhancing image clarity, speed, and diagnostic accuracy. By reducing human error and automating abnormality detection, we help neurologists make faster, more informed decisions to improve patient care.
AI for Early Detection of Neurological Disorders
One of AI’s most valuable contributions to neurology imaging is early disease detection, which identifies subtle brain changes long before symptoms appear. Many neurological conditions, such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, multiple sclerosis, and epilepsy, develop gradually and often go undiagnosed until significant damage has occurred.
AI-powered imaging models detect key biomarkers of neurodegeneration, such as:
- Beta-amyloid plaques and tau tangles in Alzheimer’s disease.
- Dopaminergic neuron loss and motor dysfunction indicators in Parkinson’s.
- Demyelination patterns in multiple sclerosis, predicting disease progression and treatment response.
AI analyzes thousands of brain scans to create predictive models that estimate a person’s risk of developing neurodegenerative diseases. These models help inform earlier interventions through lifestyle changes, medications, or clinical trials.
AI-Assisted Imaging for Real-Time Stroke Detection and Severity Assessment
Stroke diagnosis requires immediate action, as delays can lead to irreversible brain damage. AI models analyze CT and MRI scans within seconds, identifying ischemic vs. hemorrhagic strokes and helping emergency teams make rapid treatment decisions.
- AI assesses stroke severity and predicts recovery outcomes, ensuring patients receive the most effective intervention.
- AI-powered blood flow analysis helps determine eligibility for clot removal (thrombectomy) or clot-dissolving therapy (thrombolysis).
- AI enhances emergency response by reducing diagnosis time and optimizing treatment strategies, leading to better survival rates and long-term recovery.

AI-Driven EEG Analysis for Seizure Prediction in Epilepsy Patients
AI is also transforming epilepsy care through real-time EEG analysis. Traditional EEG interpretation requires neurologists to review hours of brain activity manually.
However, AI-powered models:
- Automatically detect abnormal seizure activity, reducing diagnostic time.
- Predict seizure onset, allowing patients and physicians to take preventive measures.
- Differentiate between seizure types, ensuring tailored treatment plans.
By providing real-time monitoring and predictive insights, AI is helping epilepsy patients gain greater control over their condition and reduce the frequency and severity of seizures.
AI-Powered Multi-Modal Imaging Analysis
AI integrates multiple modalities to enable a more comprehensive approach to brain imaging, providing a richer, more detailed understanding of brain disorders.
- AI combines MRI, PET, and EEG data to allow for a more holistic diagnosis, identifying relationships between structural abnormalities and functional deficits.
- In psychiatric disorders like schizophrenia and depression, AI detects changes in brain connectivity and metabolic activity, aiding in earlier and more precise diagnoses.
- The AI-powered microstructural analysis identifies minute changes in white matter integrity, detecting brain abnormalities before they manifest as symptoms.
Medicai integrates AI-driven multi-modal imaging analysis, allowing neurologists to correlate data across multiple scan types for a more accurate diagnosis. By providing a complete, AI-enhanced view of brain function, Medicai helps doctors make smarter, data-driven treatment decisions.
AI-Driven Precision in Brain Imaging and Diagnosis
Artificial Intelligence is transforming brain imaging and diagnosis by enhancing tumor detection, stroke assessment, and monitoring of neurodegenerative diseases. AI imaging systems analyze MRI, CT, and PET scans more accurately, identifying abnormalities faster than traditional methods.
AI significantly enhances tumor detection, ischemic stroke identification, and neurodegenerative disease analysis. It helps radiologists differentiate between conditions that may have similar imaging characteristics. Through deep learning algorithms, AI detects-
- Anomalies
- quantifies lesion size
- tracks disease progression
- predicts patient outcomes.
AI-driven imaging workflows also reduce human error and increase efficiency. AI automates labor-intensive tasks such as segmentation, classification, and volumetric analysis, helping radiologists focus on interpreting results and making clinical decisions more efficiently.
Medicai’s AI diagnostic tools aid radiologists by automating anomaly detection and disease classification, leading to faster, more accurate imaging interpretations. Our system improves workflow efficiency for early diagnosis and data-driven treatment decisions.

AI in Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Diagnosis
AI-powered imaging models analyze CT and MRI scans within seconds, identifying the type and severity of ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes6.
AI-driven stroke detection tools:
- Identify blocked arteries or brain hemorrhages, determining stroke subtype for appropriate treatment.
- Predict stroke recovery outcomes, guiding rehabilitation strategies tailored to individual patients.
