A DICOM viewer isn’t just a tool—it’s the gateway to precise diagnostics, streamlined workflows, and better patient care.
However, what does a strong and smart DICOM viewer offer? It’s DICOM viewer functionality.
DICOM viewer functionalities include tools for viewing, analyzing, and managing medical images accurately. Key features include 2D/3D visualization, MPR, AI automation, measurement tools, annotations, and PACS integration. These functionalities enhance workflows, collaboration, and diagnostic accuracy in modern radiology.
However, not all DICOM viewers are created equal, and choosing the right one can drastically improve workflow efficiency and patient outcomes.
Let’s break down the key functionalities of DICOM viewers, why they matter, and what essential features to look for.

What is a DICOM Viewer?
A DICOM viewer is specialized software designed to open, view, analyze, and manipulate DICOM images. Unlike regular image formats like JPEG or PNG, medical images contain multiple data layers, including 3D reconstructions, patient details, and imaging parameters.
A DICOM viewer helps medical professionals interpret these images precisely, adjust visualization settings, compare historical scans, and collaborate remotely with colleagues.
For radiologists and clinicians, a DICOM viewer is more than just a tool—it’s an essential part of patient care. With features like zooming, contrast adjustments, 3D rendering, and multi-planar reconstruction, these viewers allow for a detailed and accurate analysis of internal structures.
In today’s fast-paced medical environment, efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility are non-negotiable. A powerful DICOM viewer ensures that healthcare professionals can:
- Quickly access and analyze medical images without delays.
- Enhance diagnostic accuracy through advanced visualization tools.
- Collaborate with specialists worldwide using cloud-based platforms.
- Ensure patient data security and compliance with HIPAA and other regulations.

Key Functionalities of a DICOM Viewer Functionality
From basic image viewing to AI-powered automation, DICOM viewers offer a range of functionalities that enhance diagnostic accuracy, streamline workflows, and improve patient outcomes.
Let’s explore the key features that make a DICOM viewer an indispensable tool in medical imaging.
2D and 3D Image Viewing
Most medical imaging modalities—X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, ultrasounds, and PET scans—generate high-resolution 2D image slices. A DICOM viewer allows clinicians to open, navigate, and analyze these slices, providing a detailed look at anatomical structures, organs, and pathologies.
Features of 2D image viewing include:
- Slice Navigation: Move through different scan layers for a more detailed analysis.
- Zoom and Pan: Adjust image focus to examine small details.
- Window Leveling: Modify brightness and contrast to highlight different tissue densities (e.g., distinguishing between bone and soft tissue in an MRI).
- Grayscale and Color Mapping: Enhance image contrast to differentiate structures.
While 2D images are helpful, 3D visualization takes medical imaging to the next level. DICOM viewers can reconstruct 2D slices into interactive 3D models.

Key techniques of 3D visualization include:
- Multiplanar Reconstruction (MPR) Converts 2D slices into axial, coronal, and sagittal views to improve anatomical assessment.
- 3D Volumetry – Enables precise volume analysis for tracking tumor growth, organ size, or fluid accumulation over time.
- Surface Rendering: Displays the outer surfaces of structures, which is useful for surgical planning.
- Maximum Intensity Projection (MIP) – Improves visualization of bright structures like blood vessels or tumors by projecting the brightest pixels into a single image.
3D image viewing is serving significantly for several clinical applications, including-
- Oncology: Identifying tumors and planning radiation therapy.
- Cardiology: Analyzing blood flow and heart structure in 3D echocardiography.
- Neurosurgery: Mapping brain structures before surgery.
- Orthopedics: Evaluating fractures and joint replacements in greater detail.
Image Manipulation Tools
A DICOM viewer provides various image adjustment tools to help radiologists and physicians enhance the clarity and precision of medical images. These include:
- Zoom & Pan: Helps focus on specific areas of interest.
- Rotate & Flip: Adjust image orientation for better visualization.
- Contrast and Brightness Adjustment: Improves visibility of anatomical structures.
Several advanced image manipulation techniques also make DICOM viewers praiseworthy. These include-
- Window Leveling: Improves brightness and contrast for better differentiation of tissues, bones, and fluids.
- Color Mapping & Filters: Boosts contrast with artificial colorization for better abnormality detection.
- Cine Loop Playback: Plays sequential images like a movie, useful for echocardiograms and functional MRIs.
Measurement & Annotation Tools
Accurate measurement of anatomical structures is crucial for diagnosing and monitoring medical conditions. DICOM viewers provide:
- Distance Measurement: Measures the length of fractures, tumor size, or organ dimensions.
- Angle Measurement: Determines angles in spinal deformities or joint assessments.
- Area and Volume Calculation: Essential for measuring lesion growth over time.
Radiologists and physicians often need to annotate images and share insights with other healthcare professionals. DICOM viewers allow:
- Text Annotations: Add clinical notes directly onto the image.
