What if your medical images could do more than just sit in storage? Imagine if they could think—analyzing themselves, spotting red flags, and helping doctors make faster, smarter decisions tailored to each patient.
Well, that’s no longer science fiction. It’s happening now.
With the rise of AI and cloud-based imaging platforms, medical diagnostics is entering a new era. Cloud PACS is the engine driving this transformation. Clinical decision support has become more predictive, personalized, and powerful than ever.
Let’s unpack how AI and imaging analytics are revolutionizing clinical workflows.

What Is Cloud PACS, and How Does It Differ?
Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) are essential for digital medical imaging. Traditionally, these systems required hospitals and clinics to install and maintain on-premise servers to store and access images such as MRIs, CT scans, and X-rays.
Cloud PACS modernizes that framework. Instead of hosting the data locally, cloud PACS systems store imaging files securely on remote servers, accessible via the internet. This shift offers immense benefits regarding convenience and how healthcare providers manage, share, and analyze medical images in real time.
What sets cloud PACS apart is where the data lives and how it powers collaboration, analytics, and AI integration across healthcare systems.
Advantages of Cloud PACS
The benefits of cloud PACS are immense.
1. Scalability and Flexibility
One of the most compelling features of cloud PACS is its ability to scale. Cloud storage grows with your imaging demands, whether you’re a small clinic or a multi-site hospital network.
There’s no need to invest upfront in expensive hardware or future upgrades. Storage limits and performance bottlenecks are eliminated.
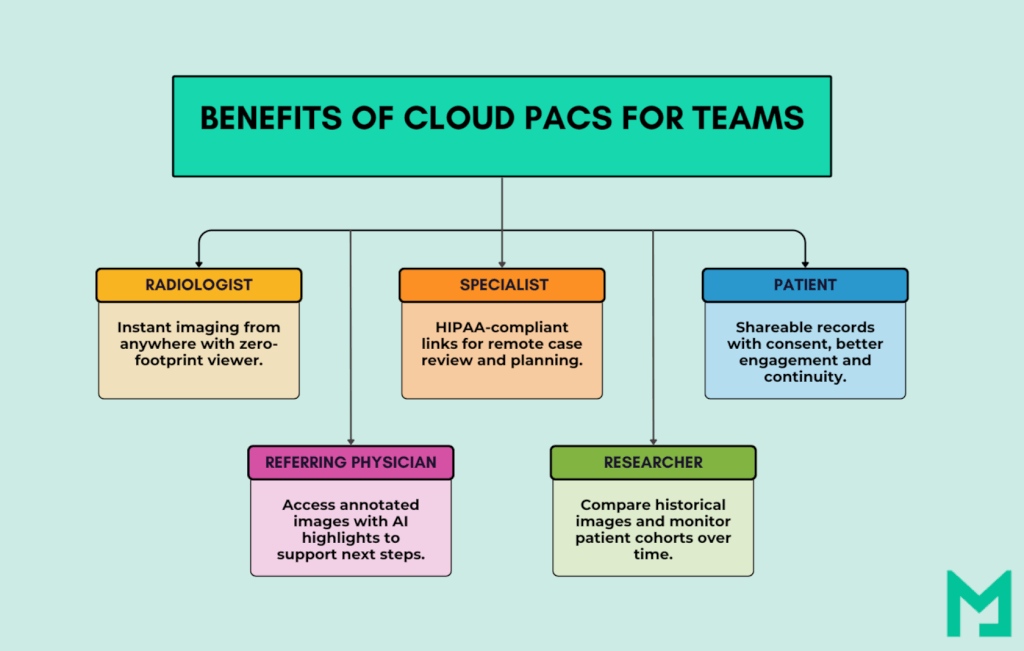
2. Enhanced Collaboration
With cloud PACS, radiologists, referring physicians, and specialists can access imaging studies anytime, anywhere. This is especially valuable for multi-disciplinary teams or second-opinion consultations across institutions.
Instead of shipping discs or relying on VPNs, providers can share imaging studies securely through web portals with controlled access.
3. Cost-Effectiveness and Reduced Infrastructure Overhead
Healthcare organizations face increasing pressure to optimize IT costs without compromising performance or compliance. Cloud PACS minimizes capital expenditures on servers, cooling systems, and dedicated IT personnel.
Providers also benefit from automatic software updates, enhanced cybersecurity protocols, and built-in disaster recovery, all managed by the vendor.
Platforms like Medicai are redefining modern imaging infrastructure. Medicai’s cloud-based PACS is fully HIPAA-compliant and designed with compliance in mind, ensuring data privacy and security at every step.