- Analyze blood flow and infarct size to assess long-term cognitive and motor impairments.
Another breakthrough is AI-enhanced ambulance-based stroke triage systems. These portable AI imaging systems help paramedics perform rapid stroke assessments and transmit real-time AI-analyzed data to hospitals.
This enables neurologists to prepare for immediate intervention before the patient arrives, significantly reducing treatment delays.
AI in Brain Tumor and Lesion Detection
AI-powered MRI analysis can detect tumors early and accurately distinguish between benign and malignant growths.
AI assists in:
- Automated tumor segmentation, identifying tumor borders more precisely than human radiologists.
- Surgical planning, guiding neurosurgeons in tumor resection while minimizing damage to healthy brain tissue.
- Post-surgery monitoring, tracking tumor regrowth or response to treatment using AI-powered imaging comparison.
AI also predicts tumor growth and treatment response using radiomics, which extracts imaging features to determine tumor behavior and therapy effectiveness. This allows oncologists to adjust treatment plans proactively, improving patient outcomes.
AI in Epilepsy and Neurodegenerative Disease Imaging
AI is revolutionizing epilepsy diagnostics and neurodegenerative disease monitoring. It provides early warnings and precisely tracks disease progression.
In epilepsy, AI-powered EEG analysis detects seizure patterns and localizes affected brain regions, allowing for:
- Faster and more accurate epilepsy diagnoses, reducing manual interpretation time.
- Seizure prediction models enable preventive treatment adjustments.
- Personalized surgical planning, improving the success rate of epilepsy surgery.
For neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, AI enhances PET and MRI scans by detecting:
- Early-stage brain atrophy, beta-amyloid deposits, and tau protein accumulation in Alzheimer’s.
- Dopaminergic neuron loss and structural deterioration in Parkinson’s, aiding in early treatment initiation.
Machine learning models analyze changes, predicting disease progression and cognitive decline. They help neurologists adjust treatments proactively.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations in AI Neuroimaging
AI’s integration into healthcare comes with data privacy, transparency, bias, and regulatory approval challenges.
Data Privacy and Security
AI models rely on large-scale medical imaging datasets containing sensitive patient information. Without stringent security measures, there is a risk of data breaches, unauthorized access, and ethical concerns regarding patient consent.
Compliance with HIPAA and GDPR, strong encryption protocols, and de-identified datasets are essential to protect patient privacy and maintain trust in AI-driven diagnostics.
The Black Box Problem: AI Transparency and Interpretability
One of AI’s most significant challenges in neuroimaging is its lack of transparency. Many deep learning models function as “black boxes,” meaning their decision-making processes are not easily explainable. This raises concerns for neurologists and radiologists, who must trust AI-generated diagnoses without fully understanding how AI reaches its conclusions.
Developing explainable AI (XAI) can help bridge the gap between AI insights and human decision-making, allowing for greater clinical trust and validation.
Bias in AI Models: Addressing Disparities in Neurological Imaging
AI models trained on non-representative datasets may show lower accuracy in diagnosing neurological conditions across different demographics. If an AI system is primarily trained on data from high-income populations or specific ethnic groups, its effectiveness for underrepresented populations may be compromised.
Potential risks include:
- Misdiagnosis or underdiagnosis in patients from diverse ethnic backgrounds.
- Gender-related disparities in diagnosing conditions like Alzheimer’s or multiple sclerosis.
- Increased healthcare inequality due to biased AI decision-making.
To mitigate bias, AI models must be trained on diverse, well-balanced datasets, undergo bias audits, and continuously improve based on real-world clinical performance.
Regulatory Challenges: Standardizing AI in Medical Imaging
AI-driven medical imaging faces regulatory challenges, as most approval frameworks were designed for static medical devices, not AI models that continuously evolve. Standardized validation methods are lacking, making it difficult to ensure long-term reliability and clinical safety.
Regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA must establish AI-specific approval pathways. They should focus on continuous monitoring, post-market surveillance, and clear liability policies to ensure safe AI deployment in neurology imaging.
Conclusion
AI transforms neurology imaging, enabling earlier diagnoses, sharper brain scans, and more precise treatment planning. From stroke detection to neurodegenerative disease monitoring, AI enhances efficiency while supporting neurologists with data-driven insights.
With Medicai’s AI-powered imaging solutions, healthcare providers can achieve faster, smarter, and more accurate diagnostics, shaping the future of neurological care with innovation and precision.