- Arrows & Markers: Highlight key areas of concern.
- Automated Reporting: Some viewers generate structured reports, reducing documentation workload.
Comparative Studies & Serial Imaging
Comparative imaging helps healthcare professionals to track changes over time, including tumor growth, bone healing, and treatment effectiveness. This, in turn, leads to better clinical decisions.
Key features of comparative imaging in DICOM viewers include:
- Overlaying Past and Present Scans: Comparing past and current scans reveals subtle anatomical or pathological changes. It is instrumental for:
- Tracking tumor growth in oncology patients.
- Assessing bone healing after fractures or orthopedic surgery.
- Monitoring neurological conditions like brain atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease.
- Side-by-Side Modality Comparison: DICOM viewers allow clinicians to:
- Compare X-rays and MRIs for soft tissue and bone issues.
- Use PET-CT fusion for simultaneous metabolic and structural imaging.
- Analyze ultrasound with CT for a comprehensive cardiac assessment.
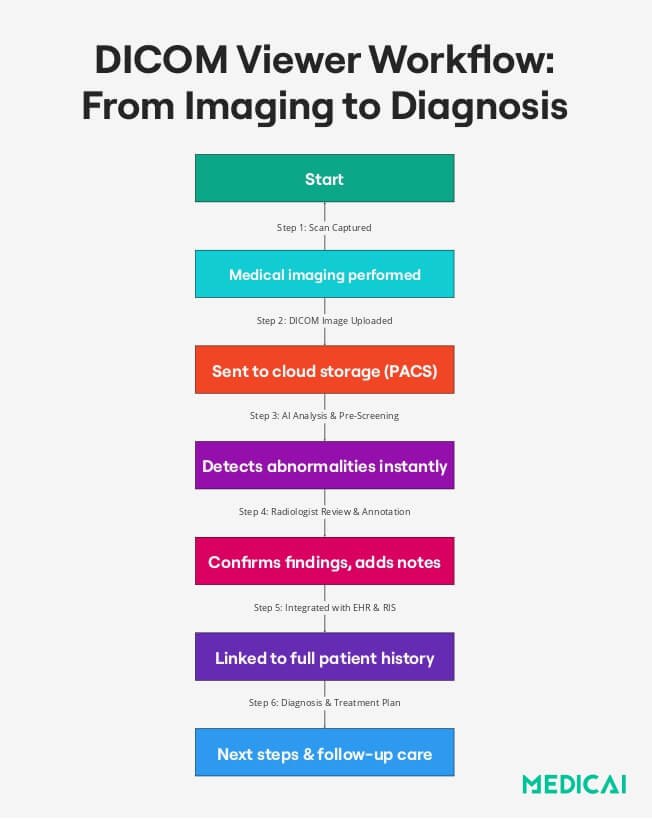
Integration with PACS, RIS & EHR
A DICOM viewer is most effective when integrated with hospital-wide systems, allowing seamless access to imaging data and patient records. Modern healthcare relies on three major digital systems:
PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System)
- Store imaging data digitally, eliminating physical film.
- Instantly retrieve patient images to enhance diagnostic speed and workflow.
- Enable remote access to support telemedicine and off-site consultations.

RIS (Radiology Information System)
A RIS is a specialized software solution used in radiology departments to:
- Schedule imaging appointments and track patient workflows.
- Manage radiology reports and clinical documentation.
- Fulfill imaging requests efficiently to reduce patient wait times.
EHR (Electronic Health Records) Integration
EHRs centralize all patient data, allowing doctors to:
- Link imaging data directly to a patient’s medical history.
- Access imaging reports alongside lab results, medications, and prior diagnoses.
PACS-enabled DICOM viewers provide several benefits, including-
- Faster access to imaging data across multiple departments.
- Eliminates the need for physical film storage.
- Reduces medical errors by ensuring all patient data is centralized.
Multi-Planar Reconstruction (MPR) for Advanced Views
MPR enables clinicians to visualize medical images in multiple planes, improving diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning. It’s commonly used in neurosurgery, cardiology, and orthopedics to assist with pre-surgical planning, treatment evaluation, and disease diagnosis.
Key MPR views include-
- Axial (Horizontal Slices): Common in CT and MRI scans, used for brain, lung, and abdominal assessments.
- Coronal (Frontal View): Essential for evaluating lung conditions, spinal injuries, and cardiac abnormalities.
- Sagittal (Side View): Provides insights into the spine, brain, and musculoskeletal system, aiding in neurology and orthopedics.
Security, Compliance, and Data Protection
Medical images contain highly sensitive patient information, making data security and regulatory compliance a top priority. Any security breach could lead to serious privacy violations and legal consequences.
Key security features in DICOM Viewers include-
- HIPAA Compliance: Ensures legal adherence to patient privacy regulations, particularly in the U.S.
