Oncology PACS: The Future of Cancer Imaging and Treatment

Cancer doesn’t wait—so why should imaging?
With cancer cases rising and imaging data growing exponentially, oncologists need a faster, smarter way to manage medical images. Enter Oncology PACS!
Oncology PACS is a specialized imaging solution for storing, retrieving, and sharing cancer-related medical images. It integrates advanced imaging modalities, AI-driven analytics, and cloud-based access, ensuring oncologists can collaborate seamlessly and make faster, data-driven decisions.
Let’s discover everything you need to know about Oncology PACS—its benefits, challenges, and how it’s reshaping oncology care.

Oncology PACS: A Specialized Imaging Solution for Cancer Care
Oncology PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) is a medical imaging technology specifically designed to address the unique needs of cancer diagnosis, treatment planning, and long-term monitoring. Unlike traditional PACS, which cater to general radiology, Oncology PACS is optimized for high-resolution, multi-modal imaging essential in oncology.
Cancer care depends on comprehensive imaging from various modalities, such as CT, MRI, PET scans, mammography, and nuclear medicine. Oncology PACS centralizes and organizes these images, enabling oncologists, radiologists, and multidisciplinary teams to collaborate effectively.
How Oncology PACS Differs from Traditional PACS
Oncology PACS is not just a storage and retrieval system; it is a critical component in precision oncology, tailored to handle the complex imaging workflows in cancer treatment.
| Feature | Traditional PACS | Oncology PACS |
| Purpose | General imaging storage and retrieval | Designed for cancer imaging, treatment planning, and monitoring |
| Imaging Scope | Primarily used for one-time diagnostics | Monitors tumor progression and treatment response over months or years through longitudinal imaging. |
| Modality Integration | Works with general radiology images (X-ray, CT, MRI) | Integrates CT, MRI, PET, SPECT, mammography, and nuclear medicine for a comprehensive cancer view |
| Radiotherapy & Treatment Planning | Limited support for radiation oncology | Seamlessly integrates with IGRT, SBRT, and radiation delivery systems |
| AI & Predictive Analytics | Basic storage and retrieval with minimal AI features | Uses AI-driven tools for tumor detection, segmentation, and outcome prediction |
| Collaboration & Access | Radiologists primarily use it for diagnostics | Supports multidisciplinary teams (oncologists, surgeons, radiologists, pathologists, and nuclear medicine specialists) with secure cloud-based access |
How Oncology PACS Works?
With the complexity of oncology imaging, a well-structured PACS workflow improves accuracy, collaboration, and patient outcomes.
- Image Acquisition: The Oncology PACS workflow starts with acquiring images from modalities like CT, MRI, PET, and mammography. These scans are automatically stored in the PACS for instant accessibility without physical film or manual transfers.
- Data Storage & Management: The system organizes patient images so oncologists can compare scans, track tumor progression, and assess treatment effectiveness. It uses advanced compression techniques for efficient high-resolution image management.
- Retrieval & Viewing: When retrieving images, Oncology PACS provides instant access, allowing specialists to view, analyze, and compare scans side by side. AI-driven PACS solutions further enhance this process by detecting abnormalities and assisting in tumor segmentation.
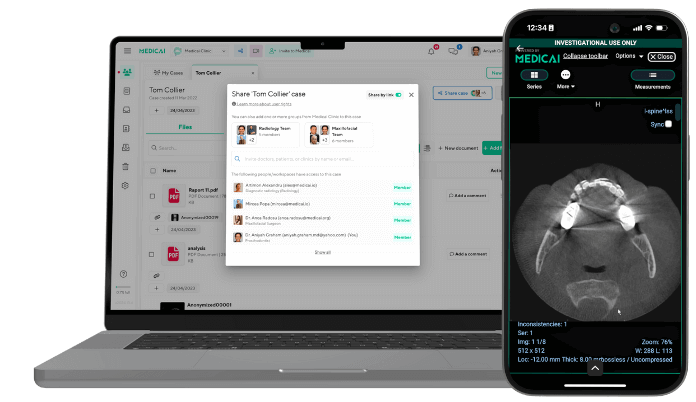
- Collaboration & Sharing: The system also supports secure sharing, enabling oncologists, radiologists, and tumor boards to collaborate in real-time, even across different locations.
