AI in Radiology: Building Trust in Reporting

AI-generated reports are reshaping radiology, but the real question isn’t whether AI can work. it’s can radiologists trust it?
Building trust in AI-generated radiology reports means more than accuracy. AI in radiology requires transparency, explainability, and seamless integration into workflows, allowing clinicians to verify findings.
Discover why trust matters in AI-generated radiology reports, how retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) enhances confidence, and what steps radiology teams can take to safely embrace AI.

Why Trust Matters in AI-Generated Radiology Reports
When it comes to radiology, trust is everything.
Radiologists and clinicians rely on reports for crucial decisions, so even minor errors can have serious consequences. An AI-generated report that misdiagnoses a fracture, misses a hemorrhage, or is unclear poses a direct risk to patient safety.
The problem is not that AI models lack power. They often outperform humans in narrow tasks, but their reliability can vary depending on context.
Large language models (LLMs) can hallucinate, generating findings that seem accurate but aren’t clinically correct. It poses risks for radiologists, creating a challenging balance between efficiency and safety. Without a trust framework, AI reports may struggle to gain acceptance in critical areas, such as trauma or emergency care.
The study highlighted how common evaluation metrics failed to catch important mistakes in AI-generated radiology reports. Many automated scoring systems, designed to assess how “good” an AI report looks, failed to reliably identify clinical errors, some significant.
This means that even when a report scores well on paper, it may still contain dangerous inaccuracies that only a trained radiologist can spot.
This gap underscores the need for trustworthy evaluation methods. Newer metrics, such as RadGraph F1 and RadCliQ, are being developed to better align with human clinical judgment, ensuring AI output is measured not just for readability, but for diagnostic accuracy.
Similarly, studies show that when AI systems are enhanced with retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and domain-specific knowledge, both accuracy and clinician trust increase significantly.
In other words, trust isn’t built on speed or technical sophistication alone. It depends on three intertwined pillars:
- Accuracy you can verify
- Transparency you can understand
- Evaluation methods that reflect real-world clinical safety
Without these, radiology AI could become a liability instead of a helpful tool. However, with AI-generated reports, AI becomes essential, enabling radiologists to provide faster, safer, and more confident care.
What Is Retrieval-Augmented Generation and Why It Works
