What if your doctor handed you a treatment plan generated by AI, without explaining why? Would you trust it?
In today’s data-driven healthcare landscape, AI is growing in diagnosing disease and guiding personalized treatment. But without transparency, even the most accurate AI can create doubt.
Explainable AI (XAI) offers clear, human-readable insights into how decisions are made. It transforms AI from a black box into a tool clinicians and patients can trust.
Let’s explore how XAI is reshaping personalized medicine, why it matters, and its challenges.
Understanding Explainable AI (XAI)
Explainable AI (XAI) refers to artificial intelligence systems designed to make their decision-making processes transparent and understandable to humans. In contrast to traditional “black-box” models that provide outputs without revealing their logic, XAI clarifies how inputs influence results.
This clarity is essential in healthcare. When an AI system suggests a diagnosis or treatment, doctors and patients must understand why. Tools like SHAP (Shapley Additive Explanations), LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations), and Grad-CAM are helpful here.
These methods reveal which features, data points, or image regions contributed to the AI’s decision, making the process interpretable for clinical use.
By offering explanations in visual, textual, or numerical forms, XAI turns complex AI outputs into actionable insights. This transparency helps align AI tools with medical reasoning and human intuition, both essential in patient care.

Why Healthcare Demands Explainability
Explainability plays a critical role in building trust. Research shows that opaque AI models reduce treatment adherence and weaken patient-provider collaboration. When AI systems lack reasoning for their outputs, clinicians struggle to validate or defend patient recommendations.
Personalized treatment requires adapting care to each individual’s history, biology, and preferences. Without understanding how an AI system evaluates these factors, personalization becomes meaningless.
Explainability aids in meeting legal and ethical standards, such as the EU’s GDPR, which stresses individuals’ rights to understand automated decisions. For healthcare providers, this means selecting AI tools to explain their reasoning.
In summary, healthcare demands explainable AI because:
- Patient safety requires clarity, not assumptions.
- Clinical trust is built on understanding, not automation.
- Legal standards demand transparency and accountability.
Why Personalized Treatment Needs XAI
XAI gives context to AI decisions. Explainable AI ensures that personalization doesn’t just happen silently in the background—it happens openly, with clarity and purpose.
When a system recommends a specific chemotherapy drug over another, or adjusts insulin dosage for a diabetic patient, XAI tools can show which factors led to that choice.
These explanations help doctors understand and communicate the recommendation more clearly to the patient. Patients must understand the trade-offs of long-term treatments in chronic care and oncology.
Trust, Adherence, and Shared Decisions
Trust is the foundation of personalized medicine. Patients who don’t understand why a treatment is chosen specifically for them are more likely to question or avoid it altogether. That’s where XAI steps in.
Studies show that when patients are provided with transparent, understandable justifications for medical decisions, especially those generated by AI, they are more likely to adhere to those treatments.
In contrast, vague or opaque recommendations lead to doubt, reduced compliance, and even treatment dropout.
XAI enhances shared decision-making by allowing clinicians and patients to understand the rationale behind AI recommendations. It fosters dialogue, encouraging patients to ask better questions and enabling doctors to provide evidence-based answers based on the model’s logic.
This collaboration makes care feel more personal. With XAI, the AI explains, collaborates, and supports decisions made by humans.
Adapting to the Individual in Real Time
Personalized care is an ongoing process that adapts as patients respond to treatments, experience side effects, or develop new symptoms. Interactive XAI systems enable AI models to learn from new data and provide updated explanations for their recommendations.
Clinicians use dynamic tools instead of static reports, enabling them to understand changes over time. For instance, if a wearable detects irregular sleep or rising blood pressure, XAI can show how these patterns affect treatment predictions, supporting early intervention and care adjustments.
Core Components of XAI in Personalized Healthcare
The core components of XAI come together to make AI an active, transparent, and trusted partner in delivering truly personalized care.
Interpretable Algorithms for Real-Life Decisions
At the core of XAI is making AI understandable while maintaining accuracy. In personalized healthcare, this starts with choosing an algorithm.
Interpretable models, like decision trees, clearly show how variables influence decisions. In contrast, complex models, such as deep learning, can also be explained through XAI techniques.
For personalized medication plans, interpretable models demonstrate how weight and kidney function affect dosing recommendations, increasing doctors’ confidence in AI suggestions and helping them tailor treatments effectively.
Visual and Interactive Explanations
Visual explanation methods like Grad-CAM and saliency maps are crucial in medical imaging. They highlight areas in MRI or CT scans that AI focuses on for diagnoses. These tools aid radiologists and help patients understand findings visually.
