What’s Next for Teleradiology? Trends and Challenges

- Why Teleradiology Matters?
- The Evolution And Future of Teleradiology View more
- How Teleradiology Works: A Step-by-Step Guide View more
- Essential Infrastructure of Teleradiology View more
- The Best of Teleradiology: Use Cases That Save Lives
- The Tech Behind Teleradiology View more
- Conclusion: The Future of Teleradiology
What will you do when needing a life-saving diagnosis but the specialist is hundreds of miles away? This scenario is pretty common, especially after hours or in rural areas.
However, thanks to teleradiology, time and geographical barriers are no longer a nightmare in the healthcare ecosystem. Teleradiology unites radiologists and healthcare providers in real-time, delivering expert patient care no matter the distance.
Teleradiology enhances patient care using secure platforms, cloud technology, and AI for faster and more accurate diagnoses. It offers after-hours coverage, supports rural clinics, and allows for second opinions from specialists, effectively bridging gaps and saving lives.
But what’s the future of teleradiology? Well, thanks to technological advancements, it is pretty promising.
Discover how teleradiology serves the healthcare ecosystem, its workflows, and prospects.

Why Teleradiology Matters?
Teleradiology is a specialized branch of telemedicine. It focuses primarily on transmitting radiological images, such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasound, to radiologists in remote locations for interpretation.
Unlike traditional radiology, where specialists are on-site, teleradiology lets radiologists analyze images from anywhere. This flexibility is indeed a game-changer for modern healthcare.
With teleradiology, hospitals can ensure round-the-clock diagnostic support for patients.
The demand for teleradiology has skyrocketed in recent years. The reasons are many.
- 24/7 Specialist Access: Emergencies don’t wait for office hours. Whether it’s a midnight stroke case or a complex injury, teleradiology ensures radiologists are always available.
- Addressing Rural Gaps: Finding expert radiologists in rural areas can be challenging. Teleradiology brings top-tier specialists to underserved communities, improving patient care without long-distance traveling.
- Faster Diagnoses: With teleradiology, hospitals can speed up the diagnostic process.
- Operational Efficiency: Healthcare facilities can optimize staffing by outsourcing imaging to remote radiologists during off-hours or when in need.
The Evolution And Future of Teleradiology
Teleradiology has taken off impressively. What started as a niche service in the 1990s is now a multibillion-dollar industry.
Isn’t it astonishing?
However, teleradiology wasn’t always the seamless, high-tech system you know today. Advancements in cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and faster internet speeds have driven its growth.
The Early Days: The Birth of Teleradiology
The concept of teleradiology dates back to 1947, when the first radiographic images were successfully transmitted over telephone lines. It was a technological breakthrough at that time. However, the process was slow and limited by the capabilities of the analog system.
In the following decade, healthcare providers began using teleradiology for “nighthawk” services. The service provided after-hour coverage for emergencies, interpreting images remotely.
However, it has limitations due to the lack of digital imaging and high-speed data transmission.
The Digital Revolution: Paving The Way For Growth
The introduction of digital radiography (DR) in the 1990s changed the game.
Radiologists moved away from using physical film and started working with digital images. It became pretty easy for clinicians to save, edit, and share results electronically.
Around the same time, Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) and Radiology Information Systems (RIS) came onto the scene. These tools simplified how images are stored and accessed.
Connectivity and AI: Transforming Teleradiology
As internet speeds and data compression technology improved, teleradiology took a giant leap forward. Now, radiologists can easily share and examine massive-sized imaging files, like MRIs, on the fly.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) further revved the transformation. AI-powered algorithms analyze images, flag abnormalities, and prioritize urgent cases. It reduced turnaround times and improved diagnostic accuracy.
Will radiologists be needed in the future with these tools?
Well, AI and all the tools don’t replace radiologists. Instead, These tools will amplify their expertise, making their work faster, smarter, and more accurate.
The Future Of Teleradiology: A Vision for 2030 and Beyond
The tomorrow of teleradiology is as thrilling as its yesterday and today.