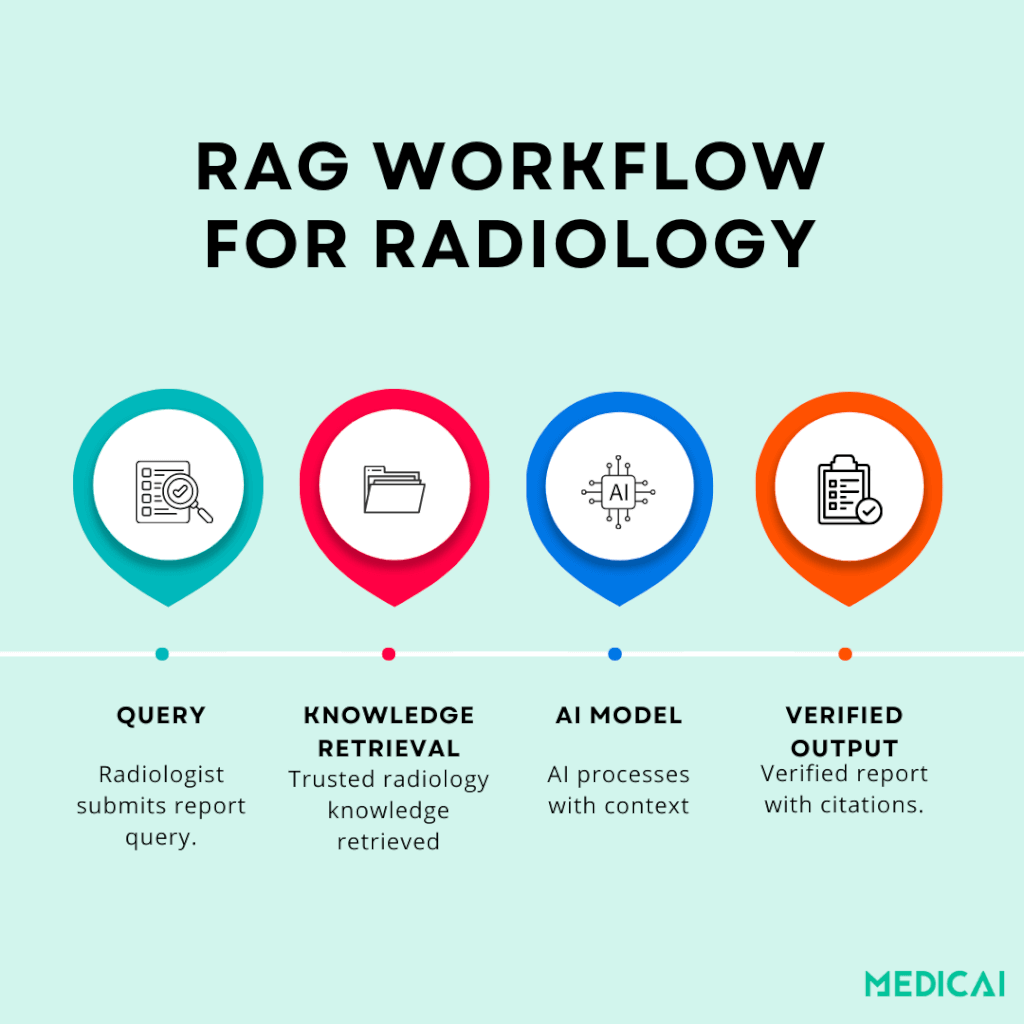
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enhances a model like GPT-4 by pairing it with a knowledge retrieval system. Instead of relying solely on what the model “remembers,” it searches trusted, domain-specific sources in real-time and uses that evidence to generate a report.
Thus, in radiology, when predicting text patterns, AI grounds its conclusions in peer-reviewed literature, institutional protocols, or expert-curated guidelines.
This approach directly addresses two of the biggest barriers to trust:
- Accuracy: By retrieving context from validated sources, the AI reduces hallucinations and delivers more consistent diagnostic language.
- Transparency: RAG systems can cite the sources they used, providing radiologists with a means to verify the reasoning behind a recommendation.
What Research Suggests about AI in Radiology?
A recent study demonstrated how GPT-4, when augmented with trauma radiology knowledge from the RadioGraphics Top Ten Reading List, achieved 100% correct diagnoses, 96% classification accuracy, and 87% grading accuracy.
In comparison, plain GPT-4 without retrieval support lagged significantly, especially in classification and grading tasks. What stood out most, however, was clinician feedback: the retrieval-augmented model consistently earned a median trust score of 5.0 for explanations and cited sources.
A similar proof-of-concept system was developed for gastrointestinal radiology, known as the Gastrointestinal Imaging Chatbot (GIA-CB). It enhanced GPT-4 with authoritative GI-specific resources. The outcome was impressive: 78% accuracy in differential diagnosis, compared to 54% with generic GPT-4.
This finding highlights why RAG works so well in radiology. Radiologists can see where the information came from, understand how it was applied, and ultimately decide whether to endorse the AI’s conclusion.
Key Principles for Building Trust in AI-Generated Radiology Reports
Recent research identifies six key principles vital for encouraging the adoption of AI-generated reports in clinical practice.
Domain-Specific Knowledge
Generic AI models are too broad to be relied on for clinical care. By focusing on subspecialty datasets, whether trauma, gastrointestinal, or neuroimaging, AI systems can deliver outputs that align with the expertise radiologists expect.
Source-Backed Transparency
Reports are far more trustworthy when they show their work. RAG-enabled systems provide citations from textbooks, guidelines, or institutional protocols. Radiologists can trace the logic behind conclusions, turning the AI from a “black box” into a transparent collaborator.
Platforms like Medicai ensure reports are verifiable, with audit trails and annotations visible in the PACS viewer.