Interactive dashboards enhance user experience by allowing clinicians and patients to adjust inputs and see changing recommendations, fostering collaborative discussions and active engagement.
Medicai integrates visual explanations like Grad-CAM directly into its image viewer, allowing clinicians to assess both the result and its reasoning in one seamless workflow.
Learning Through Feedback and Real-Time Refinement
Modern XAI’s strength lies in its ability to continuously learn from real-world interactions. Interactive Explainable systems can evolve beyond static predictions.
As clinicians provide feedback or patients’ conditions change, these models can adapt their outputs while explaining the reasons for changes. It creates an adaptive AI assistant that continually improves accuracy and remains interpretable.
Techniques and Tools in Explainable AI
Several key tools facilitate the function of explainable AI in healthcare.
Model-Agnostic Methods: Versatility Across the Board
Model-agnostic XAI techniques work with any machine learning model by focusing on output analysis rather than internal mechanics. It makes them flexible and widely applicable in healthcare systems.
Two of the most widely used techniques in this category are:
- SHAP (SHapley Additive Explanations): SHAP, from cooperative game theory, assigns contribution values to features in predictions. It helps explain why a patient with specific biomarkers is more suitable for Drug A than Drug B.
- LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations): LIME simplifies a model around a specific prediction, helping clinicians identify the key features influencing that case.
These tools empower clinicians to interpret predictions patient by patient, which is crucial for explaining treatment plans in highly individualized care settings.
Counterfactual Explanations: Exploring the “What Ifs”
Counterfactuals are a powerful way to explore alternate outcomes. They answer questions like: What would need to change in a patient’s profile for the AI to recommend a different treatment?
This kind of reasoning is intuitive for doctors and helpful in ethical reviews. It allows providers to understand the decision boundary of the AI model and consider edge cases, such as patients who might have borderline risks or ambiguous profiles.
By providing this kind of “scenario testing,” counterfactuals add a layer of clinical stability and help doctors think through alternative interventions.
Model-Specific Methods: Deeper Explanations for Specialized Models
Some XAI tools are built to work with specific types of models, such as deep learning systems used in medical imaging, pathology, or genomics.
For example,
- Grad-CAM (Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping): it highlights parts of an image that influenced a model’s decision. It is commonly used in radiology and oncology to show where the model focused when identifying tumors or lesions.
- Saliency Maps: Show pixel-level importance in image-based models. These help pathologists interpret biopsy scans and understand how the AI was diagnosed.
- Feature Visualization: it aids in interpreting deep neural networks in non-image domains by displaying neuron or layer responses to specific patterns, beneficial for genomics and predictive diagnostics.
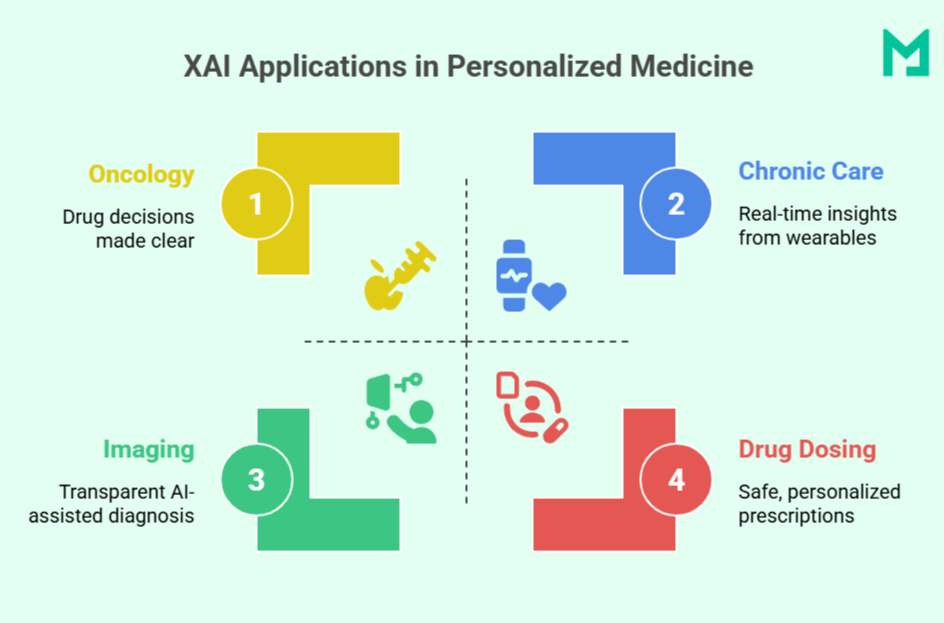
Specific Applications of XAI in Personalized Treatment
By clarifying the “why” behind the “what,” XAI brings AI-powered medicine closer to everyday, patient-centered care.