The Role of AI in Medical Imaging Analytics
AI transforms medical imaging by automating image analysis and supporting clinical decisions, especially when integrated with cloud-based PACS. As imaging volumes rise and timelines shrink, this technology is essential for radiologists and care teams to provide accurate and efficient care.
Let’s check the key capabilities of AI in imaging analytics.
Automated Detection and Triage
AI models trained on large imaging datasets can spot patterns and flag anomalies, often before they are visible to the human eye. These tools help prioritize critical cases in radiology, ensuring urgent conditions like brain bleeds or pulmonary embolisms receive immediate attention through AI healthcare solutions.
Decision Support Through Pattern Recognition
Beyond triage, AI helps highlight clinically relevant regions, measure lesion sizes, and suggest potential diagnoses. This isn’t about replacing radiologists—it’s about augmenting their expertise with consistent, objective insights.
It can help reduce the variability between readers, particularly in complex or high-volume environments.
Structured Reporting and Workflow Acceleration
AI-enabled platforms like Medicai can assist in generating structured reports, auto-filling templates based on image findings, and tagging images for future reference or education. These capabilities save time and improve communication clarity between specialists and primary care providers.
Clinical and Operational Benefits
The real-world impact of AI in imaging analytics extends far beyond technical efficiency:
- Improved Diagnostic Accuracy: AI helps reduce false negatives and supports early disease detection.
- Faster Turnaround Times: With automation handling repetitive or routine analysis, radiologists can focus on complex reads and decision-making.
- Reduced Burnout and Workload: AI offloads mundane tasks and prioritizes high-risk cases, leading to a more sustainable work environment.
- Data-Driven Insights for Research and Quality Control: Structured outputs from AI can feed into dashboards, analytics tools, and clinical studies, enhancing continuous improvement efforts.

Personalizing Clinical Decision Support with AI and Imaging Analytics
Traditional clinical decision support (CDS) tools use generalized rules, but the shift toward data-driven medicine calls for more personalized support. Combining AI and imaging analytics with cloud PACS enables patient-specific insights, improving diagnostics and outcomes.
Integrating Imaging Data with Patient Context
AI-powered CDS systems thrive on data. These systems can contextualize findings and make more nuanced recommendations by integrating imaging analytics with other clinical information, such as electronic health records (EHRs), lab results, genetic profiles, and demographics.
An AI tool can analyze a patient’s CT scan, considering factors like age, smoking history, and family cancer history, to assess malignancy risk. It can also compare current scans with past images to detect early progression or unexpected changes.
This data fusion helps AI to move from simple detection to interpretation, transforming imaging from a static visual file into a dynamic source of clinical insight.
Predictive, Personalized Decision Support in Practice
Let’s see how AI and imaging analytics support personalized decision-making:
- Tailored Risk Assessments: AI can flag patients at higher risk based on visual biomarkers and historical patterns.
- Treatment Planning Guidance: Imaging-based algorithms can help identify tumor response trends in oncology patients, suggesting whether to continue, adjust, or escalate therapy.
- Predictive Modeling: In cardiology, AI can model the likely progression of conditions like aortic stenosis by analyzing subtle changes over time.
These tools help radiologists, primary care doctors, specialists, and entire care teams determine the right next steps for a patient.
Cloud-Based AI Solutions in Action
Understanding the potential of AI and cloud PACS in theory is one thing; seeing it in action is another.
Across healthcare systems worldwide, cloud-based AI imaging solutions are already streamlining diagnostics, cutting delays, and helping clinicians make faster, more accurate decisions.
For example, platforms like Medicai are built to handle everything from secure storage to AI-powered annotation and analysis. These platforms support DICOM standards and integrate open-source frameworks to accelerate algorithm development and deployment.
- AI-Assisted Annotation Tools: Radiologists can use intelligent labeling and segmentation tools to prepare training data or validate AI outputs.
- Scalable Storage & Compute: Massive imaging datasets can be stored and processed efficiently, benefiting health systems, academic institutions, and research centers.
- Interoperability: They support integrating EHRs, FHIR servers, and other health IT systems to centralize clinical data.

Workflow of AI and Imaging Analytics in Personalized Clinical Decision Support
Integrating AI and imaging analytics into cloud-based PACS transforms raw imaging data into tailored clinical insights.
Learn how that process unfolds across a modern, cloud-enabled healthcare environment.
Step 1: Image Acquisition and Cloud Ingestion
- Imaging data is captured from hospital scanners or imaging centers.
- Instead of being stored locally, these DICOM files are directly uploaded to a Cloud PACS, such as Medicai or Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite.