DICOM Standards & Interoperability
Oncology PACS has the advantage of adhering to DICOM standards, ensuring compatibility between imaging systems. It helps seamlessly integrate PACS, imaging devices, and hospital systems, eliminating compatibility issues.

Standardization allows seamless communication of imaging modalities like CT, MRI, PET, and SPECT. It also integrates Oncology PACS with electronic health records (EHR) and radiotherapy planning software, centralizing patient data.
DICOM-compliant PACS enables hospitals and cancer centers to share imaging data securely across departments and external facilities.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premises Oncology PACS
Oncology PACS can be deployed in cloud-based or on-premises environments.
Cloud-based PACS enables remote access to imaging data, ideal for telemedicine and multidisciplinary teams. It offers scalability, automatic backups, and managed security, easing the IT burden. However, its subscription model can lead to ongoing costs.
On-premises PACS stores data on internal servers, providing control over security and compliance. However, it requires significant upfront investment and complicates scalability due to the need for infrastructure upgrades when expanding storage.
Cloud-based solutions like Medicai enable flexible, real-time collaboration for oncologists while ensuring data security and compliance. In contrast, on-premises PACS are preferred in environments with strict data security needs.
Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHR) & Hospital Information Systems (HIS)
For effective operation, Oncology PACS must integrate with EHR and HIS platforms. This integration helps oncologists to access imaging studies, pathology reports, and treatment plans in one location.
Automated image retrieval simplifies data entry and significantly reduces errors. It also provides instant access to historical images, allowing faster and more precise treatment decisions.
This integration also fosters better communication among radiologists, oncologists, and surgeons, which reduces administrative delays and ultimately enhances patient outcomes.

Oncology Workflow & PACS: A Seamless Integration
Oncology PACS is crucial in the cancer care continuum, supporting imaging needs from initial diagnosis to long-term treatment and follow-up.
Diagnosing Cancer: The Imaging Phase
Accurate diagnosis is the foundation of effective cancer treatment. Oncology PACS helps store, organize, and analyze diagnostic imaging, ensuring oncologists and radiologists have immediate access to high-resolution scans.
The key imaging modalities supported by oncology PACS include-
- MRI and CT Scans: CT scans and MRI are vital for detecting and assessing tumors. CT scans identify lung and abdominal issues, while MRI distinguishes between benign and malignant tumors.
- PET Scans and Nuclear Medicine: These methods help identify cancer spread and assess tumor activity. PET scans highlight abnormal metabolic activity, often detecting cancer earlier than CT or MRI.
- Mammography and Ultrasound: Mammography is key for breast cancer detection, while ultrasound aids in examining masses and guiding biopsies. PACS makes these images easily accessible and comparable over time.
Modern Oncology PACS integrates with artificial intelligence (AI) tools. Together, they assist radiologists by highlighting suspicious lesions, reducing false negatives, and improving early cancer detection rates.
AI-driven PACS can also streamline the second opinion process, allowing multiple specialists to review imaging remotely and collaboratively.
Intervention: Surgery & Procedural Planning
Sometimes, surgery is necessary to treat cancer. Oncology PACS enhances surgical planning and decision-making with precise imaging.
- Pre-Surgical Planning: Oncology PACS offers detailed 3D imaging and tumor mapping, helping surgeons visualize the tumor’s location and relation to surrounding organs. High-resolution scans aid in determining the best surgical approach, whether minimally invasive or extensive.
