Release of Information Process: Secure and Private Access to Data
- Understanding Release of Information (ROI) View more
- Release of Information Process: A 5-Step Guide View more
- What Information Should be Released When Requested? View more
- What is the Purpose of the Release of Information? View more
- Release of Information in the Age of Electronic Health Records
- Secure and Compliant Medical Image Sharing: Medicai Way
- Final Words
Patient data plays a pivotal role in healthcare decision-making and treatment planning. However, with the increasing concern over data breaches and privacy violations, ensuring the security and confidentiality of patient information is more critical than ever.
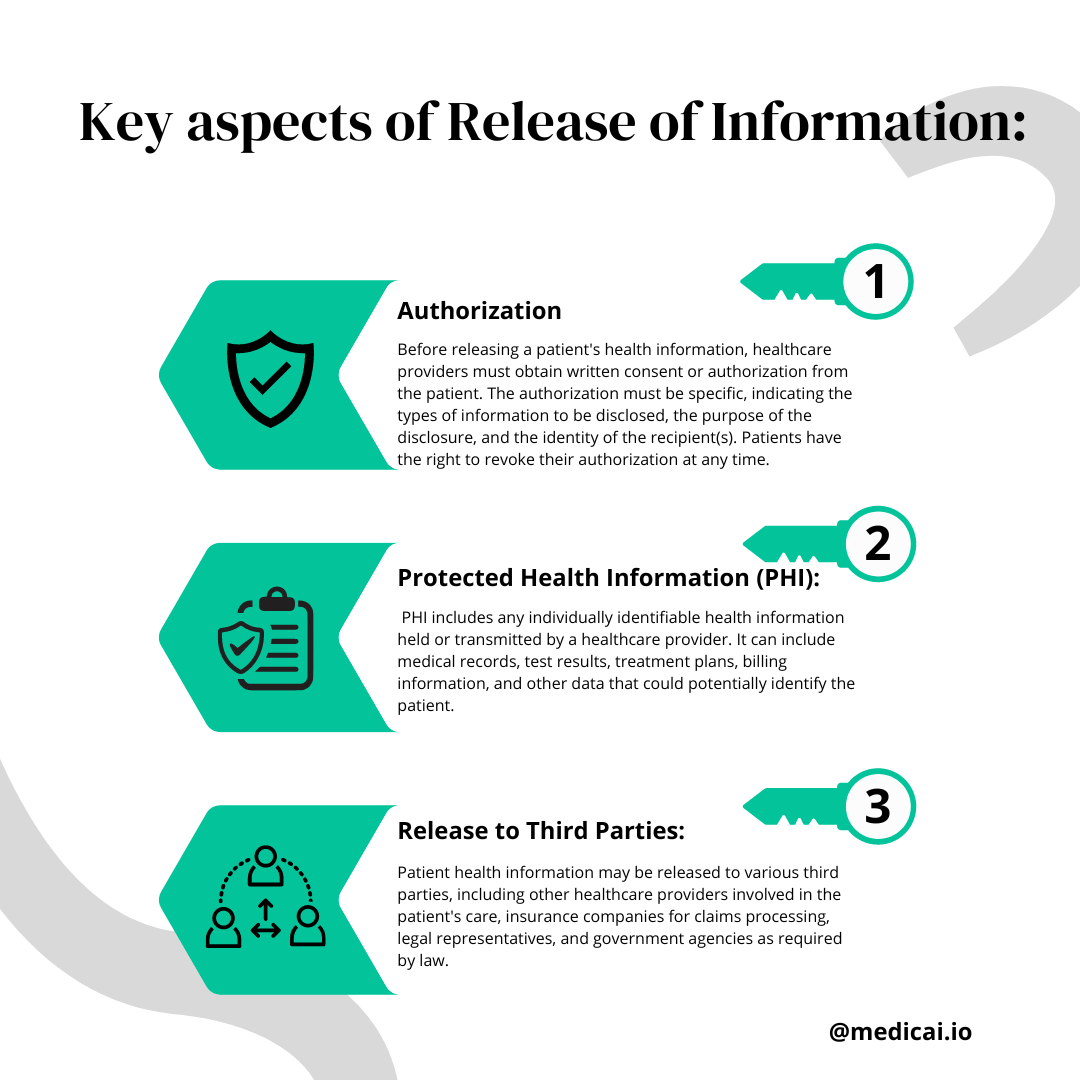
The Release of Information process is a carefully managed system that allows authorized parties to access and share patients’ protected health information (PHI) while safeguarding their privacy. In this blog post, we will explore the significance of this process and how it impacts patient care and data protection.