Precision Oncology
Cancer treatment decisions increasingly rely on molecular profiling, tumor staging, and patient history. Explainable AI (XAI) clarifies how these factors affect therapy selection.
For example, IBM Watson for Oncology uses XAI to simplify complex decisions with clear justifications, linking genetic mutations and past responses to recommendations. It helps oncologists align AI suggestions with clinical reasoning and boosts patient confidence in their care.
Risk Stratification and Chronic Disease Management
In chronic care (e.g., diabetes, hypertension), XAI enables personalized interventions by monitoring patient data from wearables or EHRs in real time. Explainability is crucial; tools like SHAP can show if a glucose spike was due to poor sleep, diet, or stress.
It allows clinicians to adjust treatment with insight into the model’s rationale, improving safety and responsiveness.
Diagnostic Imaging and Pathology
Deep learning is widely used in medical imaging, but its complexity can undermine clinical trust.
XAI helps by providing visual explanations, like Grad-CAM and saliency maps, highlighting key areas in scans or slides that influenced AI diagnoses, such as lung nodules or malignant cells. This helps radiologists and pathologists verify findings, explain them to patients, and spot potential model errors.
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
XAI-enhanced CDSS tools support treatment decisions in primary care and hospitals. Unlike traditional alerts, explainable systems like MediAssist offer clear reasoning, demonstrating how symptoms, vitals, and lab results indicate pneumonia over bronchitis.
This transparency aids clinicians in making quicker, informed choices and enhances diagnostic accuracy while reducing alert fatigue.
Personalized Drug Dosing and Pharmacogenomics
Medication response differs among individuals.
XAI enhances pharmacogenomic models to personalize drug choice and dosage by considering genetic markers, age, and liver function. Clinicians receive dosage recommendations and insights into their suitability, making precision prescribing safer and more reliable.
Clinical Benefits of XAI in Personalized Care
Explainable AI offers more than just accurate predictions.
| Stakeholder | Key Benefits | Impact |
| Clinicians | Understand which variables drive AI decisionsValidate and adapt AI suggestionsReduce uncertainty in diagnosis | Builds diagnostic confidenceEncourages faster, informed decisionsPromotes clinician trust |
| Patients | Receive clear explanations for treatmentsUnderstand how personal factors impact careFeel included in decisions | Boosts trust and satisfactionImproves treatment adherenceSupports shared decision-making |
| Healthcare Systems | Ensure transparency in AI toolsDetect and address biasComply with legal and ethical standards (e.g., GDPR, FDA) | Enables regulatory complianceImproves safety and fairnessStrengthens accountability |
Medicai’s approach to explainable imaging helps close the gap between AI diagnostics and human validation, enhancing clinician trust and patient engagement.
Challenges In Implementing Explainable AI For Personalized Treatment
A few challenges can occur while implementing XAI for personalized treatment.
Balancing Accuracy and Interpretability
A common trade-off in XAI is between model complexity and explainability. Deep learning models achieve high accuracy with complex medical data but are often difficult for clinicians to understand.
Simpler models, like decision trees, are easier to interpret but may lack predictive power in nuanced cases. Finding the right balance remains challenging, especially when lives are at stake.
Lack of Standardization
There is no universal definition of an “explainable” AI model, leading to variations in methods, formats, and details across different tools. This inconsistency complicates trust assessments for healthcare providers and challenges regulatory approvals, as agencies must evaluate each system individually without clear benchmarks.
Integration with Clinical Workflows
Many healthcare institutions rely on legacy systems and siloed databases, making the integration of explainable AI (XAI) challenging.
Custom integration with electronic health records (EHRs) can delay implementation, and clinicians need time and training to adapt and trust these new tools. It is often difficult in high-pressure environments.
Data Privacy and Security
XAI requires detailed patient data for accurate insights, which raises privacy concerns. Compliance with HIPAA and other laws is crucial, and developers must ensure that explanations do not inadvertently expose sensitive information during testing or deployment.
Conclusion
Explainable AI is redefining what it means to deliver truly personalized care by making medical decisions transparent, trustworthy, and patient-centered. In a world where AI is becoming essential to diagnosis and treatment, platforms like Medicai are leading the way by ensuring clinicians don’t just get answers, but understand them.
As healthcare evolves, explainability won’t be optional—it will be expected.




