Can radiologists work from home?
Teleradiology allows radiologists to work from home and interpret X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and other medical images remotely. Using secure PACS systems, cloud-based platforms, and AI-assisted diagnostics, remote radiologists can provide expert reports from anywhere.
Remote radiology is possible and happening on a large scale, shaping the profession’s future.
Discover how radiologists adapt to modern work practices, the technologies supporting them, and their challenges.

The Evolution of Remote Radiology Work
Not long ago, teleradiology was seen as a backup solution—providing after-hours reporting or covering shortages in specific locations. But today, it has evolved into a mainstream practice model and futuristic approach, changing how radiologists work worldwide.
Recent studies suggest that 82% of radiology practices now allow remote work, and 36% of radiologists already work fully remotely. Nearly half are in a hybrid arrangement, splitting time between home and hospitals.
Before 2020, remote radiology was growing steadily. However, the COVID-19 pandemic changed everything overnight. With hospitals overwhelmed and social distancing becoming necessary, radiology departments had to adapt quickly.
A study found that computed radiography (CR) exams rose from 15.1% to 25.4% during the pandemic’s peak, while CT and MRI exams increased from 18.9% to 28.7%.
What’s more important is that these numbers didn’t drop back down even after pandemic pressures eased. Remote radiology is now a permanent hospital model, not just an emergency solution.
Thanks to secure digital systems, hospitals can efficiently transmit high-quality scans to remote radiologists for expert interpretations as if they were on-site. This progress is supported by advancements in PACS, high-speed internet, and remote viewing workstations, which enhance patient care overall.

How Technology Helps Remote Radiology Work
Technology has made remote radiology feasible and highly efficient. Do you want to know how? Let’s find out.
PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System)
PACS is one of the most critical technologies enabling remote radiology. This system stores, retrieves, manages, and distributes medical images in a wholly digital format. It eliminates the need for physical film, making image access instant and highly organized.

With PACS, radiologists can securely access imaging studies from anywhere. The system stores high-resolution images and previous reports, allowing easy comparisons to track disease progression and improve diagnoses.
PACS integrates with electronic health records (EHRs) and hospital information systems (HIS). It allows radiologists to access patient histories and clinical notes while interpreting images, providing remote radiologists with the context for accurate reporting.
PACS also supports multiple radiologists working on the same case from different locations. This is particularly useful for subspecialist consultations, where an expert in a specific field can review an image and provide insights remotely.
DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine)
While PACS stores and organizes medical images, DICOM is the universal standard that ensures images can be shared and accessed across different healthcare systems.
Medical imaging devices such as X-ray, CT, MRI, and ultrasound machines produce images in DICOM format. This standardized format ensures that radiologists can view, analyze, and interpret the images remotely without compatibility issues regardless of the brand or type of imaging equipment used.

DICOM provides encryption and authentication for the secure transfer of medical images in teleradiology. It stores metadata, including patient information and imaging parameters, which helps radiologists better understand cases, reduce misinterpretation, and enhance diagnostic accuracy.
Cloud-Based Reporting Platforms
Cloud technology has revolutionized teleradiology by enabling real-time access to imaging studies from any device. Unlike traditional local servers, cloud-based platforms like Medicai allow radiologists to log in securely from anywhere and retrieve scans for immediate interpretation.
These platforms facilitate instant collaboration between radiologists, specialists, and referring physicians, ensuring faster diagnoses and better patient outcomes. With built-in reporting tools, radiologists can generate reports quickly, reducing turnaround times.
Besides, advanced encryption and multi-factor authentication enhance security, ensuring compliance with data protection laws.
The Role of AI in Remote Radiology
AI is essential in remote radiology, improving diagnostic efficiency, accuracy, and speed. It helps radiologists detect subtle abnormalities and prioritize cases effectively.
AI in radiology is primarily used for computer-aided detection (CAD), analyzing medical images for patterns linked to diseases like cancer and fractures. It also optimizes workflow by sorting and prioritizing imaging studies based on urgency. It is crucial for timely diagnosis in emergency and trauma cases.
AI adoption in radiology is still gradual, with 57% of radiologists not using it regularly, despite growing interest in AI-assisted diagnostics. While AI isn’t replacing human radiologists, it enhances diagnostic precision and workflow efficiency.
Security and Compliance in Remote Radiology
Protecting confidential patient data is crucial in teleradiology. Security and compliance measures are strictly implemented to prevent unauthorized access to records.
One key security tool is HIPAA-compliant VPNs (Virtual Private Networks). These VPNs encrypt data transmissions, keeping patient images and reports secure during remote access and protecting sensitive medical data from cyber threats.
