AI Data Extraction: Unlocking Hidden Value in Radiology Documents
- The Data Problem: Manual Entry in Imaging Workflows
- How AI Data Extraction Works (OCR + NLP + DICOM Metadata Mapping) View more
- Medicai’s Advantage: Seamless Data Integration with PACS
- Use Cases of AI Data Extraction in Radiology View more
- Compliance: HIPAA, GDPR, and Audit Trails
- Conclusion: From Data to Decisions — The AI Advantage
Radiology workflows are full of valuable information — yet much of it remains trapped inside scanned documents, PDFs, and unstructured reports. Radiologists, technicians, and administrators spend countless hours manually entering patient data, linking imaging results, and ensuring metadata consistency.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is now changing that reality. Through AI data extraction, healthcare providers can turn unstructured medical data into structured, interoperable information that integrates seamlessly with Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS), Electronic Health Records (EHRs), and reporting tools.
Let’s explore how AI transforms data entry into data intelligence, and how platforms like Medicai are leading the shift from manual workflows to connected, automated radiology ecosystems.

The Data Problem: Manual Entry in Imaging Workflows
Every radiology department faces the same bottleneck — the administrative overload of handling imaging orders, referrals, and lab attachments.
Before a CT or MRI study is even reviewed, staff must manually input or verify patient identifiers, exam types, referring physician details, and clinical notes. This process often involves comparing paper referrals, faxed documents, and digital uploads — all with inconsistent formats.
A study published in the National Library of Medicine found that manual data entry remains a primary source of workflow delays and diagnostic inefficiencies in radiology. These inefficiencies don’t just slow diagnosis; they introduce the risk of mislabeling, duplication, and human error.
For radiologists, time spent cross-verifying data means less time for clinical interpretation. For administrators, every minute spent manually entering information is a missed opportunity to improve coordination and accelerate care delivery.
That’s where AI-driven data extraction steps in — transforming static documents into living data.
How AI Data Extraction Works (OCR + NLP + DICOM Metadata Mapping)
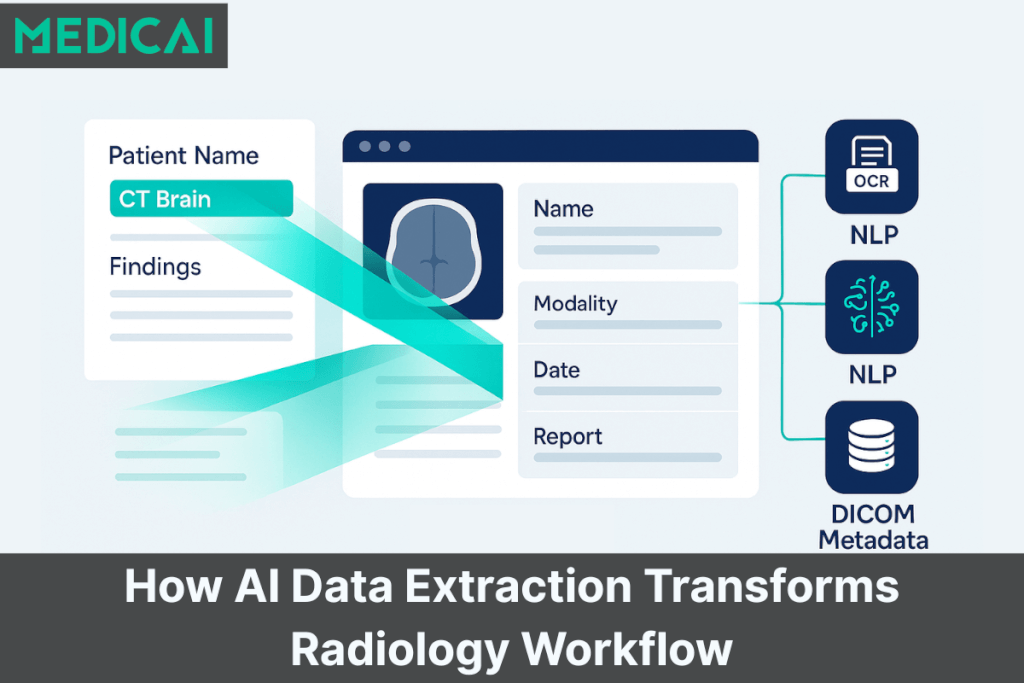
AI data extraction in healthcare is far more advanced than simple text recognition. It combines multiple layers of intelligence: Optical Character Recognition (OCR), Natural Language Processing (NLP), and context-aware data mapping aligned with DICOM metadata standards.