Understanding Release of Information (ROI)
Release of Information is a systematic process in the healthcare industry that governs the authorized disclosure of patients’ PHI to external entities.
Whether it’s medical records, lab results, or billing information, this sensitive data is vital for providing seamless patient care, facilitating insurance claims, and supporting legal proceedings, among other purposes.
Nevertheless, releasing this information must adhere to strict guidelines, including the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, to protect patient privacy and confidentiality.
Medicai is partnered with more than 1200 clinics nationwide to ensure the smooth release of information.
Ensuring PHI Security and Compliance
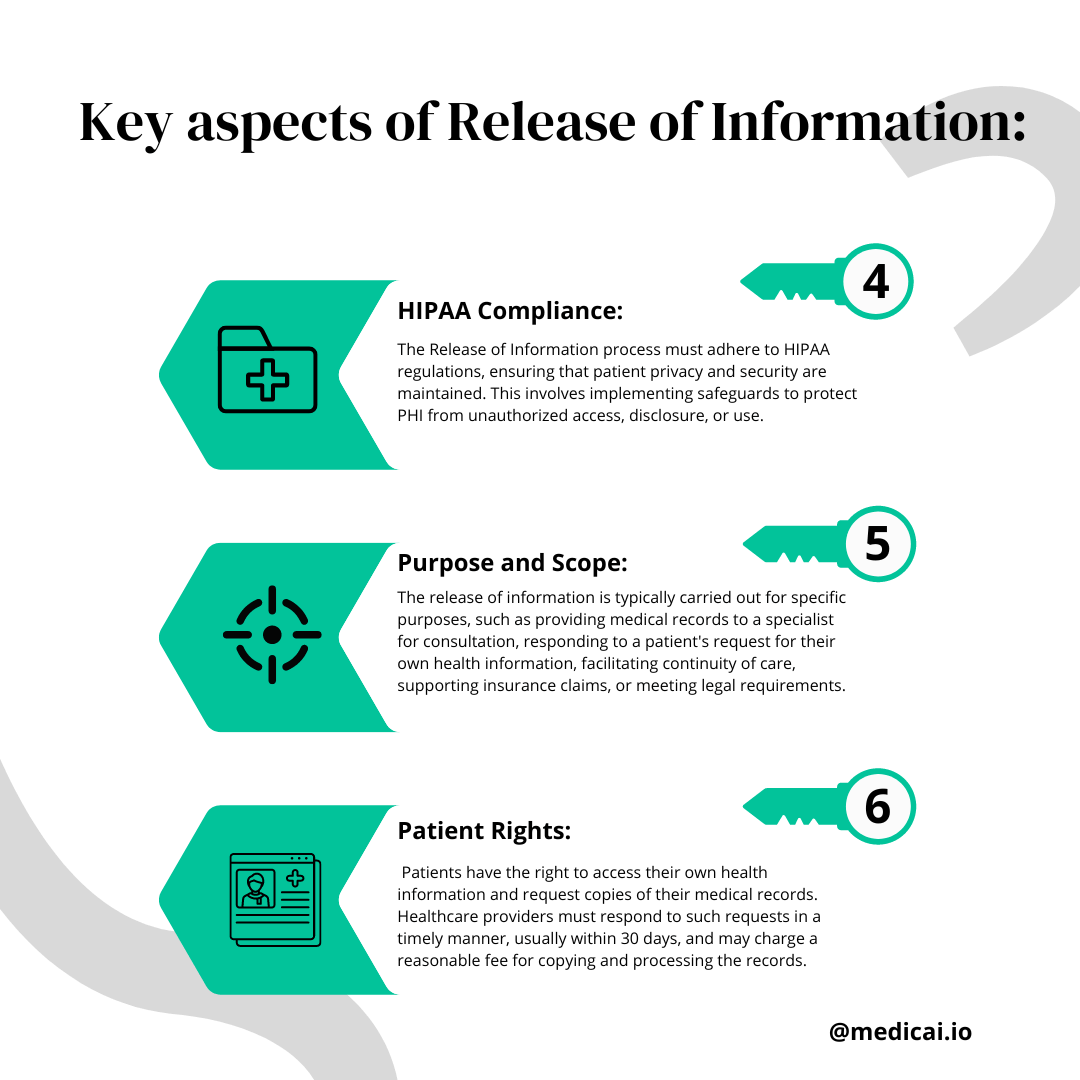
Safeguarding patient privacy is paramount during the ROI process. Healthcare providers must implement robust security measures to protect PHI from unauthorized access, disclosure, or use.
