What if your radiology workstation could not only listen, but also understand? This is the promise of voice-enabled radiology.
Voice-enabled radiology is the evolution from traditional dictation to AI-powered contextual commands. Instead of only transcribing words, modern systems understand intent. It integrates with PACS, compares priors, fills structured reports, and even reduces errors in real time.
Discover the journey of voice in radiology, its challenges, innovations, and the future that’s already taking shape.

A Brief History of Voice in Radiology
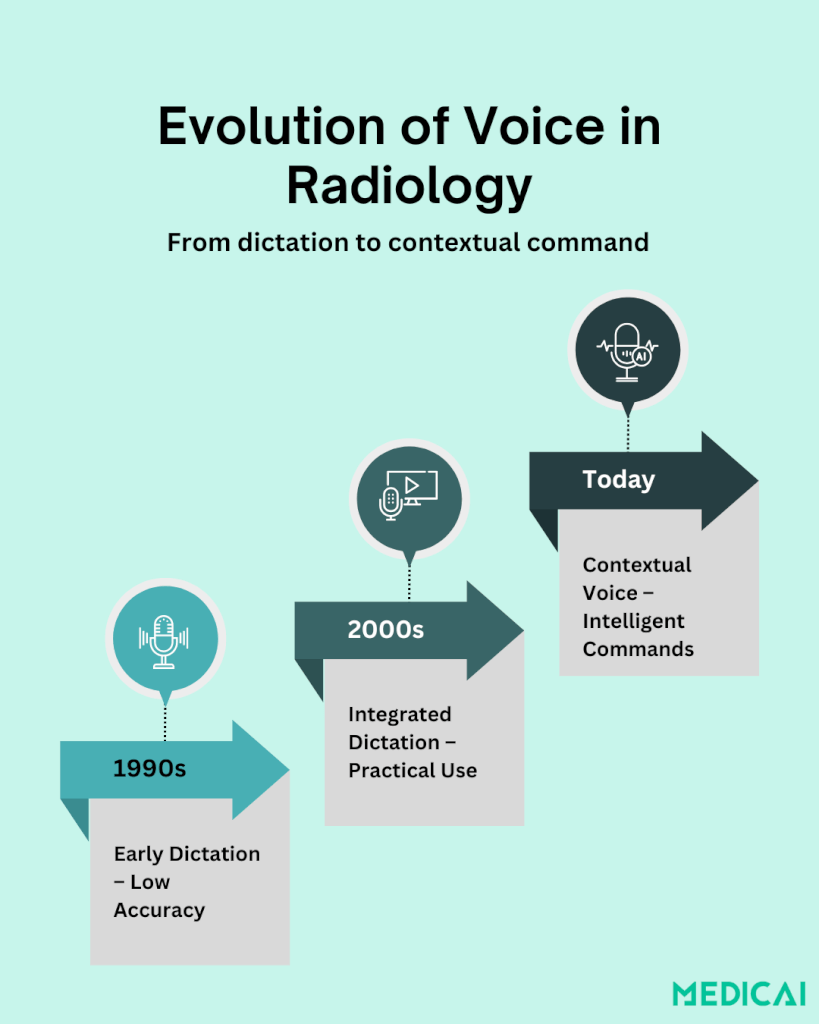
Voice technology in radiology has transformed dramatically over the past three decades. What began as an add-on for faster report turnaround is now a core part of daily practice.
In the 1990s, early voice dictation systems aimed to replace transcriptionists, but accuracy was poor. Medical jargon, background noise, and constant corrections made adoption slow and frustrating.
By the early 2000s, vendors integrated voice recognition directly into RIS and PACS, improving accuracy and streamlining workflows. Dictation became less experimental and more practical.
Today, speech recognition is standard in radiology reporting worldwide. Modern systems not only transcribe but also auto-fill templates, flag inconsistencies, and apply standardized terminology.
This evolution sets the stage for a new era: moving from dictation to interaction. Radiologists can now issue contextual voice commands, like “Show prior CT” or “Generate liver lesion template,” turning voice into an intelligent tool for managing data, controlling imaging systems, and working alongside AI.
From Dictation to Contextual Command: What Changed in Voice‑Enabled Radiology?
Radiology’s use of voice has entered a new era. What started as a tool to replace transcriptionists has now become an intelligent way to interact with imaging systems.
Dictation: The First Step
For years, voice technology in radiology meant dictation. Radiologists spoke into a microphone, and the software typed out their words. This saved time compared to traditional transcription, lowered costs, and sped up report delivery.
But dictation had limits. The system didn’t know what the words meant. It simply recorded them as text, leaving radiologists to handle everything else manually.