OCR: Digitizing Medical Text
OCR technology scans printed or handwritten medical documents — such as radiology referrals or pathology reports — and converts them into machine-readable text. This is the foundation that enables automation.
According to research on medical data processing using deep learning, modern OCR algorithms trained on clinical handwriting can achieve high accuracy in recognizing complex medical terms and abbreviations.
NLP: Understanding the Context
Once text is digitized, NLP models interpret and extract meaning from it. NLP identifies structured entities such as:
- Patient demographics (name, ID, date of birth)
- Imaging modality (CT, MRI, Ultrasound)
- Clinical indication or diagnosis
- Referring physician or department
More importantly, NLP can understand medical context, distinguishing between statements such as “rule out pneumonia” and “confirmed pneumonia.”
As described in Foreseemed’s analysis of NLP applications in healthcare, contextual understanding enables AI to deliver actionable insights rather than mere text output.

DICOM Metadata Mapping
The final step is linking extracted data to imaging workflows through DICOM metadata mapping. Each radiology image contains metadata — unique patient IDs, modality types, timestamps, and study descriptions. AI systems align the extracted textual data with this metadata, ensuring the correct document is linked to the correct scan.
This allows a referral document, for example, to automatically attach to its corresponding CT study in the PACS — without manual data entry.
A chapter from the Deep Science Research Institute highlights that integrating AI data extraction with structured DICOM attributes enhances interoperability and improves the accuracy of multi-modality image interpretation.
Medicai’s Advantage: Seamless Data Integration with PACS
Most hospitals today still rely on fragmented systems — imaging data in one place, referrals in another, and patient documents stored separately. Medicai bridges this divide.
Medicai’s AI-powered document processing pipeline integrates directly with its cloud PACS and EHR connectivity layer, creating an end-to-end automated workflow:
- Document Upload: Patients or referring providers upload imaging referrals, prescriptions, or lab results directly into Medicai’s portal.
- AI Extraction: The system automatically identifies key data — patient name, ID, modality, and clinical details.
- Smart Matching: Extracted data is matched with imaging metadata and synced with the PACS.
- Unified Case View: Radiologists, oncologists, and administrators can view all relevant documents and imaging in a single, structured patient case.
This seamless interoperability eliminates the need for manual verification while ensuring compliance with HL7, FHIR, and DICOM standards.
The result: a smarter, faster, and more connected radiology environment where every piece of information is exactly where it should be.
Use Cases of AI Data Extraction in Radiology
AI data extraction is not a standalone feature — it’s a workflow accelerator. Here are three critical use cases where Medicai’s approach brings immediate operational and clinical value.
Auto-Filling Patient Forms
Instead of having staff retype patient information from scanned referrals, AI automatically populates patient forms and metadata fields.
For instance, if a referral includes “John Doe, MRI Brain, Reason: Headache and Dizziness,” Medicai’s system extracts and syncs those details with the corresponding study folder in PACS.
This ensures accurate case creation and reduces redundant administrative effort.
Linking Lab Results to Imaging Studies
AI can connect related diagnostic information across departments. A lab result mentioning “elevated liver enzymes” can be automatically linked to an abdominal ultrasound study.
By analyzing textual patterns, NLP engines recognize clinical relationships and ensure that radiologists have all relevant diagnostic context at their fingertips.
This capability not only supports faster interpretations but also enhances multidisciplinary collaboration between imaging and pathology departments.
Generating Structured Reports
Radiology reports are often long and narrative-driven, making it difficult to search or extract key insights.
Through AI data extraction, Medicai converts narrative reports into structured fields — diagnosis, findings, impression, and follow-up.
Structured reporting makes it easier to:
- Standardize report templates
- Facilitate AI-driven analytics
- Enable faster comparison between past and current studies
This transformation supports quantitative imaging analysis and advanced AI-assisted diagnostic workflows, helping hospitals move toward truly data-driven radiology.
Compliance: HIPAA, GDPR, and Audit Trails
Automation in healthcare must prioritize data privacy and regulatory compliance.
AI document processing systems like Medicai’s are built with HIPAA-compliant architecture and GDPR-aligned encryption standards, ensuring that sensitive data never leaves secure environments.
Each action — from document upload to data extraction and mapping — is logged in an immutable audit trail, guaranteeing accountability and transparency.
This approach not only builds trust among patients and providers but also ensures that hospitals comply with interoperability and privacy regulations across regions.
Conclusion: From Data to Decisions — The AI Advantage
AI data extraction is redefining what’s possible in radiology.
It’s no longer about simply reading text — it’s about understanding context, structuring data, and bridging silos between documents and imaging.
With OCR, NLP, and DICOM-aware data mapping, healthcare organizations can unlock hidden value in their data — turning unstructured PDFs and reports into actionable insights.
Platforms like Medicai exemplify how automation can transform not only radiology workflows but the entire continuum of patient care.
By eliminating manual entry, linking diagnostic documents to imaging, and ensuring compliance, AI brings radiology one step closer to a fully interoperable, intelligent, and patient-centered ecosystem.
Related Articles

Lets get in touch!
Learn more about how Medicai can help you strengthen your practice and improve your patients’ experience. Ready to start your Journey?
Book A Free Demo