DICOM Modality Types: Powering the Future of Medical Imaging
- What is DICOM Modality?
- DICOM Modality Types
- DICOM modality tag, DICOM tag 0008,0060 Modality View more
- Why DICOM Modality Types Matter View more
- What Is the DIACOM Modality Worklist?
- DICOM modality worklist standard, PS3.4, and the MWL SOP Class View more
- How Does the DICOM Modality Worklist Work? View more
- DICOM modality worklist example, C-FIND query, and return keys
- Challenges In Managing DICOM Modality Types View more
- Conclusion
The healthcare world is changing rapidly, and so are diagnostic imaging technologies that help make accurate diagnoses and treatment plans. And behind these technologies lies a silent enabler—DICOM modality types—ensuring everything works harmoniously.
DICOM modality types are standardized labels that classify imaging procedures, such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, PET scans, etc. These identifiers enable data from diverse imaging devices to integrate seamlessly into hospital systems. They ensure efficient workflow and consistent patient records across multiple platforms and devices.
This article will uncover the significance of DICOM modality types and their role in medical imaging workflows.
What is DICOM Modality?
DIACOM, or Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine, is the global standard for managing medical images. A DIACOM modality is the type of imaging device used, like X-ray (CRI), MRI (MR), or Ultrasound (US).
Each modality is assigned a unique identifier, ensuring consistent categorization and seamless integration across the healthcare system.
DICOM modalities are labels that define imaging procedures. They help healthcare professionals organize, retrieve, and share imaging data effectively. By standardizing communication, DICOM makes it easier for different devices and systems, including PACS, HIS, and RIS, to work together.
It prevents data errors, simplifies workflows, and supports the seamless integration of new devices.
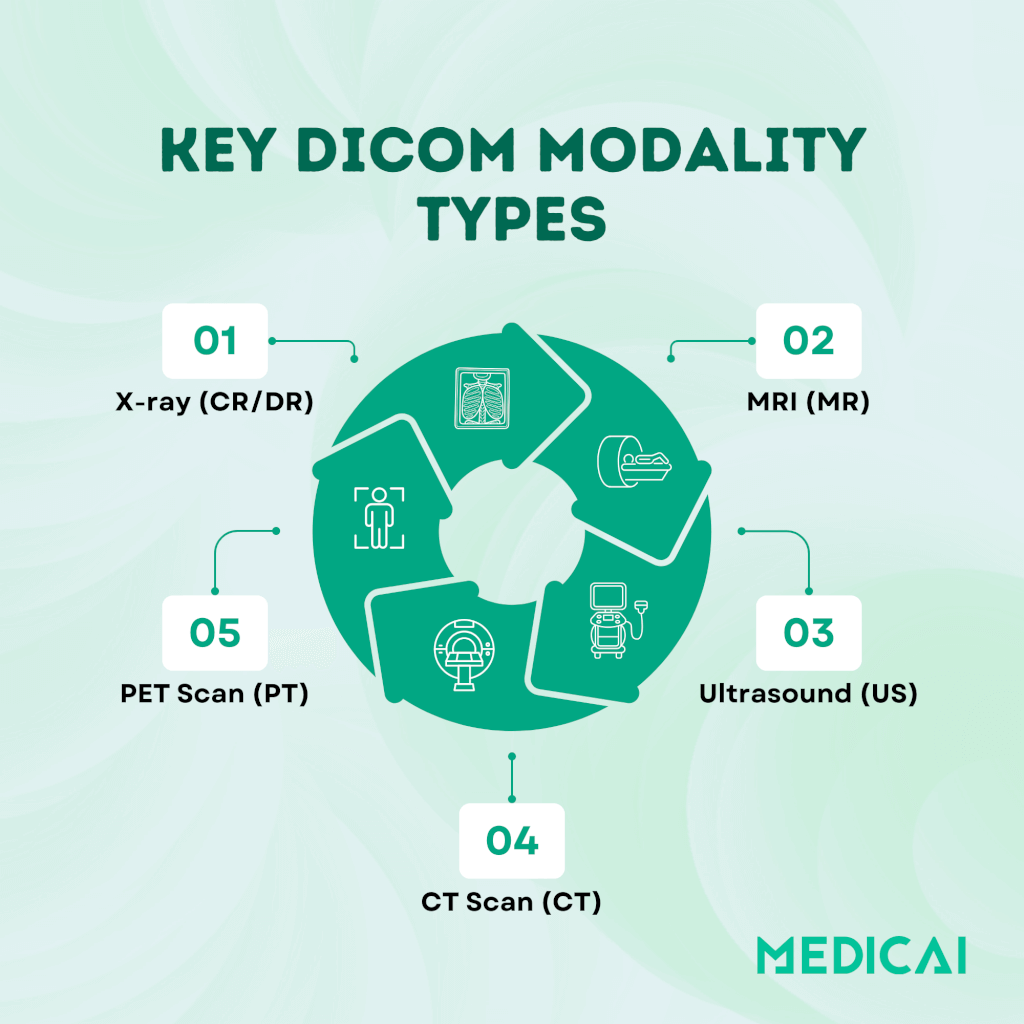
DICOM Modality Types
A standard naming system helps organize and share medical imaging data consistently across healthcare platforms. This improves communication between systems and makes patient care more efficient.