Contextual Commands: More Than Words
The next step forward is contextual voice commands. Instead of only narrating findings, radiologists can now speak commands that perform tasks.
Commands like “Compare with last MRI” or “Pull up prior chest CT” don’t just generate text; they trigger actions inside PACS and reporting software. This is a voice evolving from a note-taking tool into a true digital assistant.
The AI Leap: Understanding Intent
What makes this possible is AI-driven intent recognition. Today’s systems don’t just listen to words; they interpret the purpose behind them.
If a radiologist says, “Show axial view,” the system knows it’s a navigation command, not text for the report. By connecting speech with context, AI reduces errors and makes the workflow more natural.
Radiology is moving from voice as a transcription tool to voice as an intelligent interface-
- In PACS, radiologists can issue commands to open prior studies, zoom into specific regions, or change imaging planes without touching a keyboard.
- In structured reporting, voice can auto-populate fields with standardized phrases while leaving room for free narration.
- In ultrasound control, hands-free voice commands allow clinicians to freeze frames or adjust settings while keeping full attention on the patient.
Looking ahead, integrating voice dictation for contextual annotations in PACS could enhance user experience, similar to voice-enabled Google search. Adopting structured annotations may enable better tracking of tumor lesions over treatments and facilitate earlier detection of treatment responses or failures.
Platforms like Medicai are already exploring ways to interpret radiologists’ commands with context, helping reduce errors and make navigation effortless.
Why Voice-Enabled Radiology Matters Today
From reducing burnout to improving patient interactions, the benefits of voice-enabled radiology go beyond convenience.
Tackling Radiologist Workload and Burnout
Radiology is one of the most data-heavy specialties in medicine. A single shift can involve hundreds of images and dozens of reports. Typing, clicking, and handling through systems eats up valuable time.
Voice commands help cut through the clutter. By dictating findings or issuing quick commands, radiologists spend less time on repetitive tasks and more time focusing on accurate diagnosis and patient care.
Hands-Free Control in the Reading Room and Beyond
In areas like interventional radiology or ultrasound, hands-free control can be transformative. A radiologist can say, “Freeze frame” or “Measure diameter” without touching the machine.
With fewer physical interactions, the risk of contamination during procedures decreases, and the clinician can keep their full attention on the patient.
Improving Accuracy and Reducing Errors
Dictation alone has its pitfalls. Mishearing “left” as “right” or confusing patient details can create serious reporting errors.
AI-powered voice systems now act as a safety net. They can flag inconsistencies such as a mismatch between patient gender and the dictated anatomy. The real-time feedback improves report accuracy and reduces the risk of costly mistakes.
Enhancing Patient Engagement
When radiologists spend less time clicking through PACS and typing notes, they have more bandwidth for patient communication. In settings like ultrasound or interventional imaging, voice commands help clinicians to stay present with the patient instead of staring at a keyboard.
That shift fosters trust, comfort, and stronger doctor–patient relationships.
The Workflow of Voice-Enabled Radiology
Voice-enabled radiology changes the way radiologists interact with technology. Instead of juggling keyboards, mice, and endless clicks, the workflow becomes speech-driven, context-aware, and AI-assisted.
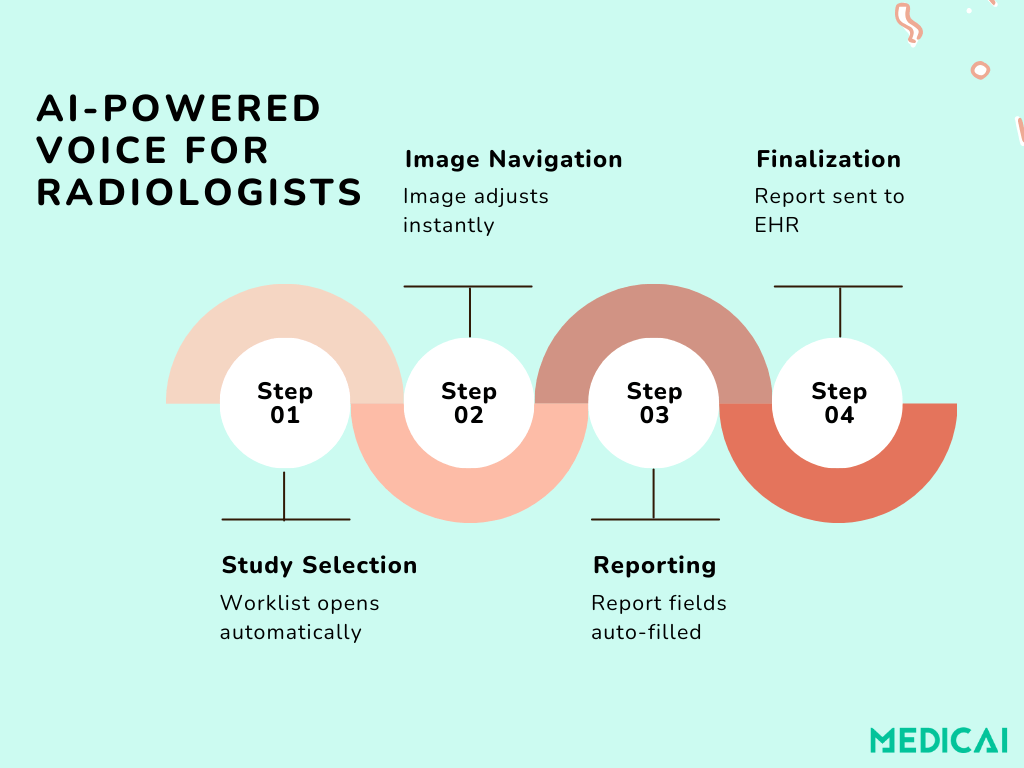
1. Study Selection and Navigation
The day begins with a simple voice command:
“Open today’s abdominal CT cases.”