This involves utilizing secure electronic health record (EHR) systems, encrypting data transmissions, and employing access controls to limit information availability to authorized personnel.
Compliance with HIPAA and other relevant regulations is mandatory, and any breach of patient privacy can result in severe legal consequences and reputational damage to the healthcare organization.
Empowering Patient Rights
Release of Information also aligns with the concept of empowering patient rights. Patients have the right to access their own health information and request copies of their medical records.
Healthcare providers must respond to these requests promptly, typically within 30 days, and may charge a reasonable fee for copying and processing the documents.
This transparency empowers patients to actively engage in their healthcare decisions and enables them to maintain continuity of care as they move between different healthcare providers.
Release of Information Process: A 5-Step Guide
Navigating the release of information (ROI) process can seem daunting, but understanding the steps involved can make it much smoother. Whether you’re a patient requesting your own records or someone needing information for legal or insurance purposes, here’s a breakdown of what typically happens:
Initiation
Determine exactly what information you need, including the specific records, date ranges, and preferred format (paper copies, electronic copies, etc.).
Besides, identify the healthcare provider, hospital, or organization that holds the records. This might be a doctor’s office, a hospital’s medical records department, or a health information exchange.
Authorization
You must complete a release of information authorization form. This form is crucial as it grants permission to release your records. You can usually obtain this form from the healthcare provider or their website.
Complete the Form Accurately: Fill out the form with all the necessary details, including:
- Your identifying information
- The specific information you’re requesting
- The time frame for the records
- The name and contact information of the recipient
- Your signature and date
Submission and Processing
Submit the completed authorization form and any required identification to the healthcare provider. There might be a fee associated with processing your request.
The healthcare provider will verify your identity and the validity of the authorization. Then, they will locate and retrieve the requested information from your medical records.
Review and Release
The provider will review the information to ensure it complies with the authorization and legal or privacy regulations. They might redact certain information if it’s not authorized for release.
The information will be sent to the designated recipient through a secure method, such as mail, fax, or a secure online portal.
Completion and Follow-up
If you have any questions or concerns about the released information, contact the healthcare provider. You might receive confirmation that your request has been completed.
You’ll receive an invoice and payment instructions if the service has a fee.
What Information Should be Released When Requested?
Typical Information that might be Released when requested include:
- Patient demographics: Name, address, date of birth, contact information
- Medical history: Diagnoses, treatments, surgeries, medications, allergies
- Mental health records: (Often subject to stricter regulations)
- Lab results and imaging reports: X-rays, blood tests, etc.
- Billing and insurance information
Here’s a breakdown of the key factors that determine what information gets released:
The Purpose of the Request
- Treatment: When sharing information with another healthcare provider for ongoing care, typically, the relevant parts of the medical history, current medications, and recent test results are shared.
- Legal: For legal cases, the specific information requested will depend on the nature of the case. It could include things like medical bills, records of injuries, or mental health evaluations.
- Insurance: Insurance companies usually require information related to diagnoses, treatments, and billing to process claims.
- Personal Use: When patients request their own records, they generally have access to everything unless there are specific legal or ethical exceptions (e.g., mental health records in some cases).
The Authorization
- Specificity: The release authorization form should clearly state what information is being released. This might be broad (e.g., “all medical records”) or very specific (e.g., “lab results from January 2023”).
- Timeframe: The authorization might specify a date range for the released information.
- Recipient: The form should clearly identify who is authorized to receive the information.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
- Minimum Necessary: The “minimum necessary” standard requires the release of only the information absolutely needed for the stated purpose.
- HIPAA: In the US, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) sets strict rules about what information can be released and to whom.
- State Laws: Individual states may have additional laws governing the release of medical information.
- Patient Consent: Patient consent is usually required for the release of their information, with some exceptions for legal or public health reasons.