Here are the different DICOM modality types, codes, and descriptions.
| Modality Code | Description |
| AR | Autorefraction |
| ASMT | Content Assessment Results |
| AU | Audio |
| BDUS | Bone Densitometry (ultrasound) |
| BI | Biomagnetic Imaging |
| BMD | Bone Densitometry (X-ray) |
| CR | Computed Radiography |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| CTPROTOCOL | CT Protocol (Performed) |
| DG | Diaphanography |
| DOC | Document |
| DX | Digital Radiography |
| ECG | Electrocardiography |
| EPS | Cardiac Electrophysiology |
| ES | Endoscopy |
| FID | Fiducials |
| GM | General Microscopy |
| HC | Hard Copy |
| HD | Hemodynamic Waveform |
| IO | Intra-Oral Radiography |
| IOL | Intraocular Lens Data |
| IVOCT | Intravascular Optical Coherence Tomography |
| IVUS | Intravascular Ultrasound |
| KER | Keratometry |
| KO | Key Object Selection |
| LEN | Lensometry |
| LS | Laser Surface Scan |
| MG | Mammography |
| MR | Magnetic Resonance |
| M3D | Model for 3D Manufacturing |
| NM | Nuclear Medicine |
| OAM | Ophthalmic Axial Measurements |
| OCT | Optical Coherence Tomography (non-Ophthalmic) |
| OP | Ophthalmic Photography |
| OPT | Ophthalmic Tomography |
| OPTBSV | Ophthalmic Tomography B-scan Volume Analysis |
| OPTENF | Ophthalmic Tomography En Face |
| OPV | Ophthalmic Visual Field |
| OSS | Optical Surface Scan |
| OT | Other |
| PLAN | Plan |
| PR | Presentation State |
| PT | Positron Emission Tomography (PET) |
| PX | Panoramic X-Ray |
| REG | Registration |
| RESP | Respiratory Waveform |
| RF | Radio Fluoroscopy |
| RG | Radiographic Imaging (conventional film/screen) |
| RTDOSE | Radiotherapy Dose |
| RTIMAGE | Radiotherapy Image |
| RTINTENT | Radiotherapy Intent |
| RTPLAN | Radiotherapy Plan |
| RTRAD | RT Radiation |
| RTRECORD | RT Treatment Record |
| RTSEGANN | Radiotherapy Segment Annotation |
| RTSTRUCT | Radiotherapy Structure Set |
| RWV | Real World Value Map |
| SEG | Segmentation |
| SM | Slide Microscopy |
| SMR | Stereometric Relationship |
| SR | SR Document |
| SRF | Subjective Refraction |
| STAIN | Automated Slide Stainer |
| TG | Thermography |
| US | Ultrasound |
| VA | Visual Acuity |
| XA | X-Ray Angiography |
| XC | External-camera Photography |
DICOM modality tag, DICOM tag 0008,0060 Modality
DICOM tag (0008,0060) Modality stores the modality code for a Series in DICOM metadata. DICOM Modality tag values like CT, MR, US, CR, DX, OT, SR, and PR let PACS, VNA, and DICOM viewers filter and route studies by modality without guessing.
DICOM Modality tag meaning stays simple. DICOM Modality tag (0008,0060) describes the type of device, process, or method that created the instances in the Series.
DICOM Modality tag values follow defined terms in the DICOM data dictionary, and DICOM Modality tag values do not always match the IOD name you expect. DICOM explicitly notes that a SOP Instance created under one IOD may list a different modality in (0008,0060) based on implementation details, so modality-based rules need real-world validation.