The system retrieves the worklist, filters studies by modality and priority, and displays them on screen. Radiologists can further proceed with commands like “Next patient” or “Show priors from 2022.”
2. Image Review and Interaction
While reviewing images, radiologists use voice to control the viewing environment:
- “Zoom into liver.”
- “Switch to coronal view.”
- “Highlight lesion in the left lobe.”
This hands-free control keeps the workflow efficient and reduces repetitive manual navigation.
3. Dictation and Structured Reporting
As findings are described out loud, the AI-driven system listens in real time. It:
- Converts spoken words into text.
- Matches findings with standardized terminology
- Populates structured fields (e.g., measurements, laterality, impression).
For example, saying “There is a 1.5 cm nodule in the right upper lobe” auto-fills the report with the correct fields and units.
4. Error Checking and Smart Prompts
If the system detects an inconsistency, it provides immediate feedback:
- “Did you mean left or right lung?”
- “Patient is female—prostate reference not applicable.”
This real-time correction improves accuracy and minimizes editing later.
5. Collaboration and Sharing
Once the report is nearly complete, the radiologist can issue workflow commands such as:
- “Send to referring physician.”
- “Flag for tumor board.”
- “Share annotated images with oncology team.”
The system routes the report and images securely, reducing delays in patient management.
6. Report Finalization
Finally, the radiologist can say, “Finalize report and sign off.”
The system closes the loop by storing the structured report in the EHR, tagging it for future AI learning, and making it instantly available for clinicians.
Challenges and Limitations of Voice‑Enabled Radiology
While voice-enabled radiology shows huge promise, it’s not without its hurdles.
Technical Barriers: Accents, Noise, and Vocabulary
Radiology language is complex. Terms like “hypoechoic,” “glioblastoma,” or “axial FLAIR” are not easy for generic speech recognition systems to handle.
Add in background noise, strong accents, or rapid speech, and accuracy drops. Misinterpretations can create frustrating errors that take time to correct.
Integration with PACS and EHR Systems
Voice tools don’t work in isolation. They need to connect seamlessly with PACS, RIS, and EHR platforms. Lack of interoperability means radiologists often juggle between voice tools and manual clicks, which defeats the purpose.
Until systems speak the same digital language, adoption will remain patchy.
Radiologist Trust and Adoption
Some radiologists still hesitate to rely on voice for critical reporting. Concerns about accuracy, speed of correction, and liability persist. If a misinterpreted command alters a report or fails to pull up the right study, confidence drops quickly.
For widespread adoption, the technology must prove itself consistently reliable.
Privacy and Security Concerns
Voice data contains sensitive patient information. Every dictated phrase or spoken command must be processed in a HIPAA-compliant environment. Cloud-based voice systems raise questions about encryption, storage, and potential breaches.
Without airtight security, trust in voice-enabled systems will be limited.
Cost and Training Requirements
Implementing advanced voice systems isn’t cheap.
Hospitals must invest in software, integration, and training. Radiologists also need time to adapt their workflows and learn how to use contextual commands effectively. For smaller practices, the return on investment may take time to justify.
Conclusion
Voice-enabled radiology has moved far beyond simple dictation. With AI-driven contextual commands, radiologists can now interact with systems in smarter, faster, and more natural ways.
Radiology is indeed entering an era where technology listens, understands, and empowers patient care.
As the field evolves, platforms like Medicai are helping radiologists embrace these innovations: integrating voice, AI, and workflow automation into one seamless experience.