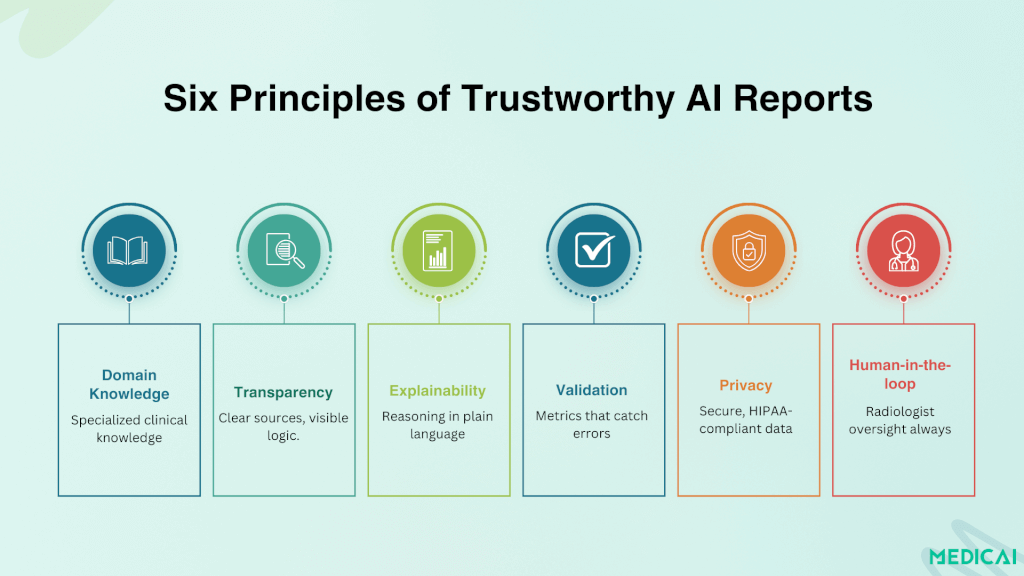
Explainability That Matches Clinical Thinking
Radiologists don’t want abstract visuals or vague probability scores. They want explanations in clear, structured clinical language, language that mirrors the reasoning they would include in their own reports.
Models that present findings alongside anatomical references, injury classifications, and citations build stronger confidence.
Strong Validation & Meaningful Metrics
Surface-level scoring systems are not enough. Tools like RadGraph F1 and RadCliQ show that evaluation must track clinically significant errors. Trust grows when reports are validated against metrics that reflect how radiologists actually practice.
Privacy-Safe Deployment
Data security is as central to trust as accuracy. Local or institutional RAG implementations enable AI to operate within secure hospital environments, ensuring compliance with HIPAA and GDPR while maintaining control over sensitive patient data.
Human-in-the-Loop Oversight
AI is most effective when it augments, not replaces, radiologists. Final responsibility should remain with the clinician, who can review, edit, and sign off on AI-generated findings. This workflow strikes a balance between accountability and efficiency.
Practical Steps for Radiology Teams
Bridging the gap between understanding trust principles and practical application is crucial for hospitals, imaging centers, and radiology groups considering AI-generated reports.
Start with Subspecialty Pilots
Instead of rolling out AI broadly, begin with a narrow focus area such as trauma, chest imaging, or gastrointestinal cases. Proof-of-concept projects demonstrate that subspecialty-focused AI achieves higher accuracy and clinician buy-in compared to general-purpose tools.
Integrate Explainability Features
Choose AI solutions that show their reasoning. Look for systems that provide citations, highlight relevant image findings, or include structured justifications. It helps radiologists to verify conclusions and feel confident in endorsing the report.
Use Evaluation Metrics That Reflect Clinical Reality
Adopt tools like RadGraph F1 or RadCliQ for internal validation. These metrics assess not only linguistic similarity, but also whether the AI is making errors that would impact clinical decision-making. Make evaluation an ongoing process, not a one-time test.
Ensure Privacy and Compliance
Work with vendors or design in-house solutions that prioritize data security. Local or institution-hosted RAG systems can prevent sensitive patient data from leaving secure environments while still delivering cutting-edge AI capabilities.
Keep Radiologists in the Loop
Position AI as a decision-support tool, not a replacement. This human-in-the-loop approach reassures clinicians and patients alike that AI enhances care without eroding professional responsibility.
Build AI Literacy Within the Team
Offer training sessions and discussions that help radiologists understand both the capabilities and limitations of AI-generated reports. A team that knows when to trust and when to question is far better equipped to use AI safely.

Conclusion
Trust is the foundation of AI in radiology. Accuracy alone isn’t enough; reports must be transparent, verifiable, and seamlessly integrated into clinical workflows.
Retrieval-augmented generation, explainability, and strong evaluation metrics are showing how AI can transition from a black box to a trusted partner.
With platforms like Medicai embedding these principles into PACS environments, radiologists can adopt AI with confidence. We help gain speed and efficiency while keeping human expertise at the heart of every decision.
Related Articles

Lets get in touch!
Learn more about how Medicai can help you strengthen your practice and improve your patients’ experience. Ready to start your Journey?
Book A Free Demo