- Metadata is automatically preserved for traceability, and encryption ensures secure transfer and storage.
This eliminates manual steps and makes images instantly accessible for AI processing and multi-site collaboration.
Step 2: AI-Powered Image Analysis and Triage
- Once ingested, AI algorithms begin analyzing the images in real time.
- The system detects anomalies (e.g., tumors, fractures, hemorrhages), prioritizes urgent cases, and flags abnormal regions.
- AI also compares current scans with prior images in some platforms to identify subtle changes over time.
This step reduces radiologists’ workload and speeds up critical case handling with automated prioritization.
Step 3: Clinical Data Integration for Personalization
- The Cloud PACS connects with Electronic Health Records (EHRs) or other clinical databases.
- AI integrates contextual information (age, history, comorbidities, genetic data) with image analysis to support personalized recommendations.
- Risk scores, staging assessments, or treatment suggestions are tailored to the individual, not generalized cohorts.
It transforms imaging from a standalone diagnostic tool into a dynamic engine for personalized medicine.
Step 4: Decision Support Output for Physicians
- AI-generated insights are fed into the radiologist’s or physician’s workflow.
- Structured reports, annotated images, and intelligent flags are integrated into the PACS viewer, eliminating the need for external dashboards.
- Providers review AI results, validate findings, and utilize support tools for enhanced diagnosis and care planning.
Thus, clinicians stay in control, using AI to enhance—not override—their judgment with data-driven support.
Step 5: Collaboration, Sharing, and Follow-Up
Through secure portals or APIs, imaging data and reports can be shared with:
- Referring physicians
- Specialists
- Clinical trial coordinators
- Even patients, when appropriate
Follow-up imaging can be automatically compared, and AI continues to learn and adapt as more data is processed. It encourages coordinated care, longitudinal tracking, and evidence-based decision-making over time.
Addressing Challenges and Ensuring Compliance
As AI and cloud PACS become integral to clinical workflows, they also introduce challenges, especially in compliance, ethics, and system integration.
Data Security and Regulatory Compliance
Cloud-based systems managing Protected Health Information (PHI) must align with frameworks like HIPAA, GDPR, and other regional standards. This includes:
- End-to-End Encryption for data protection during transfer and storage
- Access Controls to limit image access to authorized users
- Audit Logs for activity tracking and accountability
- Redundant Storage for disaster recovery and business continuity
Platforms like Medicai prioritize strong encryption, user permissions, and system transparency as core features.
Ethical Use of AI
AI’s increasing role in diagnosis demands ethical oversight:
- Transparency: Clinicians should understand how AI arrives at conclusions.
- Bias Mitigation: Algorithms must be trained on diverse datasets to avoid systemic bias.
- Human Oversight: AI supports, not replaces, clinical judgment.
Tools from Medicai prioritize explainability (XAI), offering visual reasoning cues that enhance clinical trust.
Tackling Technical Integration
AI tools must blend seamlessly into existing systems. That means:
- System Interoperability using standards like DICOM, HL7, and FHIR
- User Training to encourage adoption and ease of use
- Data Standardization to ensure clean inputs for reliable AI outputs

The Future Landscape of AI, Imaging Analytics, and Cloud PACS
The future of imaging lies in personalization, prediction, and precision.
- Real-Time Decision Support at the Point of Care: AI in healthcare provides real-time insights during consultations, quickly influencing diagnoses and treatment decisions.
- Greater Adoption Across Specialties: Fields like oncology, cardiology, neurology, and orthopedics use AI in imaging to improve diagnosis and monitoring, making clinical decision support more intuitive with specialty-specific algorithms.
- Expanded Use of Predictive Analytics: Future CDS systems will analyze images and assess risks. Predictive AI will help clinicians identify high-risk stroke or cancer recurrence patients, allowing for early intervention.
- Integration of Genomic and Omics Data: The next generation of personalized medicine will integrate imaging with genetic, proteomic, and lifestyle data to create detailed patient profiles for tailored diagnosis and treatment.
Platforms like Medicai’s AI-ready PACS enable global collaboration, use federated learning for secure AI training, and feature voice-activated tools for efficient interactions.
Conclusion
AI and cloud PACS are transforming clinical imaging by combining smart analytics with scalable cloud infrastructure. It helps in personalized decisions, improved efficiency, and better patient outcomes.
As we move forward, platforms like Medicai, which blend innovation with trust, will shape the future of diagnostics.
Are you ready to embrace smarter imaging?
Start exploring how AI-driven cloud PACS can revolutionize your workflow.