- Intraoperative Imaging: Fluoroscopy, intraoperative MRI, and real-time imaging enhance surgical precision. Oncology PACS integrates with these tools, enabling mid-procedure adjustments, which are crucial in neurosurgery and orthopedic oncology to protect critical structures.
- Post-Surgical Evaluation: After surgery, immediate imaging is needed to assess complications, residual tumors, and healing. Oncology PACS allows for quick comparison of pre-operative and post-operative scans, helping oncologists decide on further treatments like radiotherapy or chemotherapy.
Long-Term Monitoring & Treatment
Cancer treatment requires long-term imaging and monitoring to track tumor response and detect recurrence. Oncology PACS is crucial for managing and comparing imaging data over time, ensuring treatments are adapted to the patient’s changing condition.
Tracking Tumor Response & Treatment Effectiveness
Oncology PACS allows oncologists to assess how a tumor responds to treatment through size reduction, structural changes, or metabolic activity shifts seen in PET scans. It helps guide decisions on continuing, modifying, or escalating treatment protocols.
Support for Various Cancer Treatment Modalities
- Radiotherapy – Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT): Oncology PACS aids radiotherapy planning by accurately targeting tumors and sparing healthy tissue. Its integration allows oncologists to adjust radiation doses using updated imaging, enhancing treatment accuracy.
- Chemotherapy & Immunotherapy—Monitoring Tumor Shrinkage: Chemotherapy and immunotherapy require ongoing imaging to assess effectiveness. Oncology PACS allows oncologists to compare pre-and post-treatment scans to evaluate tumor control.
Longitudinal Imaging Comparisons for Recurrence Detection
Cancer recurrence is indeed a horrifying concern. Platforms like Medicai’s cloud-based oncology PACS help early detection by allowing oncologists to compare historical scans with recent imaging.
By tracking subtle changes in tumor size, density, or metabolic activity, PACS enables early intervention before a recurrence becomes more advanced.
Key Benefits of Oncology PACS
Oncology PACS is a game-changer in cancer care, streamlining imaging workflows and improving efficiency across oncology departments.
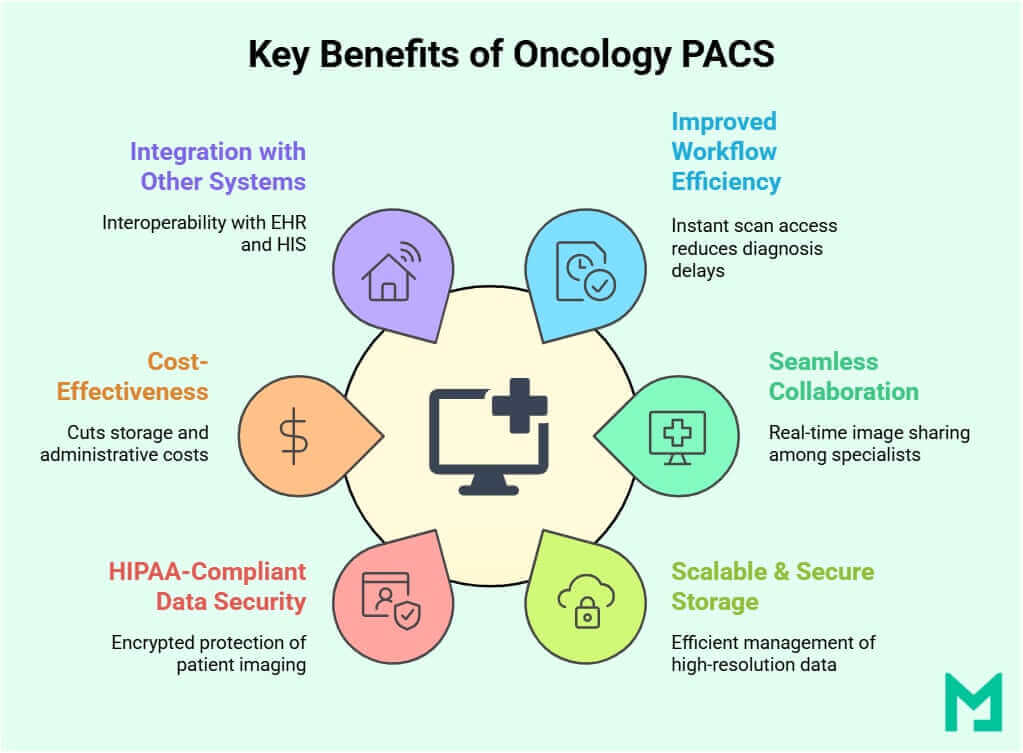
Improved Workflow Efficiency
Oncology PACS eliminates the delays associated with traditional imaging retrieval methods. Oncologists can access patient scans instantly, which reduces wait times for diagnosis and treatment planning.