What is the Purpose of the Release of Information?
The “release of information” (ROI) process might seem like another administrative hurdle in healthcare, but it serves a vital purpose.
At its core, ROI empowers patients with control over their health information. The bridge allows the secure and authorized sharing of medical records between healthcare providers, individuals, or organizations.
But why is this so important? Let’s break down the key purposes of ROI:
Continuity of Care
Imagine switching doctors or seeing a specialist. Your new healthcare provider needs access to your medical history for the most effective treatment. ROI facilitates this seamless transfer of information, ensuring everyone is on the same page and avoiding unnecessary tests or procedures.
Informed Decision-Making
You have the right to access your own medical records. ROI enables you to review your health information, understand diagnoses, and make informed decisions about your treatment options.
Legal and Administrative Purposes
Sometimes, medical records are required for legal cases, insurance claims, disability applications, or other administrative processes. ROI provides a standardized and secure way to release this information to authorized parties.
Research and Public Health
In some cases, de-identified medical information can be used for research purposes to advance medical knowledge, track disease outbreaks, and improve public health. ROI processes ensure this data is shared ethically and responsibly.
Patient Advocacy
Family members or designated caregivers may need access to medical records to advocate for the best possible care on behalf of a patient. ROI allows authorized individuals to step in and help navigate the healthcare system.

Release of Information in the Age of Electronic Health Records
Adopting Electronic Health Records (EHRs) has transformed the Release of Information process. The transition from paper-based records to digital format has enhanced efficiency, reduced administrative burdens, and facilitated seamless exchange between healthcare providers and organizations.
Patients can access their records conveniently through secure health information exchange systems and patient portals, further encouraging patient engagement.
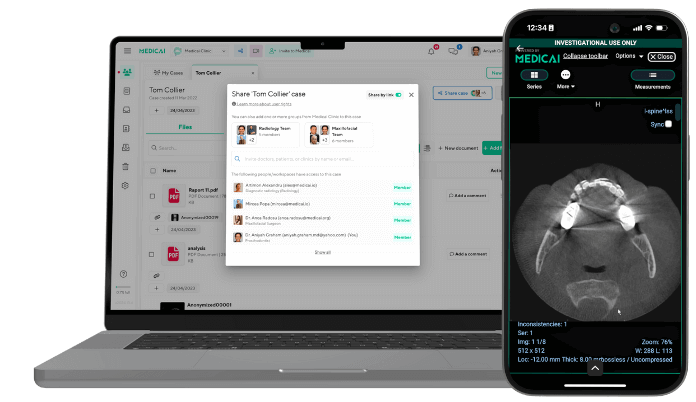
Secure and Compliant Medical Image Sharing: Medicai Way
Medicai facilitates the electronic sharing of imaging studies across different healthcare systems. When authorized by the patient, the platform allows healthcare providers to access and view a patient’s imaging records, irrespective of where the studies were initially conducted. This interoperability ensures that relevant and up-to-date imaging information supports diagnosis and treatment decisions.
ROI ensures that patient records are delivered promptly to authorized parties upon request. Medicai enables real-time access to imaging studies, reducing delays and improving patient care efficiency.
With ROI, patients can control who can access their health information, protecting their privacy. Similarly, Medicai empowers patients to be actively involved in their healthcare decisions by granting access to their imaging data to other healthcare providers involved in their care.
Medicai also ensures strict adherence to data security and privacy regulations, such as HIPAA.
Medicai’s interoperability standard supports the ROI process by facilitating the timely and accurate sharing of imaging studies, leading to better-informed healthcare decisions and enhanced patient outcomes.
Final Words
Release of Information is the backbone of patient privacy in the healthcare domain.
This process ensures the seamless delivery of patient care, supports legal and insurance proceedings, and enables patients to actively participate in their healthcare journey by providing a structured and controlled approach to sharing protected health information.
Healthcare organizations must uphold the highest security and compliance standards during the ROI process to safeguard patient trust and confidentiality. In this era of rapid technological advancement, the Release of Information process remains the key to harmonizing patient privacy, data exchange, and exceptional healthcare services.
Related Articles


Lets get in touch!
Learn more about how Medicai can help you strengthen your practice and improve your patients’ experience. Ready to start your Journey?
Book A Free Demo