- Data Encryption: Protects images from cyber threats, hacking, and unauthorized access.
- Role-Based Access Controls: These controls restrict who can view, edit, or share medical images, ensuring that only authorized personnel have access.
Cloud-based DICOM Viewers offer remote access but require strong encryption and secure login mechanisms. On the other hand, on-premise solutions provide better control over data security but may lack flexibility for remote access.
AI-Powered Enhancements in DICOM Viewers
Artificial Intelligence (AI) transforms DICOM viewers from simple image display tools into intelligent diagnostic assistants. AI-powered DICOM viewers can analyze images, detect anomalies, and automate workflows, significantly improving efficiency and accuracy.
- Automated Lesion Detection: AI identifies abnormalities like tumors or fractures for radiologists.
- Predictive Analytics: AI analyzes imaging data to predict disease progression and treatment responses.
- Smart Workflow Automation: Reduces radiologists’ workload by prioritizing images, flagging urgent cases, and generating reports.
Types of DICOM Viewers: Choosing the Right One
There are four main types of DICOM viewers, each suited for different users and healthcare settings.
Standalone DICOM Viewers
Standalone DICOM viewers are locally installed software for PCs, suitable for offline use in hospitals and clinics. They provide features like 2D/3D visualization, measurements, and annotations for accessing locally stored images.
However, they offer limited collaboration options since files must be manually transferred and require manual updates, making them less adaptable to cloud-based healthcare systems.
Web-Based DICOM Viewers
Web-based DICOM viewers allow users to access medical images via browsers without installation, reducing IT workload. Cloud storage and real-time sharing enhance collaboration among specialists.
However, they depend on a stable internet connection, which may pose challenges in areas with poor connectivity, and there are security concerns regarding cloud storage and remote access.
Mobile DICOM Viewers
Mobile DICOM viewers are apps for smartphones and tablets that offer on-the-go access to medical imaging. They allow remote access to scans with cloud integration for quick case reviews.
However, they have limited processing power and reduced functionality, making detailed analysis challenging on small screens.
Integrated DICOM Viewers (PACS/RIS/EHR)
Integrated DICOM viewers are incorporated into larger healthcare systems such as PACS, RIS, and EHR. They streamline workflows by directly connecting imaging data to patient records, facilitating collaboration among medical specialties. These viewers also include AI-powered updates that enhance efficiency.
However, they can be expensive and require complex implementation and IT support, making them challenging to use as standalone solutions.
How to Choose the Best DICOM Viewer
Selecting the right DICOM viewer requires careful evaluation of features, compatibility, integration, security, and cost.
Prioritize Essential Features
Choose a DICOM viewer supporting 2D and 3D imaging to ensure accurate scan interpretation. Advanced functionalities like multiplanar reconstruction (MPR), volume rendering, and surface rendering are crucial for complex diagnoses.
Measurement tools, annotation features, and AI-powered automation further enhance usability. If tracking disease progression is a priority, opt for a viewer with comparative imaging and serial study capabilities.
Ensure Seamless Integration with Healthcare Systems
The DICOM viewer should be fully compatible with PACS, RIS, and EHR systems for a smooth workflow. This integration enables centralized image storage, faster retrieval, and streamlined collaboration between radiologists, physicians, and specialists.
Choose a Platform-Compatible Solution
Select a DICOM viewer that matches your organization’s infrastructure and user preferences. A Windows, macOS, or Linux-compatible solution ensures smooth desktop access, while web-based viewers eliminate the need for software installation and enable remote access from any device.
For healthcare professionals who need mobility, consider a viewer with a mobile app for iOS and Android. This allows on-the-go imaging reviews and telemedicine consultations.
Prioritize Security and Compliance
Data security is non-negotiable in medical imaging. To protect patient confidentiality, ensure the DICOM viewer is HIPAA and GDPR-compliant. Built-in data encryption safeguards images and reports from cyber threats, while role-based access controls limit unauthorized usage.
If the viewer is cloud-based, verify its security protocols, backup policies, and access restrictions to prevent data breaches.
Consider Cost and Licensing Options
Evaluate the pricing model to match your budget and needs. Free DICOM viewers may work for basic viewing but often lack advanced features. For full functionality, consider enterprise solutions with one-time purchases or subscriptions.
Also, account for extra costs like cloud storage, support, and software upgrades to prevent unexpected expenses.
Conclusion
DICOM viewers are vital tools in medical imaging, turning raw scan data into valuable insights. They enhance diagnostic accuracy and streamline workflows with features like 2D and 3D visualization, multi-planar reconstruction, comparative imaging, AI analysis, and PACS integration.
Medicai takes DICOM viewer functionality further by implementing strong security measures, including HIPAA compliance and data encryption, to protect patient information. We help radiologists and healthcare providers work more efficiently and effectively.