DICOM modality abbreviations that matter most in daily radiology workflows include:
- CT, Computed Tomography
- MR, Magnetic Resonance
- US, Ultrasound
- CR, Computed Radiography
- DX, Digital Radiography
- NM, Nuclear Medicine
- PT, PET
- XA, X-Ray Angiography
- OT, Other
DICOM defines many more modality codes, and the code table above serves as a reference list of DICOM modality codes.
Medicai’s cloud-based solutions elevate the role of DICOM modality types, enabling real-time data access and collaboration across multiple locations.
Applications of DICOM Modality Types
Various medical specialties use DICOM modality types. Major applications include-
- Radiology: X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs for diagnosing fractures, infections, and internal injuries.
- Cardiology: Echocardiograms and angiograms to evaluate heart function and blood flow
- Oncology: Modalities like PET scans and radiotherapy imaging to track tumor progressions and plan treatment
- Pediatrics: Modalities with low radiation exposure, such as ultrasound or specialized X-rays
- Telemedicine: Remote access and sharing of imaging data for consultations and diagnosis
Why DICOM Modality Types Matter
DIACOM modality types are more than just labels – they are the foundation of interoperability in medical imaging. Each categorized imaging procedure under a standard identifier ensures data is shared and interpreted consistently across different systems and devices.
Let’s look at the benefits of DICOM Modality Types in diagnostic imaging
Interoperability
DICOM modalities help different imaging devices, such as CT, MRI, Ultrasound machines, etc., communicate easily. They ensure data can move freely between systems, regardless of the manufacturer.
Standardization
DICOm modality types provide a universal standard for categorizing imaging procedures. This consistency helps devices, systems, and software to work together without compatibility issues.
Efficiency
DICOm modalities reduce the time spent managing imaging data, allowing healthcare providers to focus on diagnosing and treating patients.
Data Integrity
Accuracy and security are two core elements of medical diagnostics. DICOM modalities ensure imaging data is stored and transferred correctly without errors or breaches.
What Is the DIACOM Modality Worklist?
The DICOM modality worklist (MWL) is a powerful tool that automates the flow of patient and study data between medical imaging systems and devices. It streamlines imaging workflows by integrating with healthcare systems like Radiology Information Systems (RIS) and Hospital Information Systems (HIS).
The worklist ensures that imaging orders and patient details are communicated effortlessly.
MWL also eliminates the need for manual data entry. It pulls patient demographics, study details, and imaging orders from RIS and HIS to ensure imaging devices have accurate and consistent data for every procedure.
This integration minimizes errors, speeds up processes, and enhances overall efficiency in the diagnostic imaging workflow.
DICOM modality worklist standard, PS3.4, and the MWL SOP Class
DICOM Modality Worklist is standardized in DICOM PS3.4 under the Basic Worklist Management Service Class. DICOM PS3.4 defines the Modality Worklist SOP Class and the Modality Worklist Information Model that acquisition systems query to retrieve Scheduled Procedure Step details.
DICOM Modality Worklist works as a query service, not a file export. DICOM Modality Worklist queries use C-FIND against the Modality Worklist Information Model, and the MWL server returns one response per matching worklist item.
DICOM Modality Worklist Wikipedia pages exist and help non-technical readers, but DICOM PS3.4 remains the normative source for MWL behavior, identifiers, and required attribute semantics.
DICOM modality worklist client and server, SCU vs SCP
DICOM modality worklist client software runs on the acquisition modality as an SCU (Service Class User). DICOM modality worklist server software runs as an SCP (Service Class Provider), often integrated with RIS, an interface engine, or an imaging workflow platform.
The DICOM Modality Worklist request flow follows a single pattern.
- The modality worklist DICOM client sends a C-FIND query to the MWL SCP.
- The MWL SCP returns matching Scheduled Procedure Steps as C-FIND responses.
- The modality console uses the returned demographics and procedure details to prevent re-typing and mismatch errors.
Enterprise DICOM modality worklist deployments centralize MWL SCP services, so multi-site modality fleets pull from a single, governed source with consistent configuration and monitoring. Enterprise DICOM modality worklist becomes mandatory when dozens of scanners and multiple RIS sources exist.
How Does the DICOM Modality Worklist Work?
The DICOM Modality Worklist functions by automating and organizing imaging workflows. Here’s how it works step-by-step.

Retrieving Patient Information
The MWL pulls patient demographics and study details directly from systems like RIS or HIS. It includes:
- Patient names
- IDs
- Scheduled procedures
- Imaging requirement.
Automatic Scheduling
The data collected is sent to imaging machines, like CT or MRI scanners. These machines are set up with the patient’s specific information and the necessary imaging instructions. It eliminates manual data entry, reduces errors, and saves time.