Historical imaging retrieval enhances efficiency by accurately tracking tumor progression and responses. Remote access enables oncologists to review scans anywhere, speeding decision-making.
Seamless Collaboration
Cancer care requires collaboration among radiologists, oncologists, surgeons, and pathologists. Oncology PACS supports this teamwork by providing remote, real-time access to imaging data, which enhances treatment planning and decision-making.
Scalability & Storage
Oncology imaging produces large volumes of data due to frequent scans for cancer diagnosis and treatment. Oncology PACS efficiently manages high-resolution images from various modalities (CT, MRI, PET, SPECT, mammography) while ensuring fast retrieval speeds.
Cloud-based PACS solutions enable scalable storage for hospitals without extra on-site infrastructure.
Enhanced Data Security & Compliance
Patient imaging data is sensitive, making security and compliance critical. Oncology PACS adheres to HIPAA, GDPR, and other regulations, using data encryption, access controls, and audit trails. They safeguard patient information from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Cost-Effectiveness
Transitioning to digital imaging archiving with Oncology PACS cuts hospitals’ operational costs by reducing expenses on film, storage, and administrative tasks. Cloud solutions also lower hardware maintenance costs. Cloud-based solutions like Medicai help hospitals lower physical storage and IT infrastructure costs.
Challenges in Implementing Oncology PACS
Despite its many advantages, implementing Oncology PACS has several challenges.
Interoperability Issues
A major challenge in PACS adoption is ensuring smooth integration with hospital systems.
Oncology PACS must communicate with EHRs, HISs, radiation therapy planning systems, and pathology databases. Compatibility issues due to vendor lack of standardization make interoperability essential when choosing a PACS solution.
High Data Storage Needs
Oncology imaging produces vast data from advanced techniques like 3D MRI, PET scans, and high-resolution CT. Hospitals need scalable storage solutions, whether on-premises or cloud-based, to manage the ongoing influx of imaging data.
Cybersecurity Risks
PACS security is crucial due to the rising threat of ransomware and cyberattacks on healthcare.
To safeguard patient imaging data, oncology PACS should include strong encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular updates. Hospitals must also train staff on cybersecurity best practices to prevent breaches.
Adoption & Training
Oncology PACS systems can be complex, and radiologists, oncologists, and technicians must fully understand the system’s capabilities. A lack of proper training can cause key features to be underutilized, reducing workflow efficiency.
Hospitals must invest in comprehensive training programs to ensure that all healthcare providers maximize the potential of Oncology PACS.
Conclusion
Cancer care is evolving, and Oncology PACS is leading the way—delivering faster diagnoses, smarter treatment planning, and seamless collaboration. With AI-powered and cloud-based solutions like Medicai, oncologists can track tumor progression, share imaging instantly, and confidently make data-driven decisions.
So, why wait? Embrace the next-generation PACS revolution and redefine cancer care!
Related Articles

Lets get in touch!
Learn more about how Medicai can help you strengthen your practice and improve your patients’ experience. Ready to start your Journey?
Book A Free Demo