Integration With Telemedicine Platforms
Teleradiology is becoming a valuable part of telemedicine. Now, patients can easily get imaging services, making their telehealth experience even better and more convenient!
A virtual consultation with a cardiologist may include real-time imaging analysis by a radiologist, all within the same platform. This integration eliminates delays, fosters collaboration, and ensures comprehensive patient care.
AI-Powered Personalized Medicine
AI will play a pivotal role in tailoring diagnostics and treatment. Analyzing imaging data alongside genetic and lifestyle factors can deliver insights beyond the image.
For example, AI can analyze tumor characteristics to recommend targeted therapies.
Expanding Global Collaboration
Teleradiology has already demolished geographical barriers. However, its global impact is set to grow.
Expanded networks of radiologists will connect underserved regions with world-class expertise. For example, a rural African clinic can send a complex oncology case to a European subspecialist.
With teleradiology, the collaboration can happen in hours, not weeks.
Cutting-edge Imaging Technologies
New imaging modalities will redefine what radiologists can see and diagnose.
- 3D and 4D Imaging: This will offer a more detailed view of anatomy, improving surgical planning and disease monitoring.
- Molecular and Functional Imaging: It will provide insights at the cellular level, enabling earlier and more precise diagnoses.
- Virtual Reality (VR): Radiologists may use VR to explore imaging studies in immersive 3D, enhancing education and diagnostics.
Data Security And Privacy
Technology is emerging, and so is the cyber threat. Therefore, strong security has become even more essential in today’s world.
Blockchain technology can play a significant role in ensuring data integrity.
- Tamper-Proof Data: Blockchain records every interaction with imaging data, creating a transparent, unalterable trail.
- Enhanced Privacy: Patient control who accesses their data, facilitating trust and compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR.
Real-Time Diagnostics with 5G
The rollout of the 5G network is unlocking real-time diagnostics. High-speed, low-latency connections help with instant image sharing, even for large files like MRIs.
For example, an ambulance with imaging tools can transmit scans to the hospital in real-time. By the time the patient arrives, the care team has reviewed the images and planned the next steps.

How Teleradiology Works: A Step-by-Step Guide
Teleradiology workflows are all about precision, speed, and seamless collaboration.
Step 1: Image Acquisition And Secure Transmission
Teleradiology workflows start at the healthcare facility, where a patient gets an imaging study captured in advanced imaging systems. When the images are ready, they are sent to PACS, the digital medical imaging storehouse.
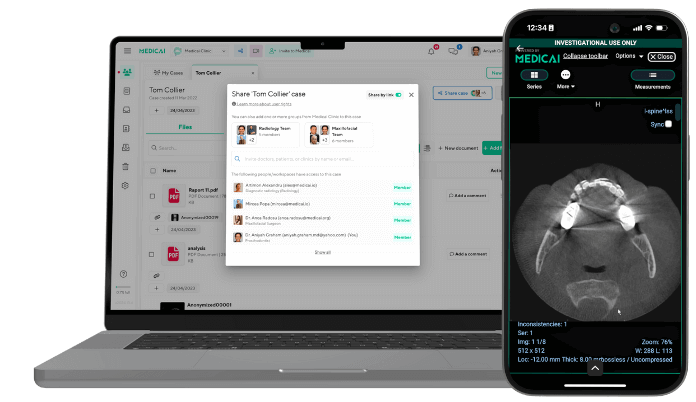
Secure communication protocols, such as Virtual Private Networks (VPN) or encrypted cloud platforms, ensure that sensitive patient data stays safe during transfer. At Medicai, we use HIPAA-compliant encryption to guarantee this security.
Step 2: Image Distribution And Assignment
When the images arrive on the teleradiology platform, the system distributes them to the appropriate radiologist. This step is strategic, not random.
Firstly, the system considers load, that is, how many cases a radiologist gets. It ensures no one radiologist is overwhelmed with cases.
Secondly, the system assigns cases based on the radiologist’s specialties. For example, a pediatric radiologist would handle a child’s chest X-rays, while a neurologist would interpret brain scans for stroke patients.