Delivery to Imaging Modalities
The modality worklist delivers all relevant information to the imaging device. It confirms the technicians have the correct details before starting the procedure, streamlines preparation, and enhances workflow efficiency.
Execution and Data Feedback
The device ensures results and sends them back to connected systems like PACS during imaging. These results are stored securely and integrated with the patient’s medical record for easy access and analysis.
Medicai enhances MWL by integrating secure cloud storage solutions. It provides real-time updates, reduces errors, and enables seamless sharing of imaging results.
DICOM modality worklist example, C-FIND query, and return keys
DICOM modality worklist example queries use C-FIND to retrieve one worklist item per Scheduled Procedure Step. DICOM PS3.4 describes the MWL C-FIND identifier and the attributes that act as matching keys and return keys.
DICOM modality worklist example, simple “today’s CT list for one scanner”.
- Matching key, Scheduled Procedure Step Start Date inside Scheduled Procedure Step Sequence
- Matching key, Scheduled Station AE Title for the scanner AET
- Matching key, Modality (0008,0060) set to CT
- Return keys, Patient Name, Patient ID, Accession Number, Requested Procedure ID, Scheduled Procedure Step Start Time
DICOM modality worklist query tool output returns one response per matching scheduled step, so a busy CT room sees a list, not one giant payload.
DICOM modality worklist query tool options are available to both IT teams and developers.
- DCMTK findscu works as a modality worklist DICOM SCU for C-FIND testing against MWL SCP endpoints.
- FO-DICOM exposes DicomCFindRequest for C-FIND modality worklist queries inside .NET applications and integration services.
DICOM modality worklist definition stays consistent across implementations. The DICOM modality worklist provides scheduled procedure step details to imaging modalities, reducing manual typing and improving patient safety.
Challenges In Managing DICOM Modality Types
Like the darkness of the moon, DICOM modality types come with challenges.
- Complex Integration: It requires powerful IT support as healthcare facilities often use devices and systems from different manufacturers, leading to integration issues.
- Regular Compliance: DICOM data must comply with privacy laws like HIPAA to ensure secure storage and transfer of sensitive patient information.
- Technical Maintenance: Configuring and maintaining the modality worklist can be resource-intensive, especially with limited IT infrastructure.
DICOM modality worklist tester tools, modality emulators, and MWL servers
DICOM modality worklist tester tools reduce MWL integration failures by validating MWL responses before a live RIS connection. DICOM modality emulator tools simulate modality behavior, and MWL servers simulate RIS behavior, so technicians and PACS admins test edge cases without risking production scheduling.
Free DICOM modality worklist servers and open-source options cover three common needs.
DICOM modality worklist server, file-based MWL SCP for quick testing
- DCMTK wlmscpfs implements a Basic Worklist Management SCP and listens for MWL C-FIND requests.
- Orthanc sample worklists plugin mimics wlmscpfs behavior by serving worklists stored in a filesystem folder.
Enterprise DICOM modality worklist server, MWL SCP integrated with orders and workflow
dcm4chee includes a Modality Worklist SCP and manages worklist entries that tie into HL7 orders in typical enterprise setups.
DICOM modality worklist tester and modality emulator, tooling for QA and integration testing
DVTk RIS Emulator emulates a RIS worklist source using the Modality Worklist Information Model, and logs requests and responses for debugging.
DICOM modality worklist software selection stays simple when you align tools to the question.
- MWL server open source, DCMTK wlmscpfs or dcm4chee MWL SCP.
- DICOM modality worklist query tool, DCMTK findscu, or FO-DICOM C-FIND request objects.
- DICOM modality worklist tester, DVTk RIS Emulator for repeatable scenario testing.
However, you can involve several strategies to manage these challenges.
- Advanced IT support to manage integration and troubleshooting
- Cloud-based platform for scalability, security, and easy access to manage DICOM modalities.
- Regular training is needed to inform staff about the capabilities and limitations of DICOM modalities.

Conclusion
DICOM modality types ensure seamless communication and integration across diverse devices and systems. They enable efficient workflow, accurate diagnoses, and enhanced collaboration among healthcare professionals through standardized categorization and sharing.
With a platform like Medicai, the potential of DICOM modality types reaches new heights. Real-time access, secure data sharing, and streamlined workflow transform the imaging process, helping providers focus on what truly matters—exceptional patient care.
Related Articles

Lets get in touch!
Learn more about how Medicai can help you strengthen your practice and improve your patients’ experience. Ready to start your Journey?
Book A Free Demo