Data encryption keeps imaging data safe by making it unreadable to unauthorized users during transfer and storage. It helps prevent breaches.
Healthcare organizations also utilize multi-factor authentication (MFA) to ensure only authorized access. Radiologists must confirm their identity through multiple steps, such as a password and a secure code sent to their device.
Can Radiologists Work from Home? How Do They Work
Working remotely as a radiologist isn’t just about having a computer and an internet connection. They provide timely and accurate reports to healthcare facilities, ensuring necessary diagnostic insights are available even without radiologists.
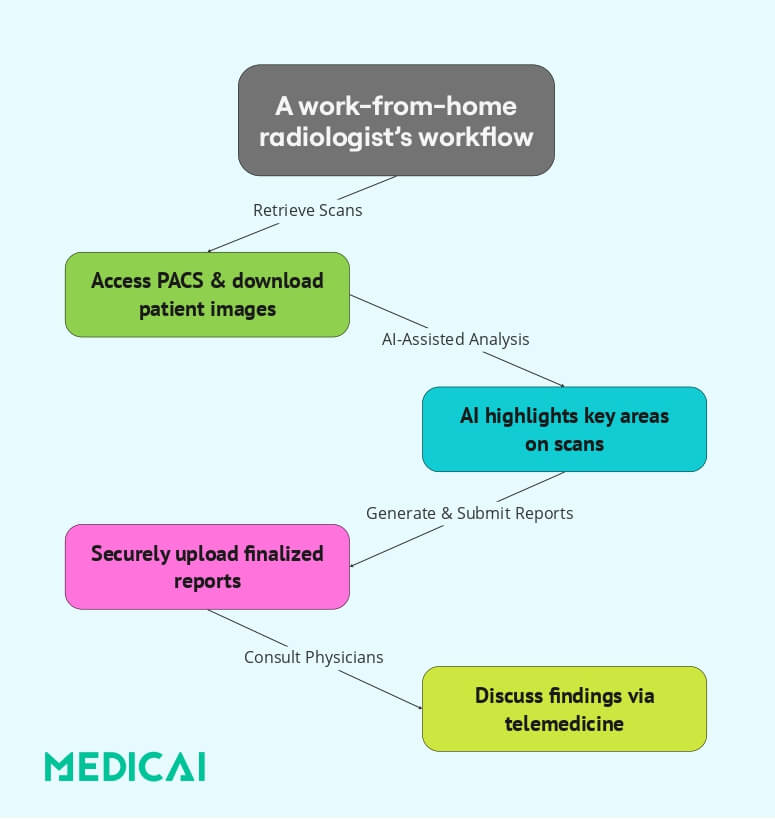
Interpreting Medical Images
One of the primary tasks remote radiologists handle is analyzing medical images. They review X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds, identifying abnormalities and assisting in disease detection.
After evaluating the scans, they create detailed reports that help referring physicians make informed decisions about diagnosis and treatment.
Consulting with Referring Physicians
Remote radiologists also collaborate with healthcare teams through telemedicine platforms. They discuss complex cases with physicians, providing additional insights to ensure accurate diagnoses.
In emergencies, they work closely with trauma and critical care teams to deliver urgent readings that can significantly impact patient outcomes.
AI-Assisted Diagnostic Support
Artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming an essential tool in remote radiology. Many radiologists use AI-powered systems to enhance accuracy, helping detect subtle abnormalities that might go unnoticed.
AI also assists in prioritizing high-risk cases, ensuring critical conditions are identified and addressed faster.
Benefits of Remote Radiology Work
The rise of remote radiology has brought significant advantages for radiologists, healthcare institutions, and patients.
Increased Flexibility and Work-Life Balance
One of the biggest benefits of remote radiology is greater flexibility in work schedules. Studies show that 84% of radiologists cite flexible work hours as a significant advantage.
Working from home reduces commuting stress, allowing radiologists to begin their shifts refreshed. Studies show that shorter commutes can lower anxiety and increase overall life satisfaction.
Remote work enables radiologists to schedule their hours around personal commitments, fostering a better balance between work and life, and a better payout.
Reduction of Burnout and Stress
Burnout is a major issue in radiology, with 54% of radiologists citing it as their biggest challenge. Long hours, night shifts, and increasing workloads contribute to emotional exhaustion and job dissatisfaction.
Remote work reduces burnout, especially by minimizing night shifts. Studies indicate that 63% of radiologists find night shifts hurt performance, making teleradiology a valuable option for working regular hours while covering global time zones.
Also, a study on remote work revealed that productivity increased by 13%, and over time, this rose to 22% as radiologists adjusted to their home work environments. With fewer workplace distractions, radiologists can focus more on accurate reporting, improving patient outcomes.