Step 3: Radiologist Interpretation
In this step, expertise meets technology.
Radiologists log into their teleradiology platforms, access the transmitted images, and analyze them. Some work solo, while others may use AI-powered tools to detect abnormalities, perform faster reviews, etc.
Step 4: Quality Assurance
Accuracy is non-negotiable in radiology. So, many teleradiology workflows include a quality assurance stage to minimize errors.
Often, a second radiologist reviews the initial findings to maintain accuracy. Two radiologists may independently analyze the same study and cross-check the results in complex cases.
Step 5: Report Generation and Delivery
When the radiologists complete the analysis, they generate a detailed report. The report usually includes-
- Findings: what radiologists observe in the images
- Recommendations: The next step is either additional imaging or specific treatments.
- Annotated Images: Marked-up visuals to clarify observations for the referring physicians.
Then, the finalized report is securely transmitted to the referring physician through the teleradiology platform.
Step 6: Consultation and Collaboration
Complex cases often require teamwork. Teleradiology platforms help radiologists collaborate with other healthcare professionals through teleconference or secure chat.
Step 7: Archiving and Follow-Up
After the case is closed, the images and reports aren’t discarded. Instead, they are stored for future use.
- Vendor Neutral Archives (VNAs): These systems store imaging data from various sources in one centralized location, ensuring easy retrieval.
- Disaster Recovery Strategies: Backups and redundant systems protect data from loss due to equipment failure or cyberattacks.
Every step in the teleradiology process focuses on one main goal: improving patient care.
Teleradiology platforms like Medicai allow for secure image sharing and teamwork between doctors, making the process faster, safer, and more efficient.

Essential Infrastructure of Teleradiology
Teleradiology works with a solid foundation, providing a secure and efficient infrastructure. It ensures images are captured, stored, transmitted, and interpreted without a hitch.
Here are the key components of teleradiology infrastructure.
PACS: The Backbone of Image Storage and Access
Picture Archiving And Communication Systems (PACS) are the heart of teleradiology. They are a digital library that stores and manages all medical images.
PACS provides several benefits, including:
- It stores images like X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs in a centralized system.
- It helps radiologists to retrieve, view, and share images instantly.
- It declines the need for physical storage or transporting film.
Modern platforms like Medicai enhance the system by integrating cloud-based PACS, which offers unlimited storage and instant access from any device, anytime, anywhere.
RIS: Workflow Management Made Easy
The Radiology Information System (RIS) is the organizational brain behind radiology departments. It handles all the administrative chores and keeps things moving smoothly.
RIS helps with:
- Scheduling appointments and managing patient records
- Tracking imaging studies from start to finish
- Generating and distributing diagnostic reports.
Secure Data Transmission: Protecting Patient Privacy
Protecting patient data is a great challenge. In teleradiology, it’s even more crucial as sensitive patient data travel across networks.
The system uses encryption to secure data during transfer. Thanks to the encryption, the data can’t be read even if it is breached.
Besides, secure transmission works with VPNs. It creates a secure “tunnel” for data, adding an extra layer of protection.
At Medicai, we take security seriously, ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR. Our end-to-end encryption and secure access controls never compromise your privacy.
VNAs: Centralized Data Repositories
A Vendor Neutral Archive (VNA) is a centralized hub for storing imaging data. It’s like a universal library for medical images, regardless of their sources.
VNAs offer several advantages, including:
- Interoperability: It works with any imaging system. So, sharing data across different facilities becomes easy.
- Unified Access: All images are stored in one place so radiologists and healthcare providers can easily retrieve them.
- Long-Term Storage: VNAs preserve imaging data for a long time for future use, whether for follow-up or research.
High-Performance Workstations: Tools for Precision
Radiologists need more than just a computer. They need specialized workstations designed for image analysis.
Key features of these workstations include:
- High-resolution monitors for detailed analysis.
- Advanced visualization tools for 3D reconstruction or zooming
- Annotation and measurement tools for marking abnormalities, measuring tumor size, or documenting findings.
Disaster Recovery: Keeping Services Running
Cyberattacks, equipment failure, or natural disasters – no system is immune to disruption. So, disaster recovery strategies are a must for teleradiology infrastructure.
Effective disaster recovery includes:
- Regular backups
- Redundant system
- Cloud solution
Medicai integrates cloud-based PACS, RIS, VNAs, and AI tools into a user-friendly system. We ensure scalability, security, and efficiency like no one else.
The Best of Teleradiology: Use Cases That Save Lives
Discover how teleradiology supports patient care.
- Emergency Medicine: In emergencies, speed is everything. Teleradiology helps radiologists to provide rapid diagnoses, ensuring immediate intervention. This workflow, known as “time is brain,” saves lives.
- After-Hour Coverage: Teleradiology provides seamless coverage during nights, weekends, and holidays. This reduces hospital costs, allows radiologists to be flexible, and ensures all-time patient care.
- Rural Healthcare: Accessing medical specialists is challenging in rural areas. Teleradiology brings expert diagnostics closer to home, ensuring every patient is provided expert care.
- Subspecialty Consultation: Teleradiology links hospitals with a worldwide network of specialists, ensuring patients get the expert care they need.
- International Collaboration: Teleradiology connects radiologists and healthcare providers across continents, ensuring international collaboration to provide the best possible care to patients.
- Second Opinions: A second opinion can make all the difference when cases are complex. Teleradiology makes it possible with a fast and simple process.
The Tech Behind Teleradiology
Let’s look at the game-changing technological innovations that are shaping teleradiology.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI is transforming the world, and the same goes for teleradiology. It’s making radiologists work smarter, faster, and more error-free.
How is AI helping teleradiology? Here are the answers.
- Automated Detection of Abnormalities: AI algorithms analyze the image within seconds and flag the suspicious parts that might be overlooked.
- Workflow Optimization: It prioritizes urgent cases, ensuring they reach the radiologists first. It queues routine cases for later, creating a smoother process.
- Segmentation and Measuring Tools: AI tools quickly provide precise measurements or segment areas of concern, giving radiologists more time to focus on complex cases.
Cloud Computing: Unlimited Storage, Seamless Access
Gone are the days of bulky servers and limited storage. Cloud computing is indeed revolutionizing data storage, access, and sharing.
Cloud Computing provides:
- Scalable storage for growing volumes of imaging data. So, gone are the worry of running out of space or upgrading hardware.
- Enhanced data security and compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR to protect data during transmission.
- Seamless access anytime, anywhere, with just a secure internet connection.
5G and IoT: Real-Time Imaging and Beyond
5G and IoT are making teleradiology faster and more connected, breaking down barriers between patients, providers, and specialists.
5G network enables real-time image transmission, even in remote areas. On the other hand, IoT devices like wearable scanners can integrate with teleradiology platforms, enhancing diagnostics.
Blockchain For Data Security: Transparent and Tamper-Proof
Blockchain offers an unbreakable layer of protection in teleradiology. It creates a permanent, transparent log of every transaction. Besides, it provides secure and transparent data sharing, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
Emerging Imaging Modalities: Seeing Beyond The Surface
New imaging technologies are expanding what radiologists may oversee.
- Functional imaging shows how organs and tissues work in real-time
- Molecular imaging looks at cellular and molecular activity, which is crucial for early disease detection.
- 3D and 4D imaging for more detailed view
Conclusion: The Future of Teleradiology
Teleradiology is more than a technological advancement; it’s a revolution in healthcare. It breaks down the barriers of time, geography, and resources, ensuring every patient can access expert care.
Medicai is leading this evolution to a new height, seamlessly connecting radiologists, healthcare providers, and patients in one platform. As technology advances, teleradiology’s future looks brighter than ever.
Related Articles
Lets get in touch!
Learn more about how Medicai can help you strengthen your practice and improve your patients’ experience. Ready to start your Journey?
Book A Free Demo