Improved Patient Care & Faster Reporting
Teleradiology benefits radiologists and enhances patient care. Many radiologists believe remote radiology helps clear backlogs, speeds up imaging study processing, and reduces patient wait times.
Radiologists also note that teleradiology enhances patient care by enabling faster report turnaround and quicker clinical decisions.
Remote radiology enhances access to subspecialty expertise for smaller hospitals lacking in-house specialists. Hospitals can send scans to remote radiologists for expert readings, eliminating geographical barriers and reducing wait times for consultations.
Geographic Independence and Hiring Opportunities
Teleradiology offers significant advantages by overcoming geographic limitations. It enables radiologists to work from anywhere. Hospitals can also hire specialists remotely, addressing shortages in underserved areas and ensuring high-quality patient care.
Besides, it creates more job opportunities for radiologists, offering flexibility and opportunities for career growth.
Can radiologists work from home? The Challenges
Remote radiology offers flexibility but poses several challenges.
Decreased Collaboration and Visibility
Remote radiologists have fewer direct interactions with referring physicians and medical teams, making collaboration less seamless. Although radiologists can easily consult in real time in a hospital, remote work often limits these spontaneous discussions.
There’s concern that radiologists may become “invisible” within the healthcare system, potentially diminishing their professional presence and influence. Virtual collaboration tools help bridge this gap but don’t entirely replace in-person engagement.
Impact on Medical Education & Mentorship
Remote work reduces in-person teaching opportunities for radiology trainees. Many believe this negatively affects their education, as they miss hands-on mentorship.
Despite this, 77% of trainees and 63% of faculty support hybrid models that balance remote flexibility with on-site learning. Structured virtual mentorship programs may help sustain training quality in teleradiology.
Limitations in Certain Radiology Specialties
While diagnostic radiologists can work remotely, interventional radiologists, mammographers, and fluoroscopy specialists require physical presence for hands-on procedures.
Specific tasks, such as contrast administration and real-time image guidance, cannot be performed remotely, which limits remote work opportunities for these specialists.
Technology and Licensing Barriers
Remote radiologists depend on high-speed internet, secure VPNs, and HIPAA-compliant software. However, system failures or weak connections can delay reports and affect patient care.
Besides, licensing varies across states and countries, making it difficult for radiologists to work across multiple regions. Streamlining licensing regulations could make cross-border teleradiology more accessible.
How to Transition to a Remote Radiology Career
Follow these steps to ensure a smooth transition to remote radiology
Step 1: Get Licensed and Stay Compliant
Teleradiologists must comply with state and national regulations, often requiring multiple state licenses for cross-border work. Partnering with teleradiology providers that offer credentialing support can simplify this process while ensuring HIPAA compliance.
Step 2: Set Up a Secure Workstation
A high-speed internet connection, secure VPN, and encrypted cloud access are essential for fast and secure image transmission. An ergonomic home setup with DICOM-compliant monitors and AI-assisted reporting tools enhances accuracy and efficiency.
Step 3: Join a Teleradiology Provider or Negotiate Remote Work
Radiologists can work remotely by joining a teleradiology company or negotiating a hybrid/remote position with their current employer. Factors to consider include company reputation, case volume, compensation models, and tech support.
Step 4: Stay Connected with the Radiology Community
Remote work can be isolating, so active networking is key. Engage in virtual meetings, conferences, and online forums to maintain professional growth and stay updated on industry trends.
Step 5: Keep Up with AI and Technology
AI is reshaping radiology, assisting in case prioritization and automated diagnostics. Staying informed through AI webinars, training, and new software tools ensures long-term career success in teleradiology.
Remote Radiologist Salary
In the United States, remote radiologists earn an average annual salary from $300,000 to $400,000. Compensation varies based on experience, workload, and employer type. Pay-per-click models offer $30–$40 per wRVU, with private practices and hospitals generally paying more than dedicated teleradiology companies.
Factors that affect teleradiologists’ salary include-
- Experience & Subspecialty – Interventional and neuroradiologists earn more.
- Work Volume & Shift Timing – Night shifts and emergency readings pay premiums.
- Employment Type – Independent contractors earn higher rates but lack benefits.
- Technology & AI Integration – Increased efficiency may impact earnings structure.
Conclusion
Remote radiology is shaping the future of diagnostic imaging. With advanced teleradiology platforms, AI-driven workflows, and secure cloud-based solutions, radiologists can work from anywhere while maintaining accuracy and efficiency.
Medicai empowers radiologists with seamless imaging access, secure data sharing, and AI-driven diagnostics. Whether working remotely or integrating teleradiology, our cutting-edge tools redefine radiology for the